CELL DIVISION
... Chromosomes • Chromosomes are the structures that contain genetic material we are passing from generation to generation in our cells. • Chromatin is the relaxed form of DNA in a cell’s nucleus. • Chromosomes are much more organized than chromatin. ...
... Chromosomes • Chromosomes are the structures that contain genetic material we are passing from generation to generation in our cells. • Chromatin is the relaxed form of DNA in a cell’s nucleus. • Chromosomes are much more organized than chromatin. ...
The cell is like a car - APBiology2015-2016
... • like the fuel pump in your car if the tank is the amino acid the gas is the protein ...
... • like the fuel pump in your car if the tank is the amino acid the gas is the protein ...
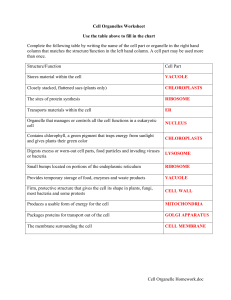
Cell Organelle Homework.doc Cell Organelles Worksheet
... Use the table above to fill in the chart Complete the following table by writing the name of the cell part or organelle in the right hand column that matches the structure/function in the left hand column. A cell part may be used more than once. Structure/Function ...
... Use the table above to fill in the chart Complete the following table by writing the name of the cell part or organelle in the right hand column that matches the structure/function in the left hand column. A cell part may be used more than once. Structure/Function ...
Mitosis Notes
... (chromatin) as the start, but as each chromosome and its copy (sister chromosome) change to sister chromatids at end of this phase ...
... (chromatin) as the start, but as each chromosome and its copy (sister chromosome) change to sister chromatids at end of this phase ...
CLASS COPY Macromolecules, Membranes, and Transport Practice
... The process that joins monomers into polymers and produces water is: __________________________ The process that breaks up polymers into monomers and uses water is: __________________________ ...
... The process that joins monomers into polymers and produces water is: __________________________ The process that breaks up polymers into monomers and uses water is: __________________________ ...
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
... Bakers/brewers yeast Eukaryote Complete genome sequenced ~6000 genes Experimentally tractable Available genetic and molecular toolkit Lots of natural genetic variation to exploit ...
... Bakers/brewers yeast Eukaryote Complete genome sequenced ~6000 genes Experimentally tractable Available genetic and molecular toolkit Lots of natural genetic variation to exploit ...
Document
... This feedback loop is the basis of the autocatalytic, self-reproducing behavior of living organisms ...
... This feedback loop is the basis of the autocatalytic, self-reproducing behavior of living organisms ...
Name
... 28. ______________________: makes proteins 29. ______________________: “powerhouse” of cell; makes energy 30. _____________________: garbage man; cleans up and digests proteins, viruses, lipids, etc. 31. _____________________: outside cell membrane; only in plant cells 32. _____________________: mak ...
... 28. ______________________: makes proteins 29. ______________________: “powerhouse” of cell; makes energy 30. _____________________: garbage man; cleans up and digests proteins, viruses, lipids, etc. 31. _____________________: outside cell membrane; only in plant cells 32. _____________________: mak ...
Cell Organelles
... Site of protein synthesis Found attached to rough ER or floating free in cytosol Produced in a part of the nucleus called the nucleolus That looks familiar…what is a polypeptide? ...
... Site of protein synthesis Found attached to rough ER or floating free in cytosol Produced in a part of the nucleus called the nucleolus That looks familiar…what is a polypeptide? ...
Looking Inside Cells
... 4. Where is the cell membrane located in cells that have cell walls? just inside the cell wall 5. Where is the cell membrane located in cells that do NOT have cell walls? it’s the outside boundary that separates the cell from the environment 6. What is the main function of the cell membrane? It allo ...
... 4. Where is the cell membrane located in cells that have cell walls? just inside the cell wall 5. Where is the cell membrane located in cells that do NOT have cell walls? it’s the outside boundary that separates the cell from the environment 6. What is the main function of the cell membrane? It allo ...
