Section 5-2: Active Transport
... 1. How it Works A portion of the cell membrane moves inward, forming a pouch. Molecules enter this pouch and the membrane continues pinching inward, eventually completely surrounding the molecules. The pouch pinches off completely from the cell membrane and becomes a vesicle. 2. Pinocytosis – ...
... 1. How it Works A portion of the cell membrane moves inward, forming a pouch. Molecules enter this pouch and the membrane continues pinching inward, eventually completely surrounding the molecules. The pouch pinches off completely from the cell membrane and becomes a vesicle. 2. Pinocytosis – ...
Enzymes and Cell Transport study guide
... Does NOT require energy, moves from HIGH concentrations to LOW concentrations ...
... Does NOT require energy, moves from HIGH concentrations to LOW concentrations ...
Parts of a Cell: Animal Cells
... The transport system of the cell. It transports molecules that need certain changes and also molecules to their destination. Thee are two types, rough and smooth. Rough has ribosomes bound to it, making it appear rough; while the smooth does not have the ribosomes. ...
... The transport system of the cell. It transports molecules that need certain changes and also molecules to their destination. Thee are two types, rough and smooth. Rough has ribosomes bound to it, making it appear rough; while the smooth does not have the ribosomes. ...
Cells: Organelles - Biology Courses Server
... Smooth endoplasmic reticulum has a variety of functions • Smooth ER no ribosomes on surface • Smooth ER makes lipids (fatty acids, phospholipids and steroids) • In liver cells, it regulates carbohydrate metabolism and breaks down toxins and drugs • In muscle cells it stores calcium needed for muscl ...
... Smooth endoplasmic reticulum has a variety of functions • Smooth ER no ribosomes on surface • Smooth ER makes lipids (fatty acids, phospholipids and steroids) • In liver cells, it regulates carbohydrate metabolism and breaks down toxins and drugs • In muscle cells it stores calcium needed for muscl ...
The Cell Membrane 2015
... charged to cross the lipid bilayer. If a substance is able to diffuse across a membrane, the membrane is said to be permeable to it. A membrane is impermeable to substances that cannot pass across it. Most biological membranes are selectively permeable, meaning that some substances can pass across t ...
... charged to cross the lipid bilayer. If a substance is able to diffuse across a membrane, the membrane is said to be permeable to it. A membrane is impermeable to substances that cannot pass across it. Most biological membranes are selectively permeable, meaning that some substances can pass across t ...
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
... Found mostly in white blood cells Have been linked to diseases, such as Tay Sach’s Tay Sach’s is a disorder that is caused by a genetic defect that prevents the formation of an essential enzyme that breaks down lipids These lipids build up in the body and can cause nerve damage; prognosis is not goo ...
... Found mostly in white blood cells Have been linked to diseases, such as Tay Sach’s Tay Sach’s is a disorder that is caused by a genetic defect that prevents the formation of an essential enzyme that breaks down lipids These lipids build up in the body and can cause nerve damage; prognosis is not goo ...
CELL ORGANELLES
... • Controls cell activities • Keeps DNA out of the cytoplasm, but allows RNA to move through the nuclear pores and ribosomes • Cell reproduction starts here ...
... • Controls cell activities • Keeps DNA out of the cytoplasm, but allows RNA to move through the nuclear pores and ribosomes • Cell reproduction starts here ...
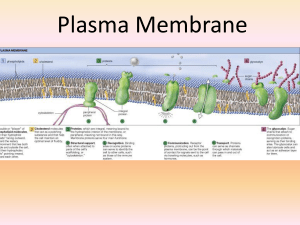
Plasma Membrane
... specific shapes exposed to the exterior that fit the shape of specific hormones 2. Enzymes – catalyze chemical reactions; may be on interior or exterior of the cell membrane; often grouped together for a chain reaction (called metabolic pathway) 3. Cell adhesion – proteins hook together to provide t ...
... specific shapes exposed to the exterior that fit the shape of specific hormones 2. Enzymes – catalyze chemical reactions; may be on interior or exterior of the cell membrane; often grouped together for a chain reaction (called metabolic pathway) 3. Cell adhesion – proteins hook together to provide t ...
How does the structure of the cell membrane contribute to its function?
... •Proteins for communication •Chemicals sent from other cells must fit •Lock and key concept ...
... •Proteins for communication •Chemicals sent from other cells must fit •Lock and key concept ...
Day 18
... popular magazine articles on biological topics, as well as Silent Spring (1962), her book warning of the long-term effects of pesticides, which is now seen as the start of the modern environmental movement. ...
... popular magazine articles on biological topics, as well as Silent Spring (1962), her book warning of the long-term effects of pesticides, which is now seen as the start of the modern environmental movement. ...
Cell Organelles Review Package
... For each statement write true or false: 4. ________ Since prokaryotes can make proteins there are more prokaryotes than eukaryotes. 5. ________ The endoplasmic reticulum that has ribosomes is called the smooth ER. 6. ________ Vesicles resemble one another in that they all contain the same type of en ...
