Project Cellular Structures and Functions
... Part Five. Intercellular junctions [p73-75]: Neighboring cells often adhere, interact, and communicate through special patches of direct physical contact called intercellular junctions. For the cell type that your chose for your project (either animal or plant), create a short story concerning the i ...
... Part Five. Intercellular junctions [p73-75]: Neighboring cells often adhere, interact, and communicate through special patches of direct physical contact called intercellular junctions. For the cell type that your chose for your project (either animal or plant), create a short story concerning the i ...
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN PLANT AND ANIMAL MITOSIS : 1. Since
... plate divides the cell into two daughter cells ...
... plate divides the cell into two daughter cells ...
Cell Test Review - Okemos Public Schools
... List in order of ascending size bacteria, virus, animal cell. ...
... List in order of ascending size bacteria, virus, animal cell. ...
Cell Biology Study Guide
... 29. Which type of adaptation is used for movement of each of the following organisms? a. Paramecium b. Euglena c. Amoeba 30. What is the difference between positive and negative chemotaxis? 31. What is the difference between positive and negative phototaxis? 32. Be able to recognize a paramecium, a ...
... 29. Which type of adaptation is used for movement of each of the following organisms? a. Paramecium b. Euglena c. Amoeba 30. What is the difference between positive and negative chemotaxis? 31. What is the difference between positive and negative phototaxis? 32. Be able to recognize a paramecium, a ...
MAIN IDEAS
... burned and energy is released. •Golgi bodies – packages proteins and carbohydrates into vessels for export from the cell. •ER – a network of membranes – acts like a packaging system •Cytoplasm – all fluid inside cell membrane •Vacuoles – Stores food and water CELL WALL – in plant but NOT animal cell ...
... burned and energy is released. •Golgi bodies – packages proteins and carbohydrates into vessels for export from the cell. •ER – a network of membranes – acts like a packaging system •Cytoplasm – all fluid inside cell membrane •Vacuoles – Stores food and water CELL WALL – in plant but NOT animal cell ...
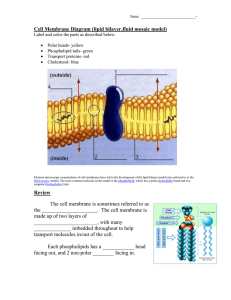
Cell Membrane Diagram (lipid bilayer,fluid mosaic model)
... fluid-mosaic model). The most common molecule in the model is the phospholipid, which has a polar (hydrophilic) head and two nonpolar (hydrophobic) tails. ...
... fluid-mosaic model). The most common molecule in the model is the phospholipid, which has a polar (hydrophilic) head and two nonpolar (hydrophobic) tails. ...
Cells
... things in pond water 2. The Cell Theory • Mathias Schleiden-Concluded all plants are made of cells • Theodor Schwann- Stated all animals are made of cells • Rudolf Virchow- Concluded new cells come from existing cells ...
... things in pond water 2. The Cell Theory • Mathias Schleiden-Concluded all plants are made of cells • Theodor Schwann- Stated all animals are made of cells • Rudolf Virchow- Concluded new cells come from existing cells ...
Cells Alive Tutorial 08-09
... Objective: You will observe computer models of cells, learn the functions and the descriptions of the cells and their components. Navigating the site: Cells alive has a navigation bar at the left. After accessing the page, click on CELL BIOLOGY on the left side navigation bar. From here, you will ac ...
... Objective: You will observe computer models of cells, learn the functions and the descriptions of the cells and their components. Navigating the site: Cells alive has a navigation bar at the left. After accessing the page, click on CELL BIOLOGY on the left side navigation bar. From here, you will ac ...
Cell Cycle Internet Activity.2
... the Molecular Expressions Photo Gallery. Then you will complete the online activity provided by the Biology Project at the University of Arizona. Use your browser to go to Online Onion Root Tips at http://www.biology.arizona.edu/cell_bio/activities/cell_cycle/assignment.html. Begin by reading the de ...
... the Molecular Expressions Photo Gallery. Then you will complete the online activity provided by the Biology Project at the University of Arizona. Use your browser to go to Online Onion Root Tips at http://www.biology.arizona.edu/cell_bio/activities/cell_cycle/assignment.html. Begin by reading the de ...
Human Body Ch 1
... 6. During interphase, the cell ________, makes a copy of it’s _______, and prepares to divide into _______ cells. 7. What is replication? 8. What does a cell need to do to prepare for cell division? Stage 2: Mitosis 9. What is mitosis? 10. During mitosis, one copy of the _________________ is distrib ...
... 6. During interphase, the cell ________, makes a copy of it’s _______, and prepares to divide into _______ cells. 7. What is replication? 8. What does a cell need to do to prepare for cell division? Stage 2: Mitosis 9. What is mitosis? 10. During mitosis, one copy of the _________________ is distrib ...
