What Is a Cell?
... • Living things are constructed of cells and can be unicellular (one cell) or multicellular (many cells). • Limits on Cell Size • Cells size is limited because cells must be able to exchange materials with their surroundings. In other words, surface area relative to the volume decreases as size of c ...
... • Living things are constructed of cells and can be unicellular (one cell) or multicellular (many cells). • Limits on Cell Size • Cells size is limited because cells must be able to exchange materials with their surroundings. In other words, surface area relative to the volume decreases as size of c ...
Unit 3 - Cells
... • B. cells are the basic unit of structure & function of all living things • C. new cells are produced from existing cells ...
... • B. cells are the basic unit of structure & function of all living things • C. new cells are produced from existing cells ...
Word Definition 1 organic compound compounds that contain
... chromatids separate; one chromatid moves along the spindle fiber to one end of the cell while the other chromatid moves to the opposite end part of mitosis where chromosomes begin to stretch out and lose their rod like appearance; a new nuclear membrane forms around each region of chromosomes the fi ...
... chromatids separate; one chromatid moves along the spindle fiber to one end of the cell while the other chromatid moves to the opposite end part of mitosis where chromosomes begin to stretch out and lose their rod like appearance; a new nuclear membrane forms around each region of chromosomes the fi ...
Word Definition 1 organic compound
... the process by which a cell makes a copy of the DNA in its 14 replication / replicates nucleus the stage of the cell cycle where the cell's nucleus divides 15 mitosis into two new nuclei first part of mitosis; chromatin forms rods and spindle fibers 16 prophase form a bridge between ends of the cell ...
... the process by which a cell makes a copy of the DNA in its 14 replication / replicates nucleus the stage of the cell cycle where the cell's nucleus divides 15 mitosis into two new nuclei first part of mitosis; chromatin forms rods and spindle fibers 16 prophase form a bridge between ends of the cell ...
Cell practice problem
... this plant’s cells under the microscope, the scientist notices that the cells from the roots look different compared to the cells from the leaves. The root cells had large vacuoles, long hair like projections and no chloroplasts. The leaf cells also have a vacuole, have no hair like projections have ...
... this plant’s cells under the microscope, the scientist notices that the cells from the roots look different compared to the cells from the leaves. The root cells had large vacuoles, long hair like projections and no chloroplasts. The leaf cells also have a vacuole, have no hair like projections have ...
Basic Structure of a Cell
... 1. In 1655, Robert ____________ used a ___________ to examine a thin slice of ___________. Were these cells living? _____ What was their shape? ________ 2. Hooke was responsible for _________ them "cells" because they looked like the ...
... 1. In 1655, Robert ____________ used a ___________ to examine a thin slice of ___________. Were these cells living? _____ What was their shape? ________ 2. Hooke was responsible for _________ them "cells" because they looked like the ...
Cell Theory/Cell Basics Notes Page
... 1. In 1655, Robert ____________ used a ___________ to examine a thin slice of ___________. Were these cells living? _____ What was their shape? ________ 2. Hooke was responsible for _________ them "cells" because they looked like the ...
... 1. In 1655, Robert ____________ used a ___________ to examine a thin slice of ___________. Were these cells living? _____ What was their shape? ________ 2. Hooke was responsible for _________ them "cells" because they looked like the ...
Review: parts of a microscope history of cell theory different types of
... have no membrane bound organelles their DNA is concentrated in a area known as the nucleoid ...
... have no membrane bound organelles their DNA is concentrated in a area known as the nucleoid ...
CELL TEST REVIEW:
... The composition and structure and parts of the cell (plasma) membrane (i.e. phospholipids, proteins, steroids/cholesterol, carbohydrates) Integral vs peripheral proteins What regions of the membrane are polar and nonpolar Understand the fluid mosaic model ...
... The composition and structure and parts of the cell (plasma) membrane (i.e. phospholipids, proteins, steroids/cholesterol, carbohydrates) Integral vs peripheral proteins What regions of the membrane are polar and nonpolar Understand the fluid mosaic model ...
Cells! - Net Start Class
... Teacher Notes • Slides 12,13, 14,17,19,22- are not tested TEK organelles.. You can review if you want to, but they will not be tested over them. ...
... Teacher Notes • Slides 12,13, 14,17,19,22- are not tested TEK organelles.. You can review if you want to, but they will not be tested over them. ...
Cells Structure and Functions
... Contain major structures inside that perform these life functions Vary in size, but contain many of the same structures ...
