Section 3 - HCABIOLOGY
... CLEARLY circle the best answer for each question, or write in the correct answer in the blank provided. 10 points each! ...
... CLEARLY circle the best answer for each question, or write in the correct answer in the blank provided. 10 points each! ...
Cell Quiz - Catawba County Schools
... 1. Which cell structure contains the cell’s genetic material and controls many of the cell’s activities? a. organelle c. cell envelope b. nucleus d. cytoplasm 2. Cells fall into two broad categories, depending on whether they a. have a cell wall. c. have a nucleus. b. contain genetic material. d. co ...
... 1. Which cell structure contains the cell’s genetic material and controls many of the cell’s activities? a. organelle c. cell envelope b. nucleus d. cytoplasm 2. Cells fall into two broad categories, depending on whether they a. have a cell wall. c. have a nucleus. b. contain genetic material. d. co ...
Cell Structure and Function Study Guide
... Relate the permeability of the cell membrane to its structure Explain the role of proteins in the cell membrane Explain how polarity, solubility, and size determine whether a substance will pass through the cell membrane Know which types of substances can move into a cell by simple diffusion Know wh ...
... Relate the permeability of the cell membrane to its structure Explain the role of proteins in the cell membrane Explain how polarity, solubility, and size determine whether a substance will pass through the cell membrane Know which types of substances can move into a cell by simple diffusion Know wh ...
7.2 ppt
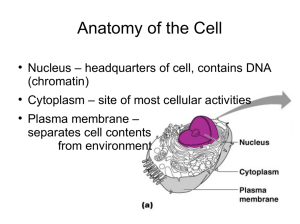
... Eukaryotes=Plants, Animals, Fungi and Protists ◦ Nucleus to house genetic material ◦ Larger and more complex ...
... Eukaryotes=Plants, Animals, Fungi and Protists ◦ Nucleus to house genetic material ◦ Larger and more complex ...
Sept28 - staff.harrisonburg.k12.va
... Spherical or sausage like in shape 2 membranes an inner and an outer Make energy for cell use from nutrients taken into the cell. Golgi Apparatus Packages and ships out extra proteins o When chemicals accumulate in the ER sections of the ER break off and form small Shpere sacs. o These sacs ...
... Spherical or sausage like in shape 2 membranes an inner and an outer Make energy for cell use from nutrients taken into the cell. Golgi Apparatus Packages and ships out extra proteins o When chemicals accumulate in the ER sections of the ER break off and form small Shpere sacs. o These sacs ...
Movement Across the Membrane
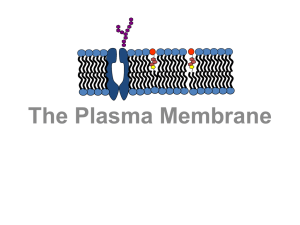
... membrane Carbon dioxide and oxygen freely diffuse across the membrane Water will also pass across the membrane, but often needs the help of a protein ...
... membrane Carbon dioxide and oxygen freely diffuse across the membrane Water will also pass across the membrane, but often needs the help of a protein ...
Biology
... BIG IDEA: How are prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells different? A. Cells membrane: They are like: Also called: ...
... BIG IDEA: How are prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells different? A. Cells membrane: They are like: Also called: ...
File
... Exocytosis – release of a substance outside of the cell membrane by the fusion of a vacuole ...
... Exocytosis – release of a substance outside of the cell membrane by the fusion of a vacuole ...
The Cell PPT File
... • Within the nucleus is an area called the nucleolus. • Nucleolus mainly composed of RNA (ribonucleic acid) which plays a vital role in protein synthesis. • Both chromatin and nucleolus are suspended in the nucleoplasm. ...
... • Within the nucleus is an area called the nucleolus. • Nucleolus mainly composed of RNA (ribonucleic acid) which plays a vital role in protein synthesis. • Both chromatin and nucleolus are suspended in the nucleoplasm. ...
Microtubules and Microfilaments
... membrane containing two phospholipid bilayers • Contains small nuclear pores – Allow substances to pass from the nucleus to cytoplasm ...
... membrane containing two phospholipid bilayers • Contains small nuclear pores – Allow substances to pass from the nucleus to cytoplasm ...
