The Cell Membrane, Passive Transport and Active Transport
... Hydrogen ion pumps are important to making ATP. Where in a cell might hydrogen ion pumps be located? ______________________________________ Vesicles move substances too large for carrier proteins across membranes. (Proteins and polysaccharides. During endocytosis, substances are moved into a cell b ...
... Hydrogen ion pumps are important to making ATP. Where in a cell might hydrogen ion pumps be located? ______________________________________ Vesicles move substances too large for carrier proteins across membranes. (Proteins and polysaccharides. During endocytosis, substances are moved into a cell b ...
Cells Cell Theory Cell size is limited Surface area Surface area
... Series of membranes throughout the cytoplasm Divides cell into compartments where different cellular functions occur One of the fundamental distinctions between eukaryotes and prokaryotes ...
... Series of membranes throughout the cytoplasm Divides cell into compartments where different cellular functions occur One of the fundamental distinctions between eukaryotes and prokaryotes ...
The Cell - Simpson
... Storage area of the cell Stores food and water Plants have one large vacuole for water Some animal cells have them & others do not ...
... Storage area of the cell Stores food and water Plants have one large vacuole for water Some animal cells have them & others do not ...
The Necessities of Life
... Some proteins = a few amino acids Some proteins = 10,000 amino acids Red blood cells contain protein called hemoglobin Hemoglobin binds to oxygen to deliver and release oxygen throughout the body Some proteins protect cells Proteins called enzymes speed up chemical reactions in cells ...
... Some proteins = a few amino acids Some proteins = 10,000 amino acids Red blood cells contain protein called hemoglobin Hemoglobin binds to oxygen to deliver and release oxygen throughout the body Some proteins protect cells Proteins called enzymes speed up chemical reactions in cells ...
CP BIO: Ch. 7 The Cell Membrane - Northern Highlands Regional HS
... - depends on: molecule size, charge, polar or nonpolar, concentration, needs of the cell ...
... - depends on: molecule size, charge, polar or nonpolar, concentration, needs of the cell ...
A Cell
... the club. The Mitochondria’s job in the cell is to produce energy or ATP, the cell runs off of these this energy. The things in a club that bring in profit are like the mitochondria because it produces the money, ATP, the club functions off of. ...
... the club. The Mitochondria’s job in the cell is to produce energy or ATP, the cell runs off of these this energy. The things in a club that bring in profit are like the mitochondria because it produces the money, ATP, the club functions off of. ...
Chapter 3 Cells - McCarter Anatomy & Physiology
... embryonic tissue • important for growth of nerve cells •lack of CAMs causes cancer to spread •wrong kind of CAM produced causes arthritis ...
... embryonic tissue • important for growth of nerve cells •lack of CAMs causes cancer to spread •wrong kind of CAM produced causes arthritis ...
Plant vs Animal Cells - Fall River Public Schools
... d. It breaks down and recycles old cell parts. 4. Which of the following best describes the role of the chloroplast in a plant cell? a. Packaging materials the cell needs and sending them around the cell. b. Capturing the sun’s energy so plants can use it to make their own food. c. Letting important ...
... d. It breaks down and recycles old cell parts. 4. Which of the following best describes the role of the chloroplast in a plant cell? a. Packaging materials the cell needs and sending them around the cell. b. Capturing the sun’s energy so plants can use it to make their own food. c. Letting important ...
Cell Structure Common Cell Traits Living cells are dynamic and
... Not all cells are created equal. Not all cells have the same function as other do either. Check out the websites listed below. Develop a summary paragraph that explains the similarities and differences among cellular organelles when referring to plant and animal cells. There are many similarities, b ...
... Not all cells are created equal. Not all cells have the same function as other do either. Check out the websites listed below. Develop a summary paragraph that explains the similarities and differences among cellular organelles when referring to plant and animal cells. There are many similarities, b ...
CHAPTER 7 STUDY GUIDE
... c. A human body has 200 different types of cells with different function, therefore different forms. d. NUCLEUS: contains chromosome, which are wrapped with special proteins into a chromatin network. i. Surrounded by a nuclear envelope that contains pores to allow for the transport of molecules like ...
... c. A human body has 200 different types of cells with different function, therefore different forms. d. NUCLEUS: contains chromosome, which are wrapped with special proteins into a chromatin network. i. Surrounded by a nuclear envelope that contains pores to allow for the transport of molecules like ...
Homework: Plant vs Animal Cells HW-35
... d. It breaks down and recycles old cell parts. 4. Which of the following best describes the role of the chloroplast in a plant cell? a. Packaging materials the cell needs and sending them around the cell. b. Capturing the sun’s energy so plants can use it to make their own food. c. Letting important ...
... d. It breaks down and recycles old cell parts. 4. Which of the following best describes the role of the chloroplast in a plant cell? a. Packaging materials the cell needs and sending them around the cell. b. Capturing the sun’s energy so plants can use it to make their own food. c. Letting important ...
Anatomy of the Eukaryotic Cell
... • Lysosomes, which store digestive enzymes that are used by the cell to break down nutrients into units small enough to be utilized by the cell. • Vacuoles, which are temporary storage for proteins, sugars, organic acids, and inorganic ions. • Peroxisomes, which oxidize toxic substances into hydroge ...
... • Lysosomes, which store digestive enzymes that are used by the cell to break down nutrients into units small enough to be utilized by the cell. • Vacuoles, which are temporary storage for proteins, sugars, organic acids, and inorganic ions. • Peroxisomes, which oxidize toxic substances into hydroge ...
botany practice test i - sample questions-doc
... PART I - Multiple Choice: Choose the best answer. Be sure to look over all possible choices before making your selection. Keep in mind that some of these questions are based entirely on information in the required reading assignments or tidbits of lecture material not found necessarily on the Intern ...
... PART I - Multiple Choice: Choose the best answer. Be sure to look over all possible choices before making your selection. Keep in mind that some of these questions are based entirely on information in the required reading assignments or tidbits of lecture material not found necessarily on the Intern ...
Cell: The Basic Unit of Life
... Cell: The Basic Unit of Life Directions: go to my school website. Click on the videos tab and find the video Discovery Ed Cell: The Basic Unit of Life. Watch, pause and rewind to answer the following questions. Turn this sheet in for credit when done. 1. FROM THE SIMPLEST MICROSCOPIC ORGANISMS UP TH ...
... Cell: The Basic Unit of Life Directions: go to my school website. Click on the videos tab and find the video Discovery Ed Cell: The Basic Unit of Life. Watch, pause and rewind to answer the following questions. Turn this sheet in for credit when done. 1. FROM THE SIMPLEST MICROSCOPIC ORGANISMS UP TH ...
ISLET-1+ HEART PROGENITORS: A PARABLE OF
... Cardiovascular Disease Program, Harvard Stem Cell Institute ...
... Cardiovascular Disease Program, Harvard Stem Cell Institute ...
Chapter 7 Study Guide
... 4. Name all organelles found in a plant cell and explain the role of each. 5. Name all organelles found in an animal cell and explain the role of each. 6. Draw and label the parts of an ATP molecule. What is it used for? 7. Draw and label the parts of the FMMOCM—know structure and function! 8. Expla ...
... 4. Name all organelles found in a plant cell and explain the role of each. 5. Name all organelles found in an animal cell and explain the role of each. 6. Draw and label the parts of an ATP molecule. What is it used for? 7. Draw and label the parts of the FMMOCM—know structure and function! 8. Expla ...
Ch 7 study guide
... • the cytoskeleton: a network of protein filaments; it helps the cell maintain its shape and is involved in movement • centrioles: organelles made from tubulins; they help organize cell division in animal cells Organelles That Build Proteins Three kinds of organelles work with the nucleus to make an ...
... • the cytoskeleton: a network of protein filaments; it helps the cell maintain its shape and is involved in movement • centrioles: organelles made from tubulins; they help organize cell division in animal cells Organelles That Build Proteins Three kinds of organelles work with the nucleus to make an ...
Standard B-2
... • Homeostasis of cells depends on appropriate movement of materials across the cell membrane. – Materials needed for cellular processes must pass into cells – Waste materials from cell processes must pass out of cells as they are produced – The cell membrane regulates the passage of material into an ...
... • Homeostasis of cells depends on appropriate movement of materials across the cell membrane. – Materials needed for cellular processes must pass into cells – Waste materials from cell processes must pass out of cells as they are produced – The cell membrane regulates the passage of material into an ...
Neuroscience 26
... 1.a. Golgi method - way of staining a neuron’s soma and dendrites completely; it also stains only a small fraction of the neurons, so each stained neuron’s structure can be seen clearly. b. Cell birthday - time of last cell division before a neuron becomes post-mitotic. c. Myelin - membranous wrappi ...
... 1.a. Golgi method - way of staining a neuron’s soma and dendrites completely; it also stains only a small fraction of the neurons, so each stained neuron’s structure can be seen clearly. b. Cell birthday - time of last cell division before a neuron becomes post-mitotic. c. Myelin - membranous wrappi ...
Cells Name: Date: 1. Which organelle is primarily concerned with
... D. the improvement in microscopes and microscopic techniques during the last ...
... D. the improvement in microscopes and microscopic techniques during the last ...
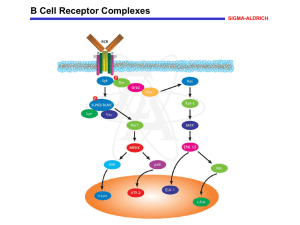
B Cell Receptor Complexes - Sigma
... family are activated initially and phosphorylate CD79 and CD79ß, thereby creating phosphotyrosine motifs that recruit downstream signaling molecules. In particular, phosphorylation of the BCR complex leads to the recruitment and activation of the protein tyrosine kinase Syk, which, in turn, promote ...
... family are activated initially and phosphorylate CD79 and CD79ß, thereby creating phosphotyrosine motifs that recruit downstream signaling molecules. In particular, phosphorylation of the BCR complex leads to the recruitment and activation of the protein tyrosine kinase Syk, which, in turn, promote ...
Bio 8/22/12 -intro: discussing syllabus -87
... One bastion left in vitalism…nature of mind and consciousness III. living organisms share certain properties (ppt) (figure in textbook) IV. all living organisms are composed of cells Cell is lowest level of organization All cells are enclosed by a membrane All cells use DNA as their genetic material ...
... One bastion left in vitalism…nature of mind and consciousness III. living organisms share certain properties (ppt) (figure in textbook) IV. all living organisms are composed of cells Cell is lowest level of organization All cells are enclosed by a membrane All cells use DNA as their genetic material ...