Document
... 2. Plant, fungi, and some bacteria cells have a rigid cell wall outside the cell membrane 3. Appendages, such as tail-like flagella or short hairlike cilia, help cells move 4. Inside a cell is the cytoplasm, a thick fluid in which cell structures are suspended a. Cells have a network of fibers in th ...
... 2. Plant, fungi, and some bacteria cells have a rigid cell wall outside the cell membrane 3. Appendages, such as tail-like flagella or short hairlike cilia, help cells move 4. Inside a cell is the cytoplasm, a thick fluid in which cell structures are suspended a. Cells have a network of fibers in th ...
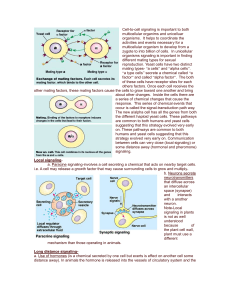
Cell-to-cell signaling is important to both multicellular organims and
... enzyme (adenlate cylase) in the plasma membrane causes this reaction to occur. In this example, epinephrine activates a receptor site, which in turns activates the Gprotein. The G protein now activates adenlyate cyclase, which then makes cAMP from ATP. cAMP activates the epinephrine pathway which ul ...
... enzyme (adenlate cylase) in the plasma membrane causes this reaction to occur. In this example, epinephrine activates a receptor site, which in turns activates the Gprotein. The G protein now activates adenlyate cyclase, which then makes cAMP from ATP. cAMP activates the epinephrine pathway which ul ...
Cell Analogy Project
... Cell Analogy Project “It takes 3 million cells to cover the head of a pin, but only one great cell project to cover a large part of your Biology grade!” Due Friday, October 14th. Directions: 1. Draw an animal cell on an unlined sheet of paper. Color the organelles with colored pencils. Include at le ...
... Cell Analogy Project “It takes 3 million cells to cover the head of a pin, but only one great cell project to cover a large part of your Biology grade!” Due Friday, October 14th. Directions: 1. Draw an animal cell on an unlined sheet of paper. Color the organelles with colored pencils. Include at le ...
The tiny structures in the cell that carry out the
... CELL WALL •A stiff wall that surrounds the cell membrane, giving the cell a rigid boxlike shape •Function: protection & support •This structure is only on the plant cell CELL MEMBRANE •Forms the outside boundary that separates the cell from its environment •Function: controls what comes in and out o ...
... CELL WALL •A stiff wall that surrounds the cell membrane, giving the cell a rigid boxlike shape •Function: protection & support •This structure is only on the plant cell CELL MEMBRANE •Forms the outside boundary that separates the cell from its environment •Function: controls what comes in and out o ...
Pre-Bio LP 1.23-2.2
... Make two T-chart that identifies the differences between 1) prokaryotes and eukaryotes, and 2) plant cells and animal cells Question/Answer in class discussion (verbal) I can describe the purpose of the major cellular organelles & cellular structures. I can differentiate between prokaryotes & eukary ...
... Make two T-chart that identifies the differences between 1) prokaryotes and eukaryotes, and 2) plant cells and animal cells Question/Answer in class discussion (verbal) I can describe the purpose of the major cellular organelles & cellular structures. I can differentiate between prokaryotes & eukary ...
Cell in its Environment - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... 20. Almost all living things depend on the process of ____________________ to supply them with the energy they need. 21. Unlike passive transport, active transport requires the cell to use ____________________. 22. Most substances must be dissolved in ____________________ to be used by cells. ...
... 20. Almost all living things depend on the process of ____________________ to supply them with the energy they need. 21. Unlike passive transport, active transport requires the cell to use ____________________. 22. Most substances must be dissolved in ____________________ to be used by cells. ...
Cellular Transport
... window screen? Why is it important to keep these things from moving through the screen? 3. How is a window screen similar to a cell membrane? 4. Why is it important to regulate what moves into and out of the cell? ...
... window screen? Why is it important to keep these things from moving through the screen? 3. How is a window screen similar to a cell membrane? 4. Why is it important to regulate what moves into and out of the cell? ...
Study Questions for Unit 1 (Chemistry and Cell Biology)
... 3. Why is a typical cell so small? 4. Describe the structure of cell membranes. What is the role of water in maintaining this structure? 5. Materials enter and leave a cell through a variety of means. Describe several of these means. For each one, describe the circumstances under which a cell utiliz ...
... 3. Why is a typical cell so small? 4. Describe the structure of cell membranes. What is the role of water in maintaining this structure? 5. Materials enter and leave a cell through a variety of means. Describe several of these means. For each one, describe the circumstances under which a cell utiliz ...
Chapter 3 Study Guide: Cells
... Proteins act as channels to allow passage of large particles and water-soluble molecules. Carbohydrates act as cell surface markers to identify specific cells; self vs. nonself. Describe the phospholipid bilayer and how its structural components (hydrophilic/hydrophobic) allow it to function as ...
... Proteins act as channels to allow passage of large particles and water-soluble molecules. Carbohydrates act as cell surface markers to identify specific cells; self vs. nonself. Describe the phospholipid bilayer and how its structural components (hydrophilic/hydrophobic) allow it to function as ...
organelle Part of Grant City Purpose in the city Purpose in the cell
... throughout the cell. Moves materials and aids in protein production. Contains the DNA which has the instructions for protein making. ...
... throughout the cell. Moves materials and aids in protein production. Contains the DNA which has the instructions for protein making. ...
The Microscope & The Cell
... a. an internal membrane system b. A system of membranes inside the cell that: 1. Modify proteins made in the Rough E.R. 2. Manufacture Lipid components of the cell membrane c. There are 2 forms of ER: a. ...
... a. an internal membrane system b. A system of membranes inside the cell that: 1. Modify