Animal Cell Coloring
... Cell Membrane (red) Nucleoplasm (yellow) Mitochondria (red) Lysosome (pink) Cytoplasm (leave white) Microtubules (brown) Ribosome (blue) Nucleolus (gray) Golgi Apparatus (purple) Smooth Endoplasmic - Reticulum (green) Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (orange) Nuclear Membrane (dark brown) Questions: 1. G ...
... Cell Membrane (red) Nucleoplasm (yellow) Mitochondria (red) Lysosome (pink) Cytoplasm (leave white) Microtubules (brown) Ribosome (blue) Nucleolus (gray) Golgi Apparatus (purple) Smooth Endoplasmic - Reticulum (green) Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (orange) Nuclear Membrane (dark brown) Questions: 1. G ...
Cell Study Guide
... answered the question?” and, “Will my answer make clear, logical sense to my teacher?” ...
... answered the question?” and, “Will my answer make clear, logical sense to my teacher?” ...
Cell Organelles - Bartlett High School
... Usually the easiest organelle to see under a microscope Usually one per cell ...
... Usually the easiest organelle to see under a microscope Usually one per cell ...
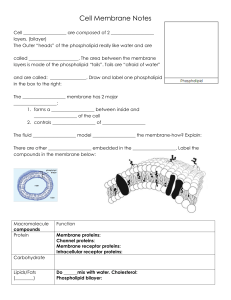
Cell Membrane Notes
... Cell ___________________ are composed of 2 ___________________ layers. (bilayer) The Outer “heads” of the phospholipid really like water and are called ______________________. The area between the membrane layers is made of the phospholipid “tails”. Tails are “afraid of water” and are called: ______ ...
... Cell ___________________ are composed of 2 ___________________ layers. (bilayer) The Outer “heads” of the phospholipid really like water and are called ______________________. The area between the membrane layers is made of the phospholipid “tails”. Tails are “afraid of water” and are called: ______ ...
Building proteins
... • Produce proteins for export out of cell – protein secreting cells – packaged into transport vesicles for export Which cells have lot of rough ER? ...
... • Produce proteins for export out of cell – protein secreting cells – packaged into transport vesicles for export Which cells have lot of rough ER? ...
1. Name 4 bases (subunits) of DNA. 2. Write series of bases will
... 11. The three organelles found only in plant cells are _________________ a) mitochondria, nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum b) Golgi apparatus, lysosome, cell wall c) Chloroplast, nucleus, mitochondria d) Central vacuole, ch ...
... 11. The three organelles found only in plant cells are _________________ a) mitochondria, nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum b) Golgi apparatus, lysosome, cell wall c) Chloroplast, nucleus, mitochondria d) Central vacuole, ch ...
Cells, HL 1. The diagram below shows the structure of a cell. (a
... phosphorylation of glucose;net gain of 2 ATP / 4 ATP produced in total;production of 2NADH + H+ / reduced NAD; 3 max[9] 4. (a) small cells have larger ratio (than larger cells) / ratio decreases as size increases; surface area / membrane must be large enough to absorb nutrients / oxygen / substances ...
... phosphorylation of glucose;net gain of 2 ATP / 4 ATP produced in total;production of 2NADH + H+ / reduced NAD; 3 max[9] 4. (a) small cells have larger ratio (than larger cells) / ratio decreases as size increases; surface area / membrane must be large enough to absorb nutrients / oxygen / substances ...
END OF CHAPTER QUESTIONS
... Both facilitated diffusion and receptor-mediated endocytosis require a transport protein within the plasma membrane. ...
... Both facilitated diffusion and receptor-mediated endocytosis require a transport protein within the plasma membrane. ...
Chapter 3 Lesson 3.2
... Ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum Mitochondria Chloroplasts Golgi Complex Vesicle Lysosomes Vacuoles ...
... Ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum Mitochondria Chloroplasts Golgi Complex Vesicle Lysosomes Vacuoles ...
4.4. INTRODUCING PROKARYOTIC CELLS
... Make far more ATP from the same compounds than prokaryotic cells Hydrogen ions released from the breakdown of organic compounds accum ulate in the inner compartment by operation of transport systems ...
