Jan. 9th, 2012 Warm Up
... thousand powerpoints submitted by teachers. This is a completely free site and requires no registration. Please visit and I hope it will help in your teaching. ...
... thousand powerpoints submitted by teachers. This is a completely free site and requires no registration. Please visit and I hope it will help in your teaching. ...
03-Mitosis student HO - Alexmac
... A new ________________________ forms around each group of daughter chromosomes. ...
... A new ________________________ forms around each group of daughter chromosomes. ...
Chapter 10 Section 2 Notes
... In ________________________, cell division occurs in ______________ main stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is call ______________________. The second stage, division of the cytoplasm, is called ____________________________. Mitosis is the source of ______________ cells w ...
... In ________________________, cell division occurs in ______________ main stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is call ______________________. The second stage, division of the cytoplasm, is called ____________________________. Mitosis is the source of ______________ cells w ...
TEST REVIEW: Microscope, Cell, Viruses, Monera and
... Protists: 1. Describe the three types of protists, where they live, and how they obtain energy. 2. Are they prokaryotes or eukaryotes, unicellular or multicellular? 3. When did they evolve? 4. Describe the importance of plant like protists (algae) to life on earth. Eukaryotic Cell Functions State th ...
... Protists: 1. Describe the three types of protists, where they live, and how they obtain energy. 2. Are they prokaryotes or eukaryotes, unicellular or multicellular? 3. When did they evolve? 4. Describe the importance of plant like protists (algae) to life on earth. Eukaryotic Cell Functions State th ...
Cell Structure and Function VOCABULARY active transport p
... cilium – short, hairlike projection that functions in cells movement cytoplasm – semifluid material inside the cell’s plasma membrane cytoskeleton – supporting network of protein fibres that provide a framework for the cell within thy cytoplasm diffusion – net movement of particles from an a ...
... cilium – short, hairlike projection that functions in cells movement cytoplasm – semifluid material inside the cell’s plasma membrane cytoskeleton – supporting network of protein fibres that provide a framework for the cell within thy cytoplasm diffusion – net movement of particles from an a ...
Eukaryotic Cell Substructure
... Cells contain elaborate arrays of protein fibers that serve such functions as: • Establishing cell shape • Providing mechanical strength • Locomotion (cilia, flagella) • Chromosome separation in mitosis and meiosis • Intracellular transport of organelles ...
... Cells contain elaborate arrays of protein fibers that serve such functions as: • Establishing cell shape • Providing mechanical strength • Locomotion (cilia, flagella) • Chromosome separation in mitosis and meiosis • Intracellular transport of organelles ...
cell theory - BiologyNash
... function of the cell nucleus. •Describe the function of the major cell organelles. •Identify the main roles of the cytoskeleton. ...
... function of the cell nucleus. •Describe the function of the major cell organelles. •Identify the main roles of the cytoskeleton. ...
Word Document
... of organized biological molecules. Of those molecules, proteins serve most of the cell's functions. All cells encode the instructions to make these proteins as DNA, at least at in some point in their lives. Cells often store energy in carbohydrates, and their membranes are made of lipids. So all fou ...
... of organized biological molecules. Of those molecules, proteins serve most of the cell's functions. All cells encode the instructions to make these proteins as DNA, at least at in some point in their lives. Cells often store energy in carbohydrates, and their membranes are made of lipids. So all fou ...
Cell - Cloudfront.net
... Within the nucleus is a material called chromatin. The chromatin contains the hereditary information of the cell. When a cell reproduces, the chromatin becomes visible as long strands called chromosomes. ...
... Within the nucleus is a material called chromatin. The chromatin contains the hereditary information of the cell. When a cell reproduces, the chromatin becomes visible as long strands called chromosomes. ...
File - GarzScience!
... fibers form, and centrioles prepare for cell division Metaphase à spindle fibers attach to centromeres and move chromosomes to middle of cell Anaphase à spindle fibers pull the centromeres causing the chromosomes to split apart and move to opposite ends of cell Telophase à nuclear envelope reform ...
... fibers form, and centrioles prepare for cell division Metaphase à spindle fibers attach to centromeres and move chromosomes to middle of cell Anaphase à spindle fibers pull the centromeres causing the chromosomes to split apart and move to opposite ends of cell Telophase à nuclear envelope reform ...
Cell Parts and Function Analogy
... Pre-lab discussion and questions (p. 28 in IT) Lab-Comparing plant and animal cells (p. 28 in IT) Homework-p. 181, 1-5 (p. 25 in interactive ...
... Pre-lab discussion and questions (p. 28 in IT) Lab-Comparing plant and animal cells (p. 28 in IT) Homework-p. 181, 1-5 (p. 25 in interactive ...
The Toolbox of Science
... Proteins that speed up chemical reactions. • Cracker Experiment – allergies? ...
... Proteins that speed up chemical reactions. • Cracker Experiment – allergies? ...
Cells - Life Learning Cloud
... • All living organisms are composed of cells. • The simplest organisms are made of one single cell. • More complex organisms like animals and plants are made of many cells and are called multicellular organisms. • In multicellular organisms there are many different types of cells that are speciali ...
... • All living organisms are composed of cells. • The simplest organisms are made of one single cell. • More complex organisms like animals and plants are made of many cells and are called multicellular organisms. • In multicellular organisms there are many different types of cells that are speciali ...
What is a Cell Analogy?
... that of a cell. Each part of that object or organization has parts or departments that function into a similar capacity as that of the cell’s structure. For example: One may compare the “Starship Enterprise” from the Star Trek television shows to a cell. One may say that the ‘dilithium crystals’ tha ...
... that of a cell. Each part of that object or organization has parts or departments that function into a similar capacity as that of the cell’s structure. For example: One may compare the “Starship Enterprise” from the Star Trek television shows to a cell. One may say that the ‘dilithium crystals’ tha ...
CHAPTER 4 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
... a. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a system of membrane channels and saccules (flattened vesicles) continuous with the outer membrane of the nuclear envelope. b. Rough ER is studded with ribosomes on the cytoplasm side; it is the site where proteins are synthesized and enter the ER interior for pr ...
... a. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a system of membrane channels and saccules (flattened vesicles) continuous with the outer membrane of the nuclear envelope. b. Rough ER is studded with ribosomes on the cytoplasm side; it is the site where proteins are synthesized and enter the ER interior for pr ...
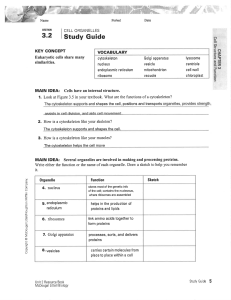
3.2 Study Guide KEY
... All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane that is flex¡ble and ¡nteracts w¡th the env¡ronmênt only certa¡n cells have a cell wâll wh¡ch ìs rigid and provides shape and support toEells ...
... All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane that is flex¡ble and ¡nteracts w¡th the env¡ronmênt only certa¡n cells have a cell wâll wh¡ch ìs rigid and provides shape and support toEells ...
Calling All Cells
... Cell Wall- Its a protective layer that surrounds the cell membrane of plant cell. Cell Membrane- It’s a thin structure that surrounds the cell. Its controls which materials can come in the cell and leave the cell. Cytoplasm- It’s a thick fluid that is most of the cell. Nucleus- Is a large structure ...
... Cell Wall- Its a protective layer that surrounds the cell membrane of plant cell. Cell Membrane- It’s a thin structure that surrounds the cell. Its controls which materials can come in the cell and leave the cell. Cytoplasm- It’s a thick fluid that is most of the cell. Nucleus- Is a large structure ...
Cell nucleus

In cell biology, the nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin nucleus or nuculeus, meaning kernel) is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types have no nuclei, and a few others have many.Cell nuclei contain most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these chromosomes are the cell's nuclear genome. The function of the nucleus is to maintain the integrity of these genes and to control the activities of the cell by regulating gene expression—the nucleus is, therefore, the control center of the cell. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm, and the nucleoskeleton (which includes nuclear lamina), a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support, much like the cytoskeleton, which supports the cell as a whole.Because the nuclear membrane is impermeable to large molecules, nuclear pores are required that regulate nuclear transport of molecules across the envelope. The pores cross both nuclear membranes, providing a channel through which larger molecules must be actively transported by carrier proteins while allowing free movement of small molecules and ions. Movement of large molecules such as proteins and RNA through the pores is required for both gene expression and the maintenance of chromosomes. The interior of the nucleus does not contain any membrane-bound sub compartments, its contents are not uniform, and a number of sub-nuclear bodies exist, made up of unique proteins, RNA molecules, and particular parts of the chromosomes. The best-known of these is the nucleolus, which is mainly involved in the assembly of ribosomes. After being produced in the nucleolus, ribosomes are exported to the cytoplasm where they translate mRNA.