Chapter 6 1. ______ ______: all organisms are made up of cells. 2
... 11. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER): __________________ and ________________ are the two regions of the ER. SER is in charge of _____________ production, metabolism of _______________, drug detoxification, and making sex hormones. RER synthesizes and packages _____________ in ___________ to move to the g ...
... 11. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER): __________________ and ________________ are the two regions of the ER. SER is in charge of _____________ production, metabolism of _______________, drug detoxification, and making sex hormones. RER synthesizes and packages _____________ in ___________ to move to the g ...
MYP Science 9 - cis myp science
... Structure: Ribosomes consist of two subunits, one large and one small. The subunits are made up of protein and ribosomal RNA. They can be found floating free or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. Function: Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis. ...
... Structure: Ribosomes consist of two subunits, one large and one small. The subunits are made up of protein and ribosomal RNA. They can be found floating free or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. Function: Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis. ...
Cell organelles
... – Membrane phospholipids and cellular lipids - Sex hormones (testosterone and estrogen) (In Specialized cells ...
... – Membrane phospholipids and cellular lipids - Sex hormones (testosterone and estrogen) (In Specialized cells ...
Name - KS Blogs
... 5. Imagine an animal cell didn’t have a golgi apparatus. How would this affect how the cell works? Imagine an animal cell didn’t have a smooth E.R. What would happen? Organelle ___ Ribosome ___ Endoplasmic reticulum ___ Golgi apparatus ___ Lysosome ___ Vacuole ___ Chloroplast ___ Mitochondrion ...
... 5. Imagine an animal cell didn’t have a golgi apparatus. How would this affect how the cell works? Imagine an animal cell didn’t have a smooth E.R. What would happen? Organelle ___ Ribosome ___ Endoplasmic reticulum ___ Golgi apparatus ___ Lysosome ___ Vacuole ___ Chloroplast ___ Mitochondrion ...
Pre-Test
... eukaryotic? (Concept 6.1 ) a) the presence or absence of a rigid cell wall b) whether or not the cell is partitioned by internal membranes c) the presence or absence of ribosomes d) whether or not the cell carries out cellular metabolism e) whether or not the cell contains DNA 2. Which statement(s) ...
... eukaryotic? (Concept 6.1 ) a) the presence or absence of a rigid cell wall b) whether or not the cell is partitioned by internal membranes c) the presence or absence of ribosomes d) whether or not the cell carries out cellular metabolism e) whether or not the cell contains DNA 2. Which statement(s) ...
Cells: Chapter 2
... – protein synthesis occurs here for those proteins that will be routed out of cell ...
... – protein synthesis occurs here for those proteins that will be routed out of cell ...
Pre-Test
... eukaryotic? (Concept 6.1 ) a) the presence or absence of a rigid cell wall b) whether or not the cell is partitioned by internal membranes c) the presence or absence of ribosomes d) whether or not the cell carries out cellular metabolism e) whether or not the cell contains DNA 2. Which statement(s) ...
... eukaryotic? (Concept 6.1 ) a) the presence or absence of a rigid cell wall b) whether or not the cell is partitioned by internal membranes c) the presence or absence of ribosomes d) whether or not the cell carries out cellular metabolism e) whether or not the cell contains DNA 2. Which statement(s) ...
Cell Structure and Function
... 1. In the endomembrane system, proteins bound for different destinations are given different carbohydrate "tags." 2. Proteins are sorted in the Golgi apparatus. ...
... 1. In the endomembrane system, proteins bound for different destinations are given different carbohydrate "tags." 2. Proteins are sorted in the Golgi apparatus. ...
Active Transport
... 1. How it Works A portion of the cell membrane moves inward, forming a pouch. Molecules enter this pouch & the membrane continues pinching inward, eventually completely surrounding the molecules. The pouch pinches off completely from the cell membrane and becomes a vesicle. 2. Pinocytosis – th ...
... 1. How it Works A portion of the cell membrane moves inward, forming a pouch. Molecules enter this pouch & the membrane continues pinching inward, eventually completely surrounding the molecules. The pouch pinches off completely from the cell membrane and becomes a vesicle. 2. Pinocytosis – th ...