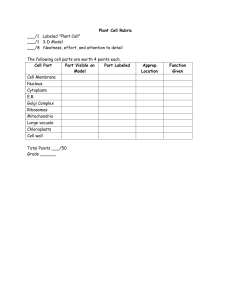
SBI 4U biochem 3
... • Proteins/lipids are pinched off to form vesicles that will exit the cell or go to another spot in that cell. • In animal cells the Golgi also produces lysosomes ...
... • Proteins/lipids are pinched off to form vesicles that will exit the cell or go to another spot in that cell. • In animal cells the Golgi also produces lysosomes ...
Layout 4
... ● Identify the organelles of eukaryotic cells and explain their functions: smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, Golgi complex, lysosomes, nucleus (including nuclear envelope, chromatin/chromosomes and nucleolus), mitochondria, plastids (including chloroplasts), vacuoles, cilia and flag ...
... ● Identify the organelles of eukaryotic cells and explain their functions: smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, Golgi complex, lysosomes, nucleus (including nuclear envelope, chromatin/chromosomes and nucleolus), mitochondria, plastids (including chloroplasts), vacuoles, cilia and flag ...
Cell Labeling Worksheet Instructions: Using the Organelle List
... “DNA,” “nucleus,” and “flagellum” are already filled in for you as an example. Organelle List: DNA, nucleus, flagellum, cell membrane, cell wall, cytoplasm, rough endoplasmic reticulum, smooth endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, golgi apparatus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, cytoskeleton, vacuoles Organ ...
... “DNA,” “nucleus,” and “flagellum” are already filled in for you as an example. Organelle List: DNA, nucleus, flagellum, cell membrane, cell wall, cytoplasm, rough endoplasmic reticulum, smooth endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, golgi apparatus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, cytoskeleton, vacuoles Organ ...
Cell Structure and Function Matching KEY
... vesicles pinch off these structures; proteins modified and packaged here cellular "stomach" selectively permeable "doorman" the most important plastid, turns CO2, H2O, sunlight into glucose membrane-bound spheres that store water & dissolved materials. Membrane surrounding it is called a tonoplast. ...
... vesicles pinch off these structures; proteins modified and packaged here cellular "stomach" selectively permeable "doorman" the most important plastid, turns CO2, H2O, sunlight into glucose membrane-bound spheres that store water & dissolved materials. Membrane surrounding it is called a tonoplast. ...
CHAPTER 7 CELL TEST REVIEW Answer the
... 6. Membranes that allow certain substances to pass through, but keep other out are said to be SELECTIVELY____________ 7. Ribsomes can be found attached to_____________. 1. Name this organelle. 8. Membrane proteins that stick into the cell 2. Give the function for #1. membrane either part way through ...
... 6. Membranes that allow certain substances to pass through, but keep other out are said to be SELECTIVELY____________ 7. Ribsomes can be found attached to_____________. 1. Name this organelle. 8. Membrane proteins that stick into the cell 2. Give the function for #1. membrane either part way through ...
Cells and Tissues - Mrs. Hille`s FunZone
... Two types of ER Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Studded with ribosomes Site where building materials of cellular membrane are formed Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Functions in cholesterol synthesis and breakdown, fat metabolism, and detoxification of drugs ...
... Two types of ER Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Studded with ribosomes Site where building materials of cellular membrane are formed Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Functions in cholesterol synthesis and breakdown, fat metabolism, and detoxification of drugs ...
Review Sheet – Biology
... 4.3 Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Features Be able to identify the following based on their function, structure, or main characteristics: ...
... 4.3 Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Features Be able to identify the following based on their function, structure, or main characteristics: ...
Chap 4 sec 2c Fact Review Sheet
... The lipids and proteins may be modified (changed into other molecules) to do different jobs. ...
... The lipids and proteins may be modified (changed into other molecules) to do different jobs. ...
Slide 1
... •site of ATP synthesis •energy of ATP fuels most of the chemical reactions in a cell •surrounded by a double membrane; outer membrane serves as a boundary and inner membrane is highly folded to form cristae, which increase the surface area available for chemical reactions that occur in the mito ...
... •site of ATP synthesis •energy of ATP fuels most of the chemical reactions in a cell •surrounded by a double membrane; outer membrane serves as a boundary and inner membrane is highly folded to form cristae, which increase the surface area available for chemical reactions that occur in the mito ...