All About Cells
... All living things are made up of cells There are millions of cells in your body New cells are constantly growing to replace old cells Cells in our body have many different jobs, but they all contain similar parts called organelles Animal and plant cells are similar, but contain a few different parts ...
... All living things are made up of cells There are millions of cells in your body New cells are constantly growing to replace old cells Cells in our body have many different jobs, but they all contain similar parts called organelles Animal and plant cells are similar, but contain a few different parts ...
Types of Microscopes
... Uses flow of electrons to create computer images of atoms on the surface of a molecule ...
... Uses flow of electrons to create computer images of atoms on the surface of a molecule ...
Paper 6-LSPT 202-BIOLOGY-II THEORY Marks: 100 Cell and
... microscopy; X-ray diffraction analysis Unit 2. Cell as a unit of Life (Ch 6 Campbell) (10 Periods) The Cell Theory; Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells; Cell size and shape; Eukaryotic Cell components Unit 3. Cell Organelles (Ch 15, 16, 17,18,19,20 Sheeler) (22 Periods) • Mitochondria: Structure, marke ...
... microscopy; X-ray diffraction analysis Unit 2. Cell as a unit of Life (Ch 6 Campbell) (10 Periods) The Cell Theory; Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells; Cell size and shape; Eukaryotic Cell components Unit 3. Cell Organelles (Ch 15, 16, 17,18,19,20 Sheeler) (22 Periods) • Mitochondria: Structure, marke ...
Chapter 6: Cell structure revision questions
... Function in the cell: Cell membrane Cell wall Nucleus Ribosome Cytosol Mitochondrion Chloroplast ...
... Function in the cell: Cell membrane Cell wall Nucleus Ribosome Cytosol Mitochondrion Chloroplast ...
Unit A, Chapter 1, Lesson 1
... All plants and animals have what in common? They are all made up of cells Name three different types of cells. 1.White blood cells 2.Red blood cells 3.Muscle cells Parts of a Cell Even smaller structures in cells are called organelles. Define these plant and animal cell organelles: Cell Membrane – a ...
... All plants and animals have what in common? They are all made up of cells Name three different types of cells. 1.White blood cells 2.Red blood cells 3.Muscle cells Parts of a Cell Even smaller structures in cells are called organelles. Define these plant and animal cell organelles: Cell Membrane – a ...
Cells
... 4. Plant Cell Structures - give the description and function for the following cell structures as seen through a compound light microscope: Cell Structure Vacuole ...
... 4. Plant Cell Structures - give the description and function for the following cell structures as seen through a compound light microscope: Cell Structure Vacuole ...
Lecture slides for 05 Cell Signallling
... membrane. The non-steroid signals never enter the cell. When the signal attaches to the receptor, it will cause a change in the shape of the receptor site. Receptors are usually proteins inserted into the plasma membrane. ...
... membrane. The non-steroid signals never enter the cell. When the signal attaches to the receptor, it will cause a change in the shape of the receptor site. Receptors are usually proteins inserted into the plasma membrane. ...
unit 4 overview
... CA State Standards: Cell Biology 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism's cells. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know cells are enclosed within semi permeable membranes t ...
... CA State Standards: Cell Biology 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism's cells. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know cells are enclosed within semi permeable membranes t ...
The Cell Study Guide Vocabulary: Cell theory Cytoplasm Organelle
... exit through the pores in the nucleus and are found in the RER. Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis, where amino acids are linked to form protein (by peptide bonds). The ER can pinch off, creating a vesicle around the protein. The vesicle—wrapped protein travels to the golgi body where the p ...
... exit through the pores in the nucleus and are found in the RER. Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis, where amino acids are linked to form protein (by peptide bonds). The ER can pinch off, creating a vesicle around the protein. The vesicle—wrapped protein travels to the golgi body where the p ...