Test Review for AP Biology Chapter 5 What molecules make up the
... 3. Know how temperature effects the cell membrane. Ie. What is one of the ways that a membrane of winter vegetation can remain fluid when cold? 4. For a protein to be an integral membrane protein would it need to be hydrophilic, hydrophobic or amphipathic? 5. Why do unsaturated fatty acids help keep ...
... 3. Know how temperature effects the cell membrane. Ie. What is one of the ways that a membrane of winter vegetation can remain fluid when cold? 4. For a protein to be an integral membrane protein would it need to be hydrophilic, hydrophobic or amphipathic? 5. Why do unsaturated fatty acids help keep ...
Cells Compared to The Human Body
... out of the body is the fat tissues in your body (It also store energy too) ...
... out of the body is the fat tissues in your body (It also store energy too) ...
Cells: the building block of all living things
... cell type. Organelles: (compartmentalization of each allows it to do its specific fxn) 1. Ribosomes: tiny, round, dark bodies made of ribosomal RNA and proteins. a) Site of protein synthesis b) Some float free; others are attached to (rough) Endoplasmic Reticulum. 2. Endoplasmic Reticulum: a system ...
... cell type. Organelles: (compartmentalization of each allows it to do its specific fxn) 1. Ribosomes: tiny, round, dark bodies made of ribosomal RNA and proteins. a) Site of protein synthesis b) Some float free; others are attached to (rough) Endoplasmic Reticulum. 2. Endoplasmic Reticulum: a system ...
Parts of a Cell
... Nucleus is covered by two membranes “Control center” of the cell A nucleus could contain a nucleolus which is where a cell begins to make ribosomes ...
... Nucleus is covered by two membranes “Control center” of the cell A nucleus could contain a nucleolus which is where a cell begins to make ribosomes ...
Into and Out of the Cell
... Wastes must be able to leave the cell. The cell membrane is “picky” about what ...
... Wastes must be able to leave the cell. The cell membrane is “picky” about what ...
Organelle Functions Organelle Function Sketch Nucleus Control
... Transports proteins (ribosomes attached to outside) ...
... Transports proteins (ribosomes attached to outside) ...
Biology Chapter 7.2-7.3 Notes on Cells 2013
... o Water is a key component to living organisms, both inside and outside of the cell o The polar phosphate group allows the cell membrane to interact with the watery environment since water is also polar. o The two layers act as a barrier creating a water soluble layer at the outer surfaces and a wat ...
... o Water is a key component to living organisms, both inside and outside of the cell o The polar phosphate group allows the cell membrane to interact with the watery environment since water is also polar. o The two layers act as a barrier creating a water soluble layer at the outer surfaces and a wat ...
MUSINGU HIGH SCHOOL BIOLOGY DECEMBER 2013 HOLIDAY
... 16 (a) What do you understand by the cell specialization as used in biology (b) Name any two specialized cells in plants and state how each is modified. 17 The set up below was prepared by a form one student study it and answer the questions that follow. ...
... 16 (a) What do you understand by the cell specialization as used in biology (b) Name any two specialized cells in plants and state how each is modified. 17 The set up below was prepared by a form one student study it and answer the questions that follow. ...
ACHAEAN- One of two prokaryote domains that includes organisms
... BIOLOGY- the study of life, living things, and the components and systems that maintain life CELL- basic unit of all life; an organized system of biological molecules enclosed by a membrane that separates the contents of the membrane from its surroundings CELL THEORY- one of the most fundamental con ...
... BIOLOGY- the study of life, living things, and the components and systems that maintain life CELL- basic unit of all life; an organized system of biological molecules enclosed by a membrane that separates the contents of the membrane from its surroundings CELL THEORY- one of the most fundamental con ...
CELLULAR PHYSIOLOGY - Eastern Mediterranean University
... • The whole complex of DNA and proteins is called chromatin. ...
... • The whole complex of DNA and proteins is called chromatin. ...
Document
... • Cells have three types of filaments that are distinguishable by the diameter. • Actin filaments (microfilaments): 5-9 nm diameter with twisted strands. ...
... • Cells have three types of filaments that are distinguishable by the diameter. • Actin filaments (microfilaments): 5-9 nm diameter with twisted strands. ...
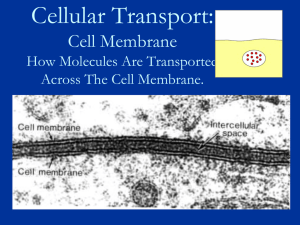
cell membrane
... • Lipid bilayer – double layer of phospholipids – polar head of one faces outside and other faces inside of cell – Non-polar tails face towards each other inside bilayer ...
... • Lipid bilayer – double layer of phospholipids – polar head of one faces outside and other faces inside of cell – Non-polar tails face towards each other inside bilayer ...
7th Grade Geography Assessment Task 1
... identify: Plasma membrane, cytoplasm, free ribosomes, vacuoles, cilium, attached ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum (smooth & rough), mitochondrion, nucleolus, nucleus, centriole, golgi apparatus, cytoskeleton, & lysosome. The plant cell must include: lysosome, mitochondrion, cytoplasm, endoplasmic re ...
... identify: Plasma membrane, cytoplasm, free ribosomes, vacuoles, cilium, attached ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum (smooth & rough), mitochondrion, nucleolus, nucleus, centriole, golgi apparatus, cytoskeleton, & lysosome. The plant cell must include: lysosome, mitochondrion, cytoplasm, endoplasmic re ...
Chapter 5
... A special protein that transports Na+ ions and K+ up their concentration gradients ...
... A special protein that transports Na+ ions and K+ up their concentration gradients ...
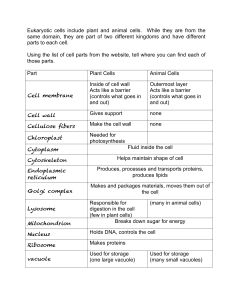
Cell membrane Cell wall Cellulose fibers Chloroplast Cytoplasm
... Acts like a barrier (controls what goes in and out) ...
... Acts like a barrier (controls what goes in and out) ...