e c n i
... The activation energy is the energy needed by a system to initiate the reaction. It is the minimum energy needed for a specific chemical reaction to occur. Once achieved, the reaction continues until reactants are ...
... The activation energy is the energy needed by a system to initiate the reaction. It is the minimum energy needed for a specific chemical reaction to occur. Once achieved, the reaction continues until reactants are ...
chemical*equations
... “Success'is'not',inal,'failure' is'not'fatal:'it'is'the'courage' to'continue'that'counts.” ''7Winston'Churchill ...
... “Success'is'not',inal,'failure' is'not'fatal:'it'is'the'courage' to'continue'that'counts.” ''7Winston'Churchill ...
Physical Science
... another substance ie. Water evaporates into water vapor, a rock is broken into pieces It’s like printing a word in a different font, it’s the same word just looks different! ...
... another substance ie. Water evaporates into water vapor, a rock is broken into pieces It’s like printing a word in a different font, it’s the same word just looks different! ...
Balancing Chemical Equations
... • Describe a chemical reaction by using a word equation and a formula equation. • Relate the conservation of mass to the rearrangement of atoms in a chemical reaction • Write and interpret a balanced chemical equation for a reaction, and relate conservation of mass to the balanced equation ...
... • Describe a chemical reaction by using a word equation and a formula equation. • Relate the conservation of mass to the rearrangement of atoms in a chemical reaction • Write and interpret a balanced chemical equation for a reaction, and relate conservation of mass to the balanced equation ...
Chemical Reactions and The Mole Review
... • Focus question: What is the law of conservation of mass and what does it have to do with balancing chemical equations? • As you watch the video, jot down your thoughts on the focus question under your catalyst. Then, be ready to share. ...
... • Focus question: What is the law of conservation of mass and what does it have to do with balancing chemical equations? • As you watch the video, jot down your thoughts on the focus question under your catalyst. Then, be ready to share. ...
Energy and Chemical Change Can changes be reversed
... Some chemical reactions need energy in the form of light. Plants and some unicellular organisms use the Sun’s energy for photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the chemical reaction by which these organisms make sugar and oxygen. This process occurs only if the organisms are exposed to light. ...
... Some chemical reactions need energy in the form of light. Plants and some unicellular organisms use the Sun’s energy for photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the chemical reaction by which these organisms make sugar and oxygen. This process occurs only if the organisms are exposed to light. ...
Atoms, Elements, Compounds File
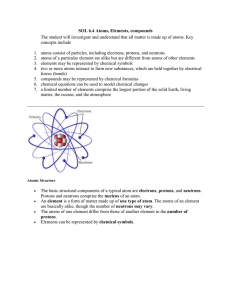
... SOL 6.4 Atoms, Elements, compounds The student will investigate and understand that all matter is made up of atoms. Key concepts include ...
... SOL 6.4 Atoms, Elements, compounds The student will investigate and understand that all matter is made up of atoms. Key concepts include ...
chemistry form iii - Covington Latin School
... Algebra I and Geometry Course Description: Students enrolled in this course will receive an introduction to the following topics: measurements in chemistry; elements and compounds; matter and energy; periodic table and chemical nomenclature; chemical reactions; quantities in chemistry; stoichiometry ...
... Algebra I and Geometry Course Description: Students enrolled in this course will receive an introduction to the following topics: measurements in chemistry; elements and compounds; matter and energy; periodic table and chemical nomenclature; chemical reactions; quantities in chemistry; stoichiometry ...
ap chemistry – 2013-2014
... Big Idea 4: Rates of chemical reactions Big Idea 5: Thermodynamics Big Idea 6: Equilibrium ...
... Big Idea 4: Rates of chemical reactions Big Idea 5: Thermodynamics Big Idea 6: Equilibrium ...
Chemistry Review: Unit2 - Menno Simons Christian School
... difficult to reverse. 7) In the table below list whether there is a chemical or physical change and how you know. Observation Sugar dissolves in water. ...
... difficult to reverse. 7) In the table below list whether there is a chemical or physical change and how you know. Observation Sugar dissolves in water. ...
Nothing Lost, Nothing Gained
... change so that they look very different, but the amount of stuff stays the same. A chemical reaction is what happens when one kind of thing changes into another kind of thing. The same number of atoms are there, but they are changed into something new. If I burn a book, all the parts that made up th ...
... change so that they look very different, but the amount of stuff stays the same. A chemical reaction is what happens when one kind of thing changes into another kind of thing. The same number of atoms are there, but they are changed into something new. If I burn a book, all the parts that made up th ...
Chapter 1: The Mole
... Heart of Chemistry Chemical formulas used. An arrow is used to separate reactants and products. Phase information is sometimes included. Equation carries no implication as to how fast the reaction occurs. ...
