Ch. 2 The Chemistry of Life
... - _____________ need to carry out _____________ that require _________ in order to stay ________ - ____________ release the energy needed to ________, breathe, __________, & even __________ through chemical reactions - Chemical reactions occur when humans ______________, or break down (__________) f ...
... - _____________ need to carry out _____________ that require _________ in order to stay ________ - ____________ release the energy needed to ________, breathe, __________, & even __________ through chemical reactions - Chemical reactions occur when humans ______________, or break down (__________) f ...
Chemical Building Blocks Chapter One
... Matter: anything that has mass and occupies space (pg. 14) Characteristic Property: a quality of a substance that never changes and can be used to identify the substances (pg. 15) Boiling Point: the temperature at which a substance changes from a liquid to a gas (pg. 16) Physical Change: a change in ...
... Matter: anything that has mass and occupies space (pg. 14) Characteristic Property: a quality of a substance that never changes and can be used to identify the substances (pg. 15) Boiling Point: the temperature at which a substance changes from a liquid to a gas (pg. 16) Physical Change: a change in ...
Matter and Energy
... -atoms found on the reactants side will also be found on the products side. They will be broken apart and rearranged to create new substances. -creates a “Balanced” equation CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O ...
... -atoms found on the reactants side will also be found on the products side. They will be broken apart and rearranged to create new substances. -creates a “Balanced” equation CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O ...
Chemical Reactions
... Balancing Chemical Equations 1. Begin by taking an element “inventory” for reactants and products. 2. Pick an element that only occurs once on each side. 3. Determine which side (product or reactant) has fewer of that element and put the coefficient that will make each side equal in front of the mo ...
... Balancing Chemical Equations 1. Begin by taking an element “inventory” for reactants and products. 2. Pick an element that only occurs once on each side. 3. Determine which side (product or reactant) has fewer of that element and put the coefficient that will make each side equal in front of the mo ...
Chemistry Unit Study Guide Key
... 7) what it means if elements are in the same family/group – They have similar ...
... 7) what it means if elements are in the same family/group – They have similar ...
673 lab three
... A) DISCUSS CHEMICAL REACTIONS: start with a definition and apply the law of conservation of mass in a chemical reaction to the reaction in this lab. Discuss balanced reactions and give three example reactions and SHOW that they are balanced. Clearly indicate the role of COEFFICIENTS., B) DISCUSS CHE ...
... A) DISCUSS CHEMICAL REACTIONS: start with a definition and apply the law of conservation of mass in a chemical reaction to the reaction in this lab. Discuss balanced reactions and give three example reactions and SHOW that they are balanced. Clearly indicate the role of COEFFICIENTS., B) DISCUSS CHE ...
File - Ingolstadt Academy
... Using proper units/labels Density (definition and equation) Dimensional analysis Instruments that measure mass, volume, pressure, etc. (lab stuff!) The Scientific Method Atomic Structure: ...
... Using proper units/labels Density (definition and equation) Dimensional analysis Instruments that measure mass, volume, pressure, etc. (lab stuff!) The Scientific Method Atomic Structure: ...
Chemical Equations and Tests for anions
... The total mass of the products of a chemical reaction is the same as the total mass of the reactants For example if 12 grams of Carbon dioxide react with 32 grams of oxygen 44 grams of carbon dioxide will be formed ...
... The total mass of the products of a chemical reaction is the same as the total mass of the reactants For example if 12 grams of Carbon dioxide react with 32 grams of oxygen 44 grams of carbon dioxide will be formed ...
What are reactions?
... boiling bubbles color compound condensation element equation gases heat products reactants reaction reversed word ...
... boiling bubbles color compound condensation element equation gases heat products reactants reaction reversed word ...
What are reactions? - UTLNET Secure Site
... boiling bubbles colour compound condensation element equation gases heat products reactants reaction reversed word ...
... boiling bubbles colour compound condensation element equation gases heat products reactants reaction reversed word ...
Document
... WHY ARE THERE CHEMICAL REACTIONS? CHEMICAL REACTIONS HAPPEN WHEN MOLECULES BUMP INTO EACH OTHER CAUSING THE STARTING BONDS TO BREAK APART, THE ATOMS REARRANGE, AND NEW BONDS ARE FORMED ...
