Normal Haemopoiesis
... – Gradual replacement of active (red) marrow by inactive (fatty) tissue – Expansion can occur during increased need for cell production ...
... – Gradual replacement of active (red) marrow by inactive (fatty) tissue – Expansion can occur during increased need for cell production ...
Cell - Capital High School
... As cell size increases, the surface area to volume ratio Decreases (small surface area to volume ratio), which can lead to death of a cell. Having a large surface area to volume ratio is important to the functioning of cells since it gets materials, nutrients, O2, & wastes into & out of it ...
... As cell size increases, the surface area to volume ratio Decreases (small surface area to volume ratio), which can lead to death of a cell. Having a large surface area to volume ratio is important to the functioning of cells since it gets materials, nutrients, O2, & wastes into & out of it ...
CELL THEORY GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS of all CELLS
... CELL • BASIC UNIT OF STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION IN ORGANISMS • SMALLEST UNIT THAT CAN CARRY ON ALL LIFE PROCESSES • TWO TYPES: PROKARYOTIC EUKARYOTIC ...
... CELL • BASIC UNIT OF STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION IN ORGANISMS • SMALLEST UNIT THAT CAN CARRY ON ALL LIFE PROCESSES • TWO TYPES: PROKARYOTIC EUKARYOTIC ...
Cell Wall Cell membrane Nucleus Nucleolus Cytoplasm Chloroplast
... Flipped Video Directions: Please go to our Schoolnotes page and find the NeoK-12 link for this assignment http://www.neok12.com/Cell-Structures.htm View the following videos, take notes on cell organelles and their function (job).. A. “Introduction to Cells”: View the many different type of cells (3 ...
... Flipped Video Directions: Please go to our Schoolnotes page and find the NeoK-12 link for this assignment http://www.neok12.com/Cell-Structures.htm View the following videos, take notes on cell organelles and their function (job).. A. “Introduction to Cells”: View the many different type of cells (3 ...
Ch 6: Cells
... 1) All living things are composed of 1 or more cells 2) Cells are the basic unit of structure and function 3) All cells are produced from existing cells ...
... 1) All living things are composed of 1 or more cells 2) Cells are the basic unit of structure and function 3) All cells are produced from existing cells ...
Biology Chapter 4 - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic unit of structure & function Cells only come from other living cells ...
... All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic unit of structure & function Cells only come from other living cells ...
PDF
... (p. 1323). Shortly after, V-ATPase expression is triggered, leading to H+ flux and to the rapid repolarisation of these cells. The genetic or biochemically induced loss of V-ATPase activity prevents tail regeneration, but not as a consequence of apoptosis. Axon patterning and tail outgrowth are rest ...
... (p. 1323). Shortly after, V-ATPase expression is triggered, leading to H+ flux and to the rapid repolarisation of these cells. The genetic or biochemically induced loss of V-ATPase activity prevents tail regeneration, but not as a consequence of apoptosis. Axon patterning and tail outgrowth are rest ...
practice - Humble ISD
... toxins in liver cells, and making membrane lipids called _S_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __. 13. The mitochondria and chloroplast have a _D_ __ __ __ __ __ membrane. 14. A cell membrane is a _B_ __ __ __ __ __ __ because the phospholipids line up in TWO ROWS to try and keep their hydrophobic tails away from w ...
... toxins in liver cells, and making membrane lipids called _S_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __. 13. The mitochondria and chloroplast have a _D_ __ __ __ __ __ membrane. 14. A cell membrane is a _B_ __ __ __ __ __ __ because the phospholipids line up in TWO ROWS to try and keep their hydrophobic tails away from w ...
Slide ()
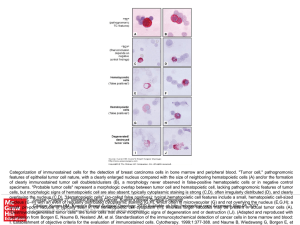
... Categorization of immunostained cells for the detection of breast carcinoma cells in bone marrow and peripheral blood. "Tumor cell," pathognomonic features of epithelial tumor cell nature, with a clearly enlarged nucleus compared with the size of neighboring hematopoietic cells (A) and/or the format ...
... Categorization of immunostained cells for the detection of breast carcinoma cells in bone marrow and peripheral blood. "Tumor cell," pathognomonic features of epithelial tumor cell nature, with a clearly enlarged nucleus compared with the size of neighboring hematopoietic cells (A) and/or the format ...
Prokaryote cells
... 1) Fill in the gaps It was once common practice to classify all living organisms as either animals or plants. With improved knowledge of living things it has become apparent that there are ______ fundamentally different types of cell. The most obvious difference between the two types is that one pos ...
... 1) Fill in the gaps It was once common practice to classify all living organisms as either animals or plants. With improved knowledge of living things it has become apparent that there are ______ fundamentally different types of cell. The most obvious difference between the two types is that one pos ...