... Heart of Chemistry Chemical formulas used. An arrow is used to separate reactants and products. Phase information is sometimes included. Equation carries no implication as to how fast the reaction occurs. ...
Chemical reactions unit
... Think: When you hear the words “Chemical Reactions”, what comes to your mind? Often times, people picture a scientist in a lab working with chemicals. ...
... Think: When you hear the words “Chemical Reactions”, what comes to your mind? Often times, people picture a scientist in a lab working with chemicals. ...
Chemical reactions unit
... Think: When you hear the words “Chemical Reactions”, what comes to your mind? Often times, people picture a scientist in a lab working with chemicals. ...
... Think: When you hear the words “Chemical Reactions”, what comes to your mind? Often times, people picture a scientist in a lab working with chemicals. ...
CHEMICAL EQUATIONS NAME PERIOD_______ DATE________
... reaction. In a chemical equation, the substances on the left side of the arrow are the starting substances. These substances are called ______________. The substances on the right side of the arrow are the substances that result from the reaction. These substances are called ____________________. Th ...
... reaction. In a chemical equation, the substances on the left side of the arrow are the starting substances. These substances are called ______________. The substances on the right side of the arrow are the substances that result from the reaction. These substances are called ____________________. Th ...
*6th Grade Science-Chapter 5 Study Guide Lesson 5.1: Observing
... *6th Grade Science-Chapter 5 Study Guide Lesson 5.1: Observing Chemical Change *Changes in matter can be described in terms of physical changes and chemical changes. *Chemical reactions involve changes in properties and changes in energy that you can often observe. Physical change-any change that al ...
... *6th Grade Science-Chapter 5 Study Guide Lesson 5.1: Observing Chemical Change *Changes in matter can be described in terms of physical changes and chemical changes. *Chemical reactions involve changes in properties and changes in energy that you can often observe. Physical change-any change that al ...
green chemistry
... 10. Use renewable feedstocks: Use raw materials and feedstocks that are renewable rather than depleting. Renewable feedstocks are often made from agricultural products or are the wastes of other processes; depleting feedstocks are made from fossil fuels (petroleum, natural gas, or coal) or are mined ...
... 10. Use renewable feedstocks: Use raw materials and feedstocks that are renewable rather than depleting. Renewable feedstocks are often made from agricultural products or are the wastes of other processes; depleting feedstocks are made from fossil fuels (petroleum, natural gas, or coal) or are mined ...
Honors Chemistry Review Packet KEY
... 35. In a physical change, the chemical composition of the substance does not change. In a chemical change, the chemical composition of the reactant(s) changes to form one or more products. 36. a) physical, b) physical, c) chemical, d) chemical 38. 43.2 grams (4.8 g hydrogen + 38.4 g oxygen = 43.2 g ...
... 35. In a physical change, the chemical composition of the substance does not change. In a chemical change, the chemical composition of the reactant(s) changes to form one or more products. 36. a) physical, b) physical, c) chemical, d) chemical 38. 43.2 grams (4.8 g hydrogen + 38.4 g oxygen = 43.2 g ...
Chemical Reactions
... What is a chemical reaction? • A chemical reaction is the process by which the atoms of one or more substances are rearranged to form ...
... What is a chemical reaction? • A chemical reaction is the process by which the atoms of one or more substances are rearranged to form ...
Chapter 14 Chemical Reactions
... The combined mass of the burning wood and oxygen is converted into carbon dioxide and water. ...
... The combined mass of the burning wood and oxygen is converted into carbon dioxide and water. ...
An Introduction to Matter
... decomposed by a chemical change into simpler substances – An element is a pure substance which cannot be broken down into anything simpler by either physical or chemical means. ...
... decomposed by a chemical change into simpler substances – An element is a pure substance which cannot be broken down into anything simpler by either physical or chemical means. ...
Chemical plant
A chemical plant is an industrial process plant that manufactures (or otherwise processes) chemicals, usually on a large scale. The general objective of a chemical plant is to create new material wealth via the chemical or biological transformation and or separation of materials. Chemical plants use specialized equipment, units, and technology in the manufacturing process. Other kinds of plants, such as polymer, pharmaceutical, food, and some beverage production facilities, power plants, oil refineries or other refineries, natural gas processing and biochemical plants, water and wastewater treatment, and pollution control equipment use many technologies that have similarities to chemical plant technology such as fluid systems and chemical reactor systems. Some would consider an oil refinery or a pharmaceutical or polymer manufacturer to be effectively a chemical plant.Petrochemical plants (plants using chemicals from petroleum as a raw material or feedstock ) are usually located adjacent to an oil refinery to minimize transportation costs for the feedstocks produced by the refinery. Speciality chemical and fine chemical plants are usually much smaller and not as sensitive to location. Tools have been developed for converting a base project cost from one geographic location to another.