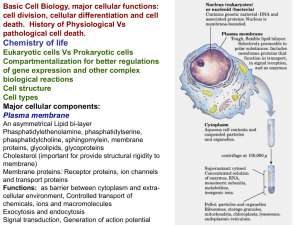
INTRODUCTION TO THE CELL NOTES
... 3. Describe the relationship between a cell’s shape and its function. ...
... 3. Describe the relationship between a cell’s shape and its function. ...
Cell
... Contains chromatins which carry DNA. DNA consists of a number of genes. Genes produce mRNA which controls the ribosome to synthesize specific polypeptide/ protein. mRNA leaves the nucleus through the nuclear pores. ...
... Contains chromatins which carry DNA. DNA consists of a number of genes. Genes produce mRNA which controls the ribosome to synthesize specific polypeptide/ protein. mRNA leaves the nucleus through the nuclear pores. ...
CELL TEST REVIEW:
... The composition and structure and parts of the cell (plasma) membrane (i.e. phospholipids, proteins, steroids/cholesterol, carbohydrates) Integral vs peripheral proteins What regions of the membrane are polar and nonpolar Understand the fluid mosaic model ...
... The composition and structure and parts of the cell (plasma) membrane (i.e. phospholipids, proteins, steroids/cholesterol, carbohydrates) Integral vs peripheral proteins What regions of the membrane are polar and nonpolar Understand the fluid mosaic model ...
Cell Organelle Powerpoint
... Function: control center of cell Surrounded by double membrane (nuclear envelope) Continuous with the rough ER Nuclear pores: control what enters/leaves nucleus Chromatin: complex of DNA + proteins; makes up chromosomes Nucleolus: region where ribosomal subunits are formed ...
... Function: control center of cell Surrounded by double membrane (nuclear envelope) Continuous with the rough ER Nuclear pores: control what enters/leaves nucleus Chromatin: complex of DNA + proteins; makes up chromosomes Nucleolus: region where ribosomal subunits are formed ...
Practice questions for exam 2
... 11. Compare the roles of glycogen, starch, and fat. 12. Name the 2 elements that you expect to find in all organic compounds. What other elements are commonly present? 13. Name the type of movement that requires ATP to get a substance across a membrane . 14. How is the movement in question 13 differ ...
... 11. Compare the roles of glycogen, starch, and fat. 12. Name the 2 elements that you expect to find in all organic compounds. What other elements are commonly present? 13. Name the type of movement that requires ATP to get a substance across a membrane . 14. How is the movement in question 13 differ ...
Cell Organelle Chart
... instruction manual for the cells’ activities. Without the nucleus the cell will be unable to create new cells and will eventually die. ...
... instruction manual for the cells’ activities. Without the nucleus the cell will be unable to create new cells and will eventually die. ...
Slide 1
... Inner mitochondrial membrane (contains components of electron transport chain, ATP synthase, and transport proteins) Matrix space (contains enzymes and cofactors for citric acid cycle, fatty acid metabolism, mitochondrial genome, and transcription and translation machinery) Inner mitochondrial poten ...
... Inner mitochondrial membrane (contains components of electron transport chain, ATP synthase, and transport proteins) Matrix space (contains enzymes and cofactors for citric acid cycle, fatty acid metabolism, mitochondrial genome, and transcription and translation machinery) Inner mitochondrial poten ...
Honors Biology - LangdonBiology.org
... Both plant and animal cells: Nucleus (including nuclear membrane and pores) Nucleolus Ribosome (both cytosolic and rough ER, including rRNA, ribosomal proteins, and RNA is the enzyme) Rough & smooth endoplasmic reticulum Golgi Bodies Vesicles (vacuoles) Mitochondria (with endosymbiotic theory and th ...
... Both plant and animal cells: Nucleus (including nuclear membrane and pores) Nucleolus Ribosome (both cytosolic and rough ER, including rRNA, ribosomal proteins, and RNA is the enzyme) Rough & smooth endoplasmic reticulum Golgi Bodies Vesicles (vacuoles) Mitochondria (with endosymbiotic theory and th ...
Shrink Tours, Inc.
... other organelles, which helps keep the cell healthy. Keep your distance or he’ll eat you, too! *No pictures of lysosomes are available (our contract with them requires that we keep their names and records ...
