Life Science Vocabulary 2014-2015
... 7. cytoplasm – the region between the cell membrane and the nucleus; in organisms without a nucleus, the region located inside the cell membrane. 8. nucleus – a cell structure that contains nucleic acids, the chemical instructions that direct all the cell’s activities. 9. chromatin – material in cel ...
... 7. cytoplasm – the region between the cell membrane and the nucleus; in organisms without a nucleus, the region located inside the cell membrane. 8. nucleus – a cell structure that contains nucleic acids, the chemical instructions that direct all the cell’s activities. 9. chromatin – material in cel ...
T4.cells organelles
... • organelle helps store and transport products produced by the cell. – The vesicles are the transport and delivery vehicles like our mail and Federal Express trucks. Some vesicles deliver materials to parts of the cell and others transport materials outside the cell in a process called exocytosis. ...
... • organelle helps store and transport products produced by the cell. – The vesicles are the transport and delivery vehicles like our mail and Federal Express trucks. Some vesicles deliver materials to parts of the cell and others transport materials outside the cell in a process called exocytosis. ...
“Life is like a box of chocolates: you never know what you are going
... ________ is a molecule that contains information in all living things. In the cell, information (________) is stored in _____________________. Converting the DNA to __________ is a process called _______________. Once ______________ is completed, information is taken outside the _____________ by ___ ...
... ________ is a molecule that contains information in all living things. In the cell, information (________) is stored in _____________________. Converting the DNA to __________ is a process called _______________. Once ______________ is completed, information is taken outside the _____________ by ___ ...
Cell Keywords - No Brain Too Small
... f) involved in light detection within unicellular organisms g) Final modification of proteins and lipids. Sorting and storage for use in the cell or packaging molecules for export h) Organelle that contains enzymes and destroys foreign material by intracellular digestion. ...
... f) involved in light detection within unicellular organisms g) Final modification of proteins and lipids. Sorting and storage for use in the cell or packaging molecules for export h) Organelle that contains enzymes and destroys foreign material by intracellular digestion. ...
1. Describe two functions of centromere during mitosis. 2. a) Look at
... c) A cell in the G1 stage of interphase had 10 arbitrary units of DNA contained in six pairs of homologus chromosomes. If it divided by mitosis, how many units of DNA and how many chromosomes would there be, i) In the nucleus at the end of G2? ...
... c) A cell in the G1 stage of interphase had 10 arbitrary units of DNA contained in six pairs of homologus chromosomes. If it divided by mitosis, how many units of DNA and how many chromosomes would there be, i) In the nucleus at the end of G2? ...
Types of cells based on internal organization of cell organelles.
... Multicellular Organism : Organism which is formed of more than one cell of different types. Example: Higher animals. ...
... Multicellular Organism : Organism which is formed of more than one cell of different types. Example: Higher animals. ...
Macromolecules and Cell Structure
... • Made of phospholipid bilayers, proteins, and other complex biomolecules • When formed into a spherical shape, can become a vessel for hereditary material • Vary in complexity and composition depending on the type of organism • May play a vital role in the survival of organisms ...
... • Made of phospholipid bilayers, proteins, and other complex biomolecules • When formed into a spherical shape, can become a vessel for hereditary material • Vary in complexity and composition depending on the type of organism • May play a vital role in the survival of organisms ...
Outline - Membranes Membranes Membrane Phospholipids
... PROTEINS have a key role in transport across membranes I. Passive Transport 1. Always “down” a concentration gradient ...
... PROTEINS have a key role in transport across membranes I. Passive Transport 1. Always “down” a concentration gradient ...
Cellular Transport and the Cell Cycle
... Endocytosis: transport of large particles inside of a cell ...
... Endocytosis: transport of large particles inside of a cell ...
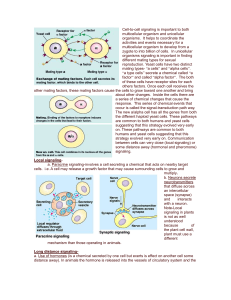
Long distance signaling
... enzyme (adenylate cyclase) in the plasma membrane causes this reaction to occur. In this example, epinephrine activates a receptor site, which in turns activates the Gprotein. The G protein now activates adenlyate cyclase, which then makes cAMP from ATP. cAMP activates the epinephrine pathway which ...
... enzyme (adenylate cyclase) in the plasma membrane causes this reaction to occur. In this example, epinephrine activates a receptor site, which in turns activates the Gprotein. The G protein now activates adenlyate cyclase, which then makes cAMP from ATP. cAMP activates the epinephrine pathway which ...
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell
... • The Golgi apparatus functions in conjunction with the ER by modifying products of the ER – Products travel in transport vesicles from the ER to the Golgi apparatus – One side of the Golgi apparatus functions as a receiving dock for the product and the other as a shipping dock – Products are modifi ...
... • The Golgi apparatus functions in conjunction with the ER by modifying products of the ER – Products travel in transport vesicles from the ER to the Golgi apparatus – One side of the Golgi apparatus functions as a receiving dock for the product and the other as a shipping dock – Products are modifi ...
The Structure and Function of Cells
... • Now that we have looked at some of the organelles, can you tell me where some of these life functions are carried out in a cell? – Nutrition ...
... • Now that we have looked at some of the organelles, can you tell me where some of these life functions are carried out in a cell? – Nutrition ...
Cell Transport
... Cell Membrane ___________what enters and leaves the cell Cell membrane is surrounded by _______ Phospholipid bilayer ...
... Cell Membrane ___________what enters and leaves the cell Cell membrane is surrounded by _______ Phospholipid bilayer ...
Power Point Cell Organelles
... Both have many of the same organelles, but plant cells also have chloroplasts, a large central vacuole, and a cell wall. ...
... Both have many of the same organelles, but plant cells also have chloroplasts, a large central vacuole, and a cell wall. ...
CELL MEMBRANE - wlhs.wlwv.k12.or.us
... ● help protect from predators by storing waste products that may also be poisonous compounds ● contractile vacuole: specialized vacuole that ...
... ● help protect from predators by storing waste products that may also be poisonous compounds ● contractile vacuole: specialized vacuole that ...
Methods of Movement in the Cell
... • All living things have certain requirements they must satisfy in order to remain alive. – Exchanging gases (usually CO2 and O2), – Taking in water, minerals, and food – Eliminating wastes ...
... • All living things have certain requirements they must satisfy in order to remain alive. – Exchanging gases (usually CO2 and O2), – Taking in water, minerals, and food – Eliminating wastes ...
(9)Before you arrive for the Diffusion and Osmosis lab, please
... If water potential in an environment is higher than its surroundings, does water flow into or out of that environment? _____________________________________________________________________ Imagine some cut flowers sitting in water. For water to move through the stems to the upper leaves, where must ...
... If water potential in an environment is higher than its surroundings, does water flow into or out of that environment? _____________________________________________________________________ Imagine some cut flowers sitting in water. For water to move through the stems to the upper leaves, where must ...
File
... is that Both mitochondria and chloroplasts divide inside the eukaryotic cell by binary fission, as bacteria do and normal eukaryotes do not divide this way. Secondly, researched also by Lynn Sagan, is that Mitochondria and chloroplasts both have double-layer membranes which are chemically similar to ...
... is that Both mitochondria and chloroplasts divide inside the eukaryotic cell by binary fission, as bacteria do and normal eukaryotes do not divide this way. Secondly, researched also by Lynn Sagan, is that Mitochondria and chloroplasts both have double-layer membranes which are chemically similar to ...
Name______________________________________
... 3. ____________________ any substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances 4. ____________________ two or more elements that are chemically combined 5. ____________________ a type of protein that speeds up a chemical reaction in a living thing 6. ____________________ energy-rich organi ...
... 3. ____________________ any substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances 4. ____________________ two or more elements that are chemically combined 5. ____________________ a type of protein that speeds up a chemical reaction in a living thing 6. ____________________ energy-rich organi ...
Chapter 2
... •Plant cells are surrounded by walls (cellulose microfibrils in matrix of pectins and hemicelluloses (1o) or lignin (2o)) •Lignin is hydrophobic and prevents cell expansion •little cell migration (cell sliding possible) •Cell expansion depends on orientation of microfibrils •Molecules fixed in cell ...
... •Plant cells are surrounded by walls (cellulose microfibrils in matrix of pectins and hemicelluloses (1o) or lignin (2o)) •Lignin is hydrophobic and prevents cell expansion •little cell migration (cell sliding possible) •Cell expansion depends on orientation of microfibrils •Molecules fixed in cell ...
2.2.6 Movement through Cell Membranes Osmosis
... plant cells are surrounded by a more concentrated solution (for example if plant cells were surrounded by salt water) the water inside the cell would move out to the more concentrated solution outside. ...
... plant cells are surrounded by a more concentrated solution (for example if plant cells were surrounded by salt water) the water inside the cell would move out to the more concentrated solution outside. ...
Cell Transport
... from over-expanding. In plants the pressure exerted on the cell wall is called tugor pressure. •A protist like paramecium has contractile vacuoles that collect water flowing in and pump it out to prevent them from over-expanding. •Salt water fish pump salt out of their specialized gills so they do n ...
... from over-expanding. In plants the pressure exerted on the cell wall is called tugor pressure. •A protist like paramecium has contractile vacuoles that collect water flowing in and pump it out to prevent them from over-expanding. •Salt water fish pump salt out of their specialized gills so they do n ...
cell analogy
... in the city including expansion and creation of another kingdom should the city grow too large. Chromosomes are found in the nucleus and directs all activities of the cell including growth and reproduction. ...
... in the city including expansion and creation of another kingdom should the city grow too large. Chromosomes are found in the nucleus and directs all activities of the cell including growth and reproduction. ...
Cell Model Expectations
... will label the structures on the models with numbers, and provide a key to identify each part of the cell. You will also complete a sheet identifying each organelle, its function, and what common object would represent each organelle. Requirements and Limits ...
... will label the structures on the models with numbers, and provide a key to identify each part of the cell. You will also complete a sheet identifying each organelle, its function, and what common object would represent each organelle. Requirements and Limits ...