Cell Transport Systems
... • Conversely, in a salt-water environment, cells must pump water into the cell. This is called a hypertonic solution. The cell can lose water and "shrivel" this is called crenation. • Cells in larger organisms are surrounded by solution with roughly equal concentrations of H2O and solvents. This is ...
... • Conversely, in a salt-water environment, cells must pump water into the cell. This is called a hypertonic solution. The cell can lose water and "shrivel" this is called crenation. • Cells in larger organisms are surrounded by solution with roughly equal concentrations of H2O and solvents. This is ...
SNC2P (1.3) Cell Differences rev
... Cell Development • All cells start their lives as identical cells called stem cells. ...
... Cell Development • All cells start their lives as identical cells called stem cells. ...
Plant-Cell
... Golgi apparatus: a flattened, layered, sac-like that looks like a stack of pancakes and is located near the nucleus. It packages proteins and carbohydrates to release from the cell. ...
... Golgi apparatus: a flattened, layered, sac-like that looks like a stack of pancakes and is located near the nucleus. It packages proteins and carbohydrates to release from the cell. ...
Chapter 7 – A Tour of the Cell
... - First used by Renaissance scientists (Remember Hooke and Von Leeuwenhoek). - Visible light is passed through a specimen and then through multiple lenses to enlarge the apparent object. - Object is usually stained so that some light is absorbed or induced to fluoresce. ...
... - First used by Renaissance scientists (Remember Hooke and Von Leeuwenhoek). - Visible light is passed through a specimen and then through multiple lenses to enlarge the apparent object. - Object is usually stained so that some light is absorbed or induced to fluoresce. ...
MITOSIS
... 2. is the longest part of the cell cycle 3. has 4 parts a. “every day life”- when the cell is just doing its thing b. G1 phase- the cell begins to double in size c. S phase- DNA duplicates (go from 46 chromatids to 92 chromatids) d. G2 phase- cell is ready to start mitosis PROPHASE 1. is the first s ...
... 2. is the longest part of the cell cycle 3. has 4 parts a. “every day life”- when the cell is just doing its thing b. G1 phase- the cell begins to double in size c. S phase- DNA duplicates (go from 46 chromatids to 92 chromatids) d. G2 phase- cell is ready to start mitosis PROPHASE 1. is the first s ...
C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator\My Documents
... Proteins are produced by ribosomes which normally attach to the ER. Ions, water, and food are stored in vacuoles in the ER. There are 5 major animal tissues including epithelial tissue which lines cavities. If a disaccharide is split, 2 monosaccharides and 1 water molecule are produced. Monosacchari ...
... Proteins are produced by ribosomes which normally attach to the ER. Ions, water, and food are stored in vacuoles in the ER. There are 5 major animal tissues including epithelial tissue which lines cavities. If a disaccharide is split, 2 monosaccharides and 1 water molecule are produced. Monosacchari ...
The Living World
... Used for long-term energy storage Also termed triglycerides or triacylglycerol Composed of three fatty acid chains linked to glycerol ...
... Used for long-term energy storage Also termed triglycerides or triacylglycerol Composed of three fatty acid chains linked to glycerol ...
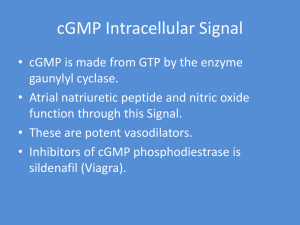
cGMP Intracellular Signal
... cytokines, reactive oxygen species, and mitogens lead to the activation of IкB kinase complex, called IKK. • IKK phosphorylate inhibitor(IкB). • This causes degradation of inhibitor(IкB). • NF-кB factor is free and it translocates to the nucleus and promote gene transcription. ...
... cytokines, reactive oxygen species, and mitogens lead to the activation of IкB kinase complex, called IKK. • IKK phosphorylate inhibitor(IкB). • This causes degradation of inhibitor(IкB). • NF-кB factor is free and it translocates to the nucleus and promote gene transcription. ...
My Cell Division Notes [PDF Document]
... same as the parent nucleus. its stages include: 1. Prophase: chromatin-chromosomes, chromosomes attach at centromeres, nuclear membrane begins to dissolve and centrioles produce spindle fibres. 2. Metaphase: chromosomes line up along equator and spindle fibres attach to ...
... same as the parent nucleus. its stages include: 1. Prophase: chromatin-chromosomes, chromosomes attach at centromeres, nuclear membrane begins to dissolve and centrioles produce spindle fibres. 2. Metaphase: chromosomes line up along equator and spindle fibres attach to ...
Role of intracellular level of glutathione on the therapeutic capacity
... enhanced therapeutic potency of MSCs. Employing a newly synthesized fluorescent probe (FreSH tracer) which exhibit reversible reaction with various thiol-compounds by forming thioether adduct, Human embryonic stem cells (hES) derived MSC (hES-MSC) were FACS sorted as GSHhigh verus GSHlow fractions. ...