UNIT 2 Part A - Loudoun County Public Schools
... a) All living things are made of one or more cells. b) All cells come from pre-existing cells. c) Cells are the basic unit of life. d) Scientist Associated with the Cell Theory (Hooke/Leeuwenhoek/Schlieden & Schwan / Virchow) (use foldable) 2. Describe specific examples that illustrate the relations ...
... a) All living things are made of one or more cells. b) All cells come from pre-existing cells. c) Cells are the basic unit of life. d) Scientist Associated with the Cell Theory (Hooke/Leeuwenhoek/Schlieden & Schwan / Virchow) (use foldable) 2. Describe specific examples that illustrate the relations ...
Looking Inside Cells
... • The gel-like material that surrounds the _________________ • Found in ________________ cells Endoplasmic Reticulum • Organelle in the ________________ that moves materials around in a cell, is made up of folded ________________; can be _________________ or _________________ Golgi Bodies • Golgi bo ...
... • The gel-like material that surrounds the _________________ • Found in ________________ cells Endoplasmic Reticulum • Organelle in the ________________ that moves materials around in a cell, is made up of folded ________________; can be _________________ or _________________ Golgi Bodies • Golgi bo ...
cell organelles keynote ppt - Concordia Shanghai Teacher Websites
... Central Vacuole found only in plant cells ...
... Central Vacuole found only in plant cells ...
MUSINGU HIGH SCHOOL BIOLOGY DECEMBER 2013 HOLIDAY
... a) Name the parts labeled B, C and D b) State the function of part labeled A. 16 (a) What do you understand by the cell specialization as used in biology (b) Name any two specialized cells in plants and state how each is modified. 17 The set up below was prepared by a form one student study it and ...
... a) Name the parts labeled B, C and D b) State the function of part labeled A. 16 (a) What do you understand by the cell specialization as used in biology (b) Name any two specialized cells in plants and state how each is modified. 17 The set up below was prepared by a form one student study it and ...
10.2 The Process of Cell Division 279-284
... 16. The chromosomes line up across the center of the cell. 17. The four circles below represent the nucleus of a cell going through mitosis. Draw four chromosomes as they go through each phase. Label each phase and describe what is happening to the DNA. ...
... 16. The chromosomes line up across the center of the cell. 17. The four circles below represent the nucleus of a cell going through mitosis. Draw four chromosomes as they go through each phase. Label each phase and describe what is happening to the DNA. ...
Judy`s Major
... Foundations of Modern Biology Cell Theory Cell theory states that the cell is the fundamental unit of life, and that all living things are composed of one or more cells or the secreted products of those cells (e.g. shells). All cells arise from other cells through cell division. In multicellular or ...
... Foundations of Modern Biology Cell Theory Cell theory states that the cell is the fundamental unit of life, and that all living things are composed of one or more cells or the secreted products of those cells (e.g. shells). All cells arise from other cells through cell division. In multicellular or ...
During interphase a cell performs all of its
... Explain how mitosis ensures that daughter nuclei are genetically identical. ...
... Explain how mitosis ensures that daughter nuclei are genetically identical. ...
cells\resources\worksheet prokaryotes info and qs
... number are often used in identification. The flagella do not have microtubules. Bacteria that possess flagella are able to detect and respond to chemical signals (chemotaxis) in their environment. The bacterial chromosome carries the genes essential for maintenance and growth. The DNA molecule is ve ...
... number are often used in identification. The flagella do not have microtubules. Bacteria that possess flagella are able to detect and respond to chemical signals (chemotaxis) in their environment. The bacterial chromosome carries the genes essential for maintenance and growth. The DNA molecule is ve ...
Notes: Intercellular Junctions
... Tight Junctions: membranes of neighboring cells are tightly pressed against each other, bound by specific proteins. Prevent leakage of estracellular fluid across epithelial cells. Desmonsomes: (aka. Anchoring junctions) function like rivets, fastening cells together into strong sheets. Filaments mad ...
... Tight Junctions: membranes of neighboring cells are tightly pressed against each other, bound by specific proteins. Prevent leakage of estracellular fluid across epithelial cells. Desmonsomes: (aka. Anchoring junctions) function like rivets, fastening cells together into strong sheets. Filaments mad ...
Cell culture

Cell culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. In practice, the term ""cell culture"" now refers to the culturing of cells derived from multicellular eukaryotes, especially animal cells, in contrast with other types of culture that also grow cells, such as plant tissue culture, fungal culture, and microbiological culture (of microbes). The historical development and methods of cell culture are closely interrelated to those of tissue culture and organ culture. Viral culture is also related, with cells as hosts for the viruses. The laboratory technique of maintaining live cell lines (a population of cells descended from a single cell and containing the same genetic makeup) separated from their original tissue source became more robust in the middle 20th century.