... WHY ARE THERE CHEMICAL REACTIONS? CHEMICAL REACTIONS HAPPEN WHEN MOLECULES BUMP INTO EACH OTHER CAUSING THE STARTING BONDS TO BREAK APART, THE ATOMS REARRANGE, AND NEW BONDS ARE FORMED ...
Bacteria and Virus Research Jigsaw
... WHY ARE THERE CHEMICAL REACTIONS? CHEMICAL REACTIONS HAPPEN WHEN MOLECULES BUMP INTO EACH OTHER CAUSING THE STARTING BONDS TO BREAK APART, THE ATOMS REARRANGE, AND NEW BONDS ARE FORMED ...
... WHY ARE THERE CHEMICAL REACTIONS? CHEMICAL REACTIONS HAPPEN WHEN MOLECULES BUMP INTO EACH OTHER CAUSING THE STARTING BONDS TO BREAK APART, THE ATOMS REARRANGE, AND NEW BONDS ARE FORMED ...
Profile - Chimney Fabricators, Erection Contractor, Erection of
... like autoclaves, reaction vessels, blenders, centrifuges etc. • Re-Tubing of heat exchangers. • Health assessment of chemical equipments and pressure vessels at site. ...
... like autoclaves, reaction vessels, blenders, centrifuges etc. • Re-Tubing of heat exchangers. • Health assessment of chemical equipments and pressure vessels at site. ...
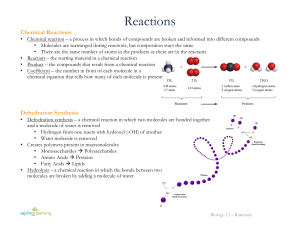
Reactions
... • Chemical reaction – a process in which bonds of compounds are broken and reformed into different compounds • Molecules are rearranged during reactions, but composition stays the same • There are the same number of atoms in the products as there are in the reactants • Reactant – the starting materi ...
... • Chemical reaction – a process in which bonds of compounds are broken and reformed into different compounds • Molecules are rearranged during reactions, but composition stays the same • There are the same number of atoms in the products as there are in the reactants • Reactant – the starting materi ...
Ch. 3 - Chemical Reactions
... A chemical reaction is a change in which one or more reactants change into one or more products. Bonds are broken and reformed ...
... A chemical reaction is a change in which one or more reactants change into one or more products. Bonds are broken and reformed ...
Study Guide – Unit Test (9-27-13)
... 7. Signs that a chemical change has occurred: Foaming/Fizzing Change in color Change in odor Rapid production of heat, light and/or sound Production of a new substance with different properties 8. Law of Conservation of Mass – matter is never created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. Example: If ...
... 7. Signs that a chemical change has occurred: Foaming/Fizzing Change in color Change in odor Rapid production of heat, light and/or sound Production of a new substance with different properties 8. Law of Conservation of Mass – matter is never created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. Example: If ...
Energy and Matter
... An Element is a substance that cannot be separated into simpler substances chemically. Found on periodic table. (ex: H, Na, B) Compounds or molecules, are two or more elements bonded together. (ex: NaCl, H2O) Pure substances are elements & compounds. ...
... An Element is a substance that cannot be separated into simpler substances chemically. Found on periodic table. (ex: H, Na, B) Compounds or molecules, are two or more elements bonded together. (ex: NaCl, H2O) Pure substances are elements & compounds. ...
Chemical plant
A chemical plant is an industrial process plant that manufactures (or otherwise processes) chemicals, usually on a large scale. The general objective of a chemical plant is to create new material wealth via the chemical or biological transformation and or separation of materials. Chemical plants use specialized equipment, units, and technology in the manufacturing process. Other kinds of plants, such as polymer, pharmaceutical, food, and some beverage production facilities, power plants, oil refineries or other refineries, natural gas processing and biochemical plants, water and wastewater treatment, and pollution control equipment use many technologies that have similarities to chemical plant technology such as fluid systems and chemical reactor systems. Some would consider an oil refinery or a pharmaceutical or polymer manufacturer to be effectively a chemical plant.Petrochemical plants (plants using chemicals from petroleum as a raw material or feedstock ) are usually located adjacent to an oil refinery to minimize transportation costs for the feedstocks produced by the refinery. Speciality chemical and fine chemical plants are usually much smaller and not as sensitive to location. Tools have been developed for converting a base project cost from one geographic location to another.