... For each statement write true or false: 4. ________ Since prokaryotes can make proteins there are more prokaryotes than eukaryotes. 5. ________ The endoplasmic reticulum that has ribosomes is called the smooth ER. 6. ________ Vesicles resemble one another in that they all contain the same type of en ...
Eukaryotic Cells
... Transports materials such as protein throughout the cell Smooth ER lacks ribosomes. Function is to make lipids and break down toxic mateirals Rough ER is covered with ...
... Transports materials such as protein throughout the cell Smooth ER lacks ribosomes. Function is to make lipids and break down toxic mateirals Rough ER is covered with ...
topic 5 -part 3 guided notes -plant vs animal cells - student
... TOPIC 5: CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION PART 3: PLANT VS. ANIMAL CELLS Plants and animals differ in their cell makeup. Structures Common to Both Plant and Animal Cells 1. cell membrane 2. nucleus 3. nuclear envelope 4. DNA 5. nucleolus 6. ribosomes ...
... TOPIC 5: CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION PART 3: PLANT VS. ANIMAL CELLS Plants and animals differ in their cell makeup. Structures Common to Both Plant and Animal Cells 1. cell membrane 2. nucleus 3. nuclear envelope 4. DNA 5. nucleolus 6. ribosomes ...
Biochemical screen for potential membrane fission catalysts
... Eukaryotic cells are functionally compartmentalized in form of an elaborate endomembrane system comprising of intracellular organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, endosomes and lysosome. Membrane budding and fission results in the generation of transport carriers that sort an ...
... Eukaryotic cells are functionally compartmentalized in form of an elaborate endomembrane system comprising of intracellular organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, endosomes and lysosome. Membrane budding and fission results in the generation of transport carriers that sort an ...
glucocerebrosidease
... The RNA travels from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. RNA binds to a free ribosome and protein synthesis begins. The ribosome moves to the rough ER were synthesis is completed. The protein is transported by a vesicle to the Golgi apparatus. In the Golgi, the protein is modified and labeled for transpor ...
... The RNA travels from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. RNA binds to a free ribosome and protein synthesis begins. The ribosome moves to the rough ER were synthesis is completed. The protein is transported by a vesicle to the Golgi apparatus. In the Golgi, the protein is modified and labeled for transpor ...
Honors Biology - LangdonBiology.org
... What is an example of a molecule that exits the nucleus? What is an example of something that enters the nucleus? 11. Describe the role of a ribosome, where they are found, and what they are made of. How does the ribosome relate to the nucleolus? 12. What is the difference between rough ER and smoot ...
... What is an example of a molecule that exits the nucleus? What is an example of something that enters the nucleus? 11. Describe the role of a ribosome, where they are found, and what they are made of. How does the ribosome relate to the nucleolus? 12. What is the difference between rough ER and smoot ...
Cell Part Cell Structure and Function Mitochondria Nucleus
... depending upon activity of cell. Cells with high metabolic activity have many lysosomes. Different types of lysosomes depend on content and density. Lysosomes work with a nucleus to make proteins. ...
... depending upon activity of cell. Cells with high metabolic activity have many lysosomes. Different types of lysosomes depend on content and density. Lysosomes work with a nucleus to make proteins. ...
ProjectCellStory
... In groups of 2-3 create a video using MovieMaker or iMovie that tells the story of a group of cell organelles. Each group will be assigned one of the topics below. Your video should tell the story of how the organelles and processes are related. Be sure to include the following: Structure of each ...
... In groups of 2-3 create a video using MovieMaker or iMovie that tells the story of a group of cell organelles. Each group will be assigned one of the topics below. Your video should tell the story of how the organelles and processes are related. Be sure to include the following: Structure of each ...
cloze 4
... • Rough ER is covered with _________that make proteins near the nucleus. Smooth ER lacks ribosomes. • Smooth ER makes lipids and breaks down toxic materials. The ER also5 functions as a _________system for the cell. Mitochondria • A mitochondrion is the main _______source of a cell. Mitochondria are ...
... • Rough ER is covered with _________that make proteins near the nucleus. Smooth ER lacks ribosomes. • Smooth ER makes lipids and breaks down toxic materials. The ER also5 functions as a _________system for the cell. Mitochondria • A mitochondrion is the main _______source of a cell. Mitochondria are ...
Organelle Sketch Function Cell Wall Cell Membrane Nucleus
... b. What substance (pigment) is necessary for this process? c. This process and these organelle are present only in ...
... b. What substance (pigment) is necessary for this process? c. This process and these organelle are present only in ...
1.3 study guide - Peoria Public Schools
... Cell membranes include phospholipids and proteins. These proteins may be classified as integral or peripheral proteins. It is the hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties of phospholipids that maintain the structure of cell membranes. Functions of membrane proteins include hormone binding sites, ...
... Cell membranes include phospholipids and proteins. These proteins may be classified as integral or peripheral proteins. It is the hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties of phospholipids that maintain the structure of cell membranes. Functions of membrane proteins include hormone binding sites, ...