... other organelles, which helps keep the cell healthy. Keep your distance or he’ll eat you, too! *No pictures of lysosomes are available (our contract with them requires that we keep their names and records ...
Cells in Anatomy
... In the cistern, the protein folds into its functional shape. Short sugar chains may be attached to the protein (forming a glycoprotein). Protein The protein is packaged in a tiny membranous sac called a transport vesicle. ...
... In the cistern, the protein folds into its functional shape. Short sugar chains may be attached to the protein (forming a glycoprotein). Protein The protein is packaged in a tiny membranous sac called a transport vesicle. ...
Zoology 145 course
... • collect, package, and distribute molecules synthesized at one location in the cell and utilized at another location • Front - cis , Back – trans and Cisternae – stacked membrane folds Many transport vesicles from the ER travel to the Golgi apparatus for modification of their contents. The Golgi bo ...
... • collect, package, and distribute molecules synthesized at one location in the cell and utilized at another location • Front - cis , Back – trans and Cisternae – stacked membrane folds Many transport vesicles from the ER travel to the Golgi apparatus for modification of their contents. The Golgi bo ...
Check Your Knowledge Set 1(Download)
... Membranous sac of hydrolytic enzymes (in animal cells) Contains enzymes that transfer hydrogen to oxygen, producing hydrogen peroxide as a by-product, which is converted to water by other enzymes Large membrane-bounded vesicle in plants for digestion, storage, waste disposal, water balance, cell gro ...
... Membranous sac of hydrolytic enzymes (in animal cells) Contains enzymes that transfer hydrogen to oxygen, producing hydrogen peroxide as a by-product, which is converted to water by other enzymes Large membrane-bounded vesicle in plants for digestion, storage, waste disposal, water balance, cell gro ...
Cell Structures and Their Function
... All cell have a nucleus at some point in their life Nucleus: Stores hereditary information in DNA. Also ...
... All cell have a nucleus at some point in their life Nucleus: Stores hereditary information in DNA. Also ...
CELLS
... substance in which all of the cell’s organelles are suspended Located between the nucleus and the cell membrane Contains the cytoskeleton ...
... substance in which all of the cell’s organelles are suspended Located between the nucleus and the cell membrane Contains the cytoskeleton ...
Centriole organelles made of microtubules involved in cell division
... Used for movement/moving substances around outside of the cell ...
... Used for movement/moving substances around outside of the cell ...
3.10 Practice Exam - Rocky View Schools
... 14. A phospholipid molecule has a head and two tails. Where are the tails found? (a) at the surfaces of the membranes (b) in the interior of the membrane (c) spanning the membrane (d) where the environment is hydrophilic 15. A scientist who is observing a protozoan notices a vacuole discharging its ...
... 14. A phospholipid molecule has a head and two tails. Where are the tails found? (a) at the surfaces of the membranes (b) in the interior of the membrane (c) spanning the membrane (d) where the environment is hydrophilic 15. A scientist who is observing a protozoan notices a vacuole discharging its ...
Eukaryotic Cell Structure
... protein found throughout the cytoplasm that are involved in protein synthesis. ...
... protein found throughout the cytoplasm that are involved in protein synthesis. ...
cell organelle webquest
... Objective: Upon completion of this activity, you should be able to describe the cell and identify its parts (organelles). You should be able to distinguish between plant and animal cells. PART I Go to: www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=AP11604 Click “Next” to begin the activity. Answer ...
... Objective: Upon completion of this activity, you should be able to describe the cell and identify its parts (organelles). You should be able to distinguish between plant and animal cells. PART I Go to: www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=AP11604 Click “Next” to begin the activity. Answer ...
Moving Molecules and Cellular Energy Crossword
... 10. movement from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration 11. process during which a cell takes in a substance by surrounding it with the cell membrane 12. diffusion of water molecules only through a membrane Down 1. series of reactions that convert light energy, water, and ...
... 10. movement from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration 11. process during which a cell takes in a substance by surrounding it with the cell membrane 12. diffusion of water molecules only through a membrane Down 1. series of reactions that convert light energy, water, and ...
Cells
... • Suspended in cytosol • Perform specific functions, divide the “work” of the cell. • Nucleus – directs all of the cells activities and houses the genetic material. ...
... • Suspended in cytosol • Perform specific functions, divide the “work” of the cell. • Nucleus – directs all of the cells activities and houses the genetic material. ...