... Contain major structures inside that perform these life functions Vary in size, but contain many of the same structures ...
ChillProtec
... Even primary cells remain intact after cold storage for a longer period of time Adherent cells, cell suspensions or small tissue pieces are able to remain intact after cold storage when kept in the new medium ChillProtec. The protective medium reduces cell damage caused by cold. Primary human hepat ...
... Even primary cells remain intact after cold storage for a longer period of time Adherent cells, cell suspensions or small tissue pieces are able to remain intact after cold storage when kept in the new medium ChillProtec. The protective medium reduces cell damage caused by cold. Primary human hepat ...
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
... ▫ Have now been found to live in many different environments In the ocean, soil, fresh water, and others ...
... ▫ Have now been found to live in many different environments In the ocean, soil, fresh water, and others ...
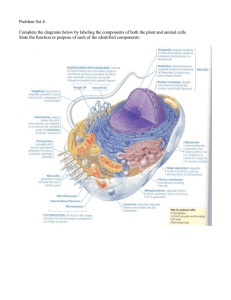
Problem Set 4:
... Complete the diagrams below by labeling the components of both the plant and animal cells. State the function or purpose of each of the identified components: ...
... Complete the diagrams below by labeling the components of both the plant and animal cells. State the function or purpose of each of the identified components: ...
Presentation on Cells
... Why are cells different? Some animal and plant cells are made of just one cell, or just few cells. All of their cells have to carry out all the processes of life. However, large organisms are more complicated and they have different organs to do different jobs. The shape and structure of each cell ...
... Why are cells different? Some animal and plant cells are made of just one cell, or just few cells. All of their cells have to carry out all the processes of life. However, large organisms are more complicated and they have different organs to do different jobs. The shape and structure of each cell ...
How Does a Cell Spend Most of it`s Life
... Note: % of cells = [(# in that stage) / (total # viewed)] x 100% Results: Create a bar graph (histogram) that shows the percentage of cells that are in each stage of the cell cycle ...
... Note: % of cells = [(# in that stage) / (total # viewed)] x 100% Results: Create a bar graph (histogram) that shows the percentage of cells that are in each stage of the cell cycle ...
Cell division File
... • Nuclear membranes form around each new nucleus. • Division of cytoplasm or cytokinesis occurs. ...
... • Nuclear membranes form around each new nucleus. • Division of cytoplasm or cytokinesis occurs. ...
Terms to know - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... anaphase - The third stage of mitosis during which all of the sister chromatid pairs break simultaneously and are tugged toward opposite ends of the cell by the spindle fibers. cell cycle - A description of the general stages of life of a eukaryotic cell. It is divided into mitosis and interphase. c ...
... anaphase - The third stage of mitosis during which all of the sister chromatid pairs break simultaneously and are tugged toward opposite ends of the cell by the spindle fibers. cell cycle - A description of the general stages of life of a eukaryotic cell. It is divided into mitosis and interphase. c ...
Plant Cell
... Rough ER is important in the synthesis of other proteins. At the ribosomes on the rough ER, the messenger RNA is translated into proteins Smooth ER is important in the synthesis of lipids and membrane proteins ...
... Rough ER is important in the synthesis of other proteins. At the ribosomes on the rough ER, the messenger RNA is translated into proteins Smooth ER is important in the synthesis of lipids and membrane proteins ...
science ch1 lesson 1
... Cell: is the smallest unit of a living thing that can perform all life processes ...
... Cell: is the smallest unit of a living thing that can perform all life processes ...
In 1839
... •Schwann remembered seeing similar structures in the cells of the notochord and instantly realized the importance of connecting the two phenomena and soon appeared in his famous Microscopic Investigations on the Accordance in the Structure and Growth of Plants and Animals. • Theodor Schwann declared ...
... •Schwann remembered seeing similar structures in the cells of the notochord and instantly realized the importance of connecting the two phenomena and soon appeared in his famous Microscopic Investigations on the Accordance in the Structure and Growth of Plants and Animals. • Theodor Schwann declared ...
Plants Animals Fungi Bacteria Protists
... A microscope is a tool we use to see small objects. ...
... A microscope is a tool we use to see small objects. ...
organelles - GEOCITIES.ws
... Produce most of the energy needed for cell functions Muscle cells have lots of these ...
... Produce most of the energy needed for cell functions Muscle cells have lots of these ...
FLASH CARD REVIEW: Cell Membrane Transport
... • The very outside! • Outside & Around the Cell Membrane! ...
... • The very outside! • Outside & Around the Cell Membrane! ...