Cell membrane transport white board activity
... 1. Be able to define and locate each of the cell organelles. (Nucleus, cytoplasm, nucleolus, ER (smooth, rough), chloroplast, cell wall, lysosome, ribosomes, central vacuole, golgi apparatus, chromatin/DNA, cilia, flagella). 2. Diagram a phospholipid bilayer, and explain why the plasma membrane is s ...
... 1. Be able to define and locate each of the cell organelles. (Nucleus, cytoplasm, nucleolus, ER (smooth, rough), chloroplast, cell wall, lysosome, ribosomes, central vacuole, golgi apparatus, chromatin/DNA, cilia, flagella). 2. Diagram a phospholipid bilayer, and explain why the plasma membrane is s ...
You Gotta Know
... varieties. In the ER, proteins undergo modifications and folding to yield the final, functional protein structures. 5. Golgi Apparatus The stack of flattened, folded membranes that forms the Golgi apparatus acts as the "post office of the cell." Here proteins from the ribosomes are stored, chemicall ...
... varieties. In the ER, proteins undergo modifications and folding to yield the final, functional protein structures. 5. Golgi Apparatus The stack of flattened, folded membranes that forms the Golgi apparatus acts as the "post office of the cell." Here proteins from the ribosomes are stored, chemicall ...
Chapter Three Review #2 KEY - Mr. Lesiuk
... 3. A vesicle is a very small membranous transport sac. A vacuole is also membranous sac but it is much larger and more often used for storage. ...
... 3. A vesicle is a very small membranous transport sac. A vacuole is also membranous sac but it is much larger and more often used for storage. ...
Homeostasis and the Cell
... • The tendency of a system to maintain its internal stability. • We sweat or shiver to maintain our body’s core temperature. • Homeostasis happens, as well, at a cellular level in order to maintain the stability of the cells. ...
... • The tendency of a system to maintain its internal stability. • We sweat or shiver to maintain our body’s core temperature. • Homeostasis happens, as well, at a cellular level in order to maintain the stability of the cells. ...
Biology Chapter 5, Lesson 1 Notes
... Phospholipids are lipid molecules that have a head and a tail. The tail or fatty acid end of a phospholipid molecule is hydrophobic (water hating) and carries a neutral charge and is nonpolar. The tails keep water from rushing into the cell, that could cause the cell to burst. The head of a ph ...
... Phospholipids are lipid molecules that have a head and a tail. The tail or fatty acid end of a phospholipid molecule is hydrophobic (water hating) and carries a neutral charge and is nonpolar. The tails keep water from rushing into the cell, that could cause the cell to burst. The head of a ph ...
QUEST Study guide Organic molecules Proteins, carbohydrates
... Be sure you understand and can discuss each of the structures AND functions of ALL these organelles Be able to discuss how ALL these organelles work together to maintain HOMEOSTASIS of the cell and therefore the organism. ***BONUS: question about organelle diseases Possible Essay Question We have st ...
... Be sure you understand and can discuss each of the structures AND functions of ALL these organelles Be able to discuss how ALL these organelles work together to maintain HOMEOSTASIS of the cell and therefore the organism. ***BONUS: question about organelle diseases Possible Essay Question We have st ...
LIFE CELLS
... • Three types of RNA polymerases (like eukarya) • May be extremophiles • Shape and size similar to bacteria (coccus/rod) • Single loop (plasmid) DNA, no nucleus EUKARYA: • Cytoplasm containing salts, minerals etc. • Nucleus= control centre, with nucleolus, nucleoplasm inside, doublemembrane nu ...
... • Three types of RNA polymerases (like eukarya) • May be extremophiles • Shape and size similar to bacteria (coccus/rod) • Single loop (plasmid) DNA, no nucleus EUKARYA: • Cytoplasm containing salts, minerals etc. • Nucleus= control centre, with nucleolus, nucleoplasm inside, doublemembrane nu ...
science chapter 1 questions
... 1A. the cell wall helps to protect and support the cell. The cell membrane controls what goes in and out of the cell. 1b. the cellulose is a material in the cell wall. 1c. the cellulose gives the wall strength. 2a. Ribosomes: It makes proteins Golgi: it gets proteins packet them and distributes them ...
... 1A. the cell wall helps to protect and support the cell. The cell membrane controls what goes in and out of the cell. 1b. the cellulose is a material in the cell wall. 1c. the cellulose gives the wall strength. 2a. Ribosomes: It makes proteins Golgi: it gets proteins packet them and distributes them ...
Organelles
... How do they know which ones to make? Instructions from DNA are sent to the ribosomes from the nucleus. ...
... How do they know which ones to make? Instructions from DNA are sent to the ribosomes from the nucleus. ...