Cells: Chapter 2
... • Tens of thousands of species have been isolated • There are more than 15,000 known species of bacteria living in the sea • Most famous is E.coli (Escherichia coli) ...
... • Tens of thousands of species have been isolated • There are more than 15,000 known species of bacteria living in the sea • Most famous is E.coli (Escherichia coli) ...
Study Guide
... Define each of the following characteristics of living things and give an example. 1. Cells 2. Growth & Development 3. Respond to stimulus 4. Evolution 5. Reproduction 6. Maintain Homeostasis What organism do scientists believe to be the ancestor to all plants? What does this organism have in common ...
... Define each of the following characteristics of living things and give an example. 1. Cells 2. Growth & Development 3. Respond to stimulus 4. Evolution 5. Reproduction 6. Maintain Homeostasis What organism do scientists believe to be the ancestor to all plants? What does this organism have in common ...
2.1 Organisms – Further questions and answers Q1. Bk Ch2 S2.1
... electron microscope can resolve even the tiniest of organelles as well as view their internal structure. ...
... electron microscope can resolve even the tiniest of organelles as well as view their internal structure. ...
Name Date ____ Period ___ #____ Parts of Prokaryotic
... HYDROPHOBIC “tails” of phospholipids make molecules line up as a LIPID bilayer with POLAR heads facing out and NON-POLAR tails facing in Proteins attached to surface (inside or outside)=marker proteins Proteins stuck into membrane = transport proteins (can go part way in or all the way through) Memb ...
... HYDROPHOBIC “tails” of phospholipids make molecules line up as a LIPID bilayer with POLAR heads facing out and NON-POLAR tails facing in Proteins attached to surface (inside or outside)=marker proteins Proteins stuck into membrane = transport proteins (can go part way in or all the way through) Memb ...
Course Description
... Apply understanding of scientific concepts instead of simply memorizing facts. Master fundamental math required in the modern Molecular Biology Lab. Be able to make and interpret figures, charts, and graphs Current techniques that are utilized in a modern Molecular Biology research laboratory. Pract ...
... Apply understanding of scientific concepts instead of simply memorizing facts. Master fundamental math required in the modern Molecular Biology Lab. Be able to make and interpret figures, charts, and graphs Current techniques that are utilized in a modern Molecular Biology research laboratory. Pract ...
2.2 Multicellular Organisms and Cell Specialization
... 3. The job of cells in the plant _____ is primarily to transport food and water to the rest of the plant, store some food and support the plant. 6. The trillions of tiny cells that make up your body are very efficient units when it comes to getting resources to the _____ within them. 10. A plant's _ ...
... 3. The job of cells in the plant _____ is primarily to transport food and water to the rest of the plant, store some food and support the plant. 6. The trillions of tiny cells that make up your body are very efficient units when it comes to getting resources to the _____ within them. 10. A plant's _ ...
Chapter 3-1 Cornell Notes Discovering Cells
... • microscope: now possible to observe/study cells; • Robert Hooke: coined the term “cells”; • Anton van Leeuwenhoek: studied cells, coined term “animacules”. ...
... • microscope: now possible to observe/study cells; • Robert Hooke: coined the term “cells”; • Anton van Leeuwenhoek: studied cells, coined term “animacules”. ...
Cells to Body Systems
... • Simple organisms such as bacteria, are single cell. • Plants and animals are made up of many cells. • Each kind of cell has a particular function. ...
... • Simple organisms such as bacteria, are single cell. • Plants and animals are made up of many cells. • Each kind of cell has a particular function. ...
Document
... More organelles: Chloroplasts: found almost only in plant cells. They capture sunlight and use it to produce food for the cell. (yes, responsible for photosynthesis and they give plants their green color) ...
... More organelles: Chloroplasts: found almost only in plant cells. They capture sunlight and use it to produce food for the cell. (yes, responsible for photosynthesis and they give plants their green color) ...
Cells - Livingstone High School
... • Simple organisms such as bacteria, are single cell. • Plants and animals are made up of many cells. • Each kind of cell has a particular function. ...
... • Simple organisms such as bacteria, are single cell. • Plants and animals are made up of many cells. • Each kind of cell has a particular function. ...
Cell culture

Cell culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. In practice, the term ""cell culture"" now refers to the culturing of cells derived from multicellular eukaryotes, especially animal cells, in contrast with other types of culture that also grow cells, such as plant tissue culture, fungal culture, and microbiological culture (of microbes). The historical development and methods of cell culture are closely interrelated to those of tissue culture and organ culture. Viral culture is also related, with cells as hosts for the viruses. The laboratory technique of maintaining live cell lines (a population of cells descended from a single cell and containing the same genetic makeup) separated from their original tissue source became more robust in the middle 20th century.