... enhanced therapeutic potency of MSCs. Employing a newly synthesized fluorescent probe (FreSH tracer) which exhibit reversible reaction with various thiol-compounds by forming thioether adduct, Human embryonic stem cells (hES) derived MSC (hES-MSC) were FACS sorted as GSHhigh verus GSHlow fractions. ...
IB Biology Chapter 1 Unit Test Study Outline
... What are the stages of the cell cycle and what are the primary steps of each stage? What the difference between haploid and diploid and which is produce from mitosis and meiosis? What are the 3 main phases of interphase and what is the G0 phase? What normal functions do cells carry out in interphase ...
... What are the stages of the cell cycle and what are the primary steps of each stage? What the difference between haploid and diploid and which is produce from mitosis and meiosis? What are the 3 main phases of interphase and what is the G0 phase? What normal functions do cells carry out in interphase ...
ELL Science Term 1 Exam 1 Study Guide
... Why is water so important to cells? Proteins are made up of units called __________ _________. What are the two types of nucleic acids? ...
... Why is water so important to cells? Proteins are made up of units called __________ _________. What are the two types of nucleic acids? ...
Bio1A Unit 2-8 Gene Expression Pt 2 Notes File
... • Contains gene for transposase - Recognizes terminal repeats - Cuts and inserts into new location • Mechanism removes transposon but leaves behind a copy of the repeats = “footprints” ...
... • Contains gene for transposase - Recognizes terminal repeats - Cuts and inserts into new location • Mechanism removes transposon but leaves behind a copy of the repeats = “footprints” ...
File
... The phospholipids of the cell membrane have two components. Which of these parts is attracted to the water outside the cell and the water in the cytoplasm? ...
... The phospholipids of the cell membrane have two components. Which of these parts is attracted to the water outside the cell and the water in the cytoplasm? ...
1.3 Cell Differences (p40-43) Cell Development All cells start their
... Specialized Cells Structure and ...
... Specialized Cells Structure and ...
Getting things where they need to go: Protein Targeting
... •Suggest problem lies in protein targeting Proteins made in cytosol (cytosolic and membrane ones) Sorting places proteins in membrane and in lumen of organelles ...
... •Suggest problem lies in protein targeting Proteins made in cytosol (cytosolic and membrane ones) Sorting places proteins in membrane and in lumen of organelles ...
Lecture 1
... • Biotechnology terminology • Common hosts and experimental organisms • Transcription and translation • Prokaryotic gene organization & expression ...
... • Biotechnology terminology • Common hosts and experimental organisms • Transcription and translation • Prokaryotic gene organization & expression ...
File - Timber Wolves
... What is a cell? (C 11) The _______________ unit of a living thing. It is the smallest part of an organism that is still considered “__________” What are unicellular They are made of a ___________ cell. They are usually too ______ for you to organisms? (C 11) _______ directly. (ex. Found in _______ w ...
... What is a cell? (C 11) The _______________ unit of a living thing. It is the smallest part of an organism that is still considered “__________” What are unicellular They are made of a ___________ cell. They are usually too ______ for you to organisms? (C 11) _______ directly. (ex. Found in _______ w ...
Cell Notes
... Cell Transport Notes Cell (Plasma)Membrane- super thin layer - called cell or plasma membrane - 2 functions → @ the same time 1. Separates the cell from the outside environment 2. Connects the cell to its surroundings by controlling what enters and leaves the cells ...
... Cell Transport Notes Cell (Plasma)Membrane- super thin layer - called cell or plasma membrane - 2 functions → @ the same time 1. Separates the cell from the outside environment 2. Connects the cell to its surroundings by controlling what enters and leaves the cells ...
The Cell Cycle: Interphase, Mitosis
... are pointing to cells in Interphase. Since Interphase is the longest phase of the cell cycle, most of the cells you observe will be in Interphase ...
... are pointing to cells in Interphase. Since Interphase is the longest phase of the cell cycle, most of the cells you observe will be in Interphase ...
Cell Structure and Function
... make their own food _______________ and are not dependent on outside sources for their food. ...
... make their own food _______________ and are not dependent on outside sources for their food. ...
Cells, Tissues, & Organs
... enzymes. Break down old cell parts • Cytoskeleton - The “skeleton” of the cell. Consists of microtubules and microfilaments • Vacuoles - Large membranous bubbles which store substances inside the cell ...
... enzymes. Break down old cell parts • Cytoskeleton - The “skeleton” of the cell. Consists of microtubules and microfilaments • Vacuoles - Large membranous bubbles which store substances inside the cell ...
Communication & cell signalling
... Communication & cell signalling Explain the term ‘cell signalling’ Explain the role for membrane-bound receptors as sites where hormones & drugs can bind ...
... Communication & cell signalling Explain the term ‘cell signalling’ Explain the role for membrane-bound receptors as sites where hormones & drugs can bind ...






![My Cell Division Notes [PDF Document]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015866407_1-8ba2d4650ee384ad6bb840fcb84f7caa-300x300.png)