... Make far more ATP from the same compounds than prokaryotic cells Hydrogen ions released from the breakdown of organic compounds accum ulate in the inner compartment by operation of transport systems ...
ch3 rev - Anatomy Corner
... 6. Is the nucleolus considered to be a cytoplasmic organelle? 7. What is diffusion? What is osmosis? 8. List and describe the stages in the life cycle of a cell. 9. List in order the phases of mitosis and tell the main events that occur in each phase. 10. What is cytosol? What is nucleoplasm? 11. A ...
... 6. Is the nucleolus considered to be a cytoplasmic organelle? 7. What is diffusion? What is osmosis? 8. List and describe the stages in the life cycle of a cell. 9. List in order the phases of mitosis and tell the main events that occur in each phase. 10. What is cytosol? What is nucleoplasm? 11. A ...
Unit 5 Cells Study Guide
... 17. What is a flagella? How does it differ in size and number from cilia? What is the function of each of these organelles? (bottom of p.181) 18. How is the composition of cilia and flagella different with reference to microtubules? Sketch that difference below. p.499 & p.501 ...
... 17. What is a flagella? How does it differ in size and number from cilia? What is the function of each of these organelles? (bottom of p.181) 18. How is the composition of cilia and flagella different with reference to microtubules? Sketch that difference below. p.499 & p.501 ...
Controls what enters and leaves the cell
... Contain powerful hydrolytic enzymes to break down food, waste, or dead organelles within the cell. ...
... Contain powerful hydrolytic enzymes to break down food, waste, or dead organelles within the cell. ...
Document
... RER also begins the compartmentalization and processing of some proteins so they can be shipped out of the cells or distributed to specific subcompartments. b. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) is a series of interconnected membrane tubules that lack ribosomes. SER and RER are continuous. One of th ...
... RER also begins the compartmentalization and processing of some proteins so they can be shipped out of the cells or distributed to specific subcompartments. b. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) is a series of interconnected membrane tubules that lack ribosomes. SER and RER are continuous. One of th ...
Presentation - University of Evansville Faculty Web sites
... RER also begins the compartmentalization and processing of some proteins so they can be shipped out of the cells or distributed to specific subcompartments. b. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) is a series of interconnected membrane tubules that lack ribosomes. SER and RER are continuous. One of th ...
... RER also begins the compartmentalization and processing of some proteins so they can be shipped out of the cells or distributed to specific subcompartments. b. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) is a series of interconnected membrane tubules that lack ribosomes. SER and RER are continuous. One of th ...
Animal Cell - Eagan High School
... Ribosomes supply the proteins to Rough ER - where they are properly folded &“packaged” - Next, a bubble around the protein forms… called a Vesicle “vehicle” (exocytosis)…... ...
... Ribosomes supply the proteins to Rough ER - where they are properly folded &“packaged” - Next, a bubble around the protein forms… called a Vesicle “vehicle” (exocytosis)…... ...
Cell Review Worksheet
... 3. Who was the first person to see living cells? What was he looking at under the microscope? ...
... 3. Who was the first person to see living cells? What was he looking at under the microscope? ...
micro intro organelles
... • Membranes physically touch one another or transfer membrane segments through tiny vessicles • Includes: - Nuclear envelope - Endoplasmic reticulum - Golgi apparatus - Lysosomes - Peroxisomes - Cell membrane ...
... • Membranes physically touch one another or transfer membrane segments through tiny vessicles • Includes: - Nuclear envelope - Endoplasmic reticulum - Golgi apparatus - Lysosomes - Peroxisomes - Cell membrane ...
Organelles
... Jelly-like substance found outside of the nucleus; holds organelles in place Makes the essential proteins that are needed by the cell to carry out life processes The “transport system” of the cell. Once the protein is made, the E.R. takes it where it needs to go ...
... Jelly-like substance found outside of the nucleus; holds organelles in place Makes the essential proteins that are needed by the cell to carry out life processes The “transport system” of the cell. Once the protein is made, the E.R. takes it where it needs to go ...