Year 12 Induction Task Induction task: The Ultrastructure of Cells
... • apply their knowledge of the function of organelles to explain the adaptations of several cells; • speculate which organelle may be the most critical in the functioning of a eukaryotic cell and support this idea with evidence from the research that you have completed. ...
... • apply their knowledge of the function of organelles to explain the adaptations of several cells; • speculate which organelle may be the most critical in the functioning of a eukaryotic cell and support this idea with evidence from the research that you have completed. ...
CELL STRUCTURE STUDY GUIDE
... concentration of solute molecules OUTSIDE the cell than inside. Draw a picture to the right and label the movement of water. ...
... concentration of solute molecules OUTSIDE the cell than inside. Draw a picture to the right and label the movement of water. ...
cell_structure_and_function_assignment_questions_value_55
... c) ( TRUE / FALSE ) The cell membrane is not a living part of the cell. d) ( TRUE / FALSE ) The cell wall is not a living part of the cell. e) ( TRUE / FALSE ) Organelles within cells have specialized jobs. f) ( TRUE / FALSE ) All cells have the same function. g) ( TRUE / FALSE ) Cells are the basic ...
... c) ( TRUE / FALSE ) The cell membrane is not a living part of the cell. d) ( TRUE / FALSE ) The cell wall is not a living part of the cell. e) ( TRUE / FALSE ) Organelles within cells have specialized jobs. f) ( TRUE / FALSE ) All cells have the same function. g) ( TRUE / FALSE ) Cells are the basic ...
Notes: Chapter 7
... 1. Cytoplasm – fluid portion outside of the nucleus 2. Nucleus – holds the genetic material 3. Chromosomes – genetic material; threadlike structures made of DNA 4. DNA – the instructions for making important proteins and other important molecules 5. Nuclear Envelope – surrounds the nucleus; contains ...
... 1. Cytoplasm – fluid portion outside of the nucleus 2. Nucleus – holds the genetic material 3. Chromosomes – genetic material; threadlike structures made of DNA 4. DNA – the instructions for making important proteins and other important molecules 5. Nuclear Envelope – surrounds the nucleus; contains ...
Stores water, nutrients, waste, etc. “Storage Sack” within the cell
... 5. See cell notes for drawings. 6. Euglenas and plants both have chloroplasts. This means both euglenas and plants can make their own food through photosynthesis. 7. Definitions: Unicellular: made of one cell ...
... 5. See cell notes for drawings. 6. Euglenas and plants both have chloroplasts. This means both euglenas and plants can make their own food through photosynthesis. 7. Definitions: Unicellular: made of one cell ...
Cell Structure and Taxonomy
... Cell Membrane Cell Wall Cytoplasm Endoplamic Reticulum Golgi Complex ...
... Cell Membrane Cell Wall Cytoplasm Endoplamic Reticulum Golgi Complex ...
Cells and Their Organelles
... of the cell. It contains DNA assembled into chromosomes, which provides the instructions necessary for the production of other cell components and for the reproduction of life. The nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear membrane. Inside the nucleus is a prominent structure called the nucleolus which m ...
... of the cell. It contains DNA assembled into chromosomes, which provides the instructions necessary for the production of other cell components and for the reproduction of life. The nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear membrane. Inside the nucleus is a prominent structure called the nucleolus which m ...
Living Systems
... 2. All living things are made up of _____one____ or ______more______ cells. 3. Cells are so _______small______ that they can only be seen under a ____microscope__________. 4. The simplest organisms, such as bacteria, are made of ____one___ cell. 5. Most plants and animals are made up of ______many__ ...
... 2. All living things are made up of _____one____ or ______more______ cells. 3. Cells are so _______small______ that they can only be seen under a ____microscope__________. 4. The simplest organisms, such as bacteria, are made of ____one___ cell. 5. Most plants and animals are made up of ______many__ ...
Mitosis
... Why Mitosis? • Allows multicellular organisms to grow • 10 m of DNA in 10 um nuclear diameter • Chromosomes = compact DNA & proteins, easy to move - facilitates division ...
... Why Mitosis? • Allows multicellular organisms to grow • 10 m of DNA in 10 um nuclear diameter • Chromosomes = compact DNA & proteins, easy to move - facilitates division ...
Ch 7.3 Cell Parts and Functions
... Plant and Animal Cell Structures Organelles are bodies within the cytoplasm that serve to physically separate the various metabolic reactions that occur within the cells Organelles are specialized structures that carry out specific cell function Nucleus ...
... Plant and Animal Cell Structures Organelles are bodies within the cytoplasm that serve to physically separate the various metabolic reactions that occur within the cells Organelles are specialized structures that carry out specific cell function Nucleus ...
Eukaryotic
... • No membrane bound nucleus • Nucleoid = region of DNA concentration • Organelles not bound by membranes ...
... • No membrane bound nucleus • Nucleoid = region of DNA concentration • Organelles not bound by membranes ...
Slide 1
... › Produced through mitosis › Has 46 chromosomes (23 pairs) Homolog – each member of a chromosome pair Diploid (2n) – total of 46 chromosomes in people – zygote & somatic cells Haploid (n) – total of 23 chromosomes in people, gametes (sperm & egg) ...
... › Produced through mitosis › Has 46 chromosomes (23 pairs) Homolog – each member of a chromosome pair Diploid (2n) – total of 46 chromosomes in people – zygote & somatic cells Haploid (n) – total of 23 chromosomes in people, gametes (sperm & egg) ...
Chitin is a component of ______ cell walls
... a. Folded membranes increase surface area for efficiency. b. Folded membranes do not form compartments in the cell. c. Endoplasmic reticulum is made up of folded membranes. d. Ribosomes are sometimes attached to folded membranes. 3. Folded membranes are an advantage to a cell because _______. a. cel ...
... a. Folded membranes increase surface area for efficiency. b. Folded membranes do not form compartments in the cell. c. Endoplasmic reticulum is made up of folded membranes. d. Ribosomes are sometimes attached to folded membranes. 3. Folded membranes are an advantage to a cell because _______. a. cel ...
Plant and Animal Cell Parts
... the primary food factory for all living things on Earth. ______________________ within the chloroplast is also responsible for producing the oxygen in the air you breathe. Both animal and plant cells have some similar structural elements. Animal and plant cells have a ________ ________________ that ...
... the primary food factory for all living things on Earth. ______________________ within the chloroplast is also responsible for producing the oxygen in the air you breathe. Both animal and plant cells have some similar structural elements. Animal and plant cells have a ________ ________________ that ...
HOMEOSTASIS AND CELL TRANSPORT NOTES SOLUTIONS
... The organelles in eukaryotic cells have their own ______________ membrane. These membranes control what goes _______ and _______. ...
... The organelles in eukaryotic cells have their own ______________ membrane. These membranes control what goes _______ and _______. ...
Plant and Animal Cell Parts - Alexmac
... Plant cells are characterized by a thick _____________ and small bodies within the cytoplasm called _________________, which give the green colour to the plants. These tiny structures are the primary food factory for all living things on Earth. ______________________ within the chloroplast is also r ...
... Plant cells are characterized by a thick _____________ and small bodies within the cytoplasm called _________________, which give the green colour to the plants. These tiny structures are the primary food factory for all living things on Earth. ______________________ within the chloroplast is also r ...
Welcome to Mrs. Gomez-Buckley General Biology Class (Room 615)
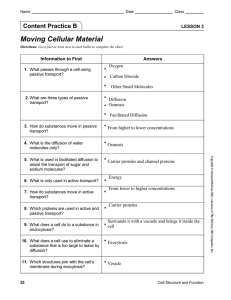
... Ways cells get molecules in and out of cell No cell energy used diffusion passive transport (facilitated diffusion) Cell energy used Active transport ...
... Ways cells get molecules in and out of cell No cell energy used diffusion passive transport (facilitated diffusion) Cell energy used Active transport ...
Cell Structures
... Vacuoles – sacs in cell which hold food, water, and enzymes Vessicles – small vacuoles formed from part of Golgi bodies to hold proteins Lysosomes – sac contains digestive enzymes to break down food or damaged organelles ...
... Vacuoles – sacs in cell which hold food, water, and enzymes Vessicles – small vacuoles formed from part of Golgi bodies to hold proteins Lysosomes – sac contains digestive enzymes to break down food or damaged organelles ...
Cell intro packet
... called vacuoles. The vacuole fills with food being digested and waste material that is on its way out of the cell. In plant cells, a large central vacuole takes up most of the space in the cell. Color and label the vacuoles purple. Mitochondria are spherical to rod-shaped organelles with a double me ...
... called vacuoles. The vacuole fills with food being digested and waste material that is on its way out of the cell. In plant cells, a large central vacuole takes up most of the space in the cell. Color and label the vacuoles purple. Mitochondria are spherical to rod-shaped organelles with a double me ...
Chp 4 Notes
... 2. ATP supplies energy for all cell processes 3. The number of Mitochondria found in cells can tell you how much energy they use i. Muscle Cells: many, Fat Cells: few 4. Structure: composed of an inner and outer membrane i. the inner membrane has many folds called “cristae” ii. Cristae contain prote ...
... 2. ATP supplies energy for all cell processes 3. The number of Mitochondria found in cells can tell you how much energy they use i. Muscle Cells: many, Fat Cells: few 4. Structure: composed of an inner and outer membrane i. the inner membrane has many folds called “cristae” ii. Cristae contain prote ...
The Four Stages of Mitosis
... with the chromosomes, which have become more dense Each of the two chromatids of a chromosome now has a kinetochore “Kinetochore Microtubules” jerk the chromosomes back and forth Nonkinetochore microtubules interact with those from the opposite pole of the spindle ...
... with the chromosomes, which have become more dense Each of the two chromatids of a chromosome now has a kinetochore “Kinetochore Microtubules” jerk the chromosomes back and forth Nonkinetochore microtubules interact with those from the opposite pole of the spindle ...
Cell nucleus

In cell biology, the nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin nucleus or nuculeus, meaning kernel) is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types have no nuclei, and a few others have many.Cell nuclei contain most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these chromosomes are the cell's nuclear genome. The function of the nucleus is to maintain the integrity of these genes and to control the activities of the cell by regulating gene expression—the nucleus is, therefore, the control center of the cell. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm, and the nucleoskeleton (which includes nuclear lamina), a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support, much like the cytoskeleton, which supports the cell as a whole.Because the nuclear membrane is impermeable to large molecules, nuclear pores are required that regulate nuclear transport of molecules across the envelope. The pores cross both nuclear membranes, providing a channel through which larger molecules must be actively transported by carrier proteins while allowing free movement of small molecules and ions. Movement of large molecules such as proteins and RNA through the pores is required for both gene expression and the maintenance of chromosomes. The interior of the nucleus does not contain any membrane-bound sub compartments, its contents are not uniform, and a number of sub-nuclear bodies exist, made up of unique proteins, RNA molecules, and particular parts of the chromosomes. The best-known of these is the nucleolus, which is mainly involved in the assembly of ribosomes. After being produced in the nucleolus, ribosomes are exported to the cytoplasm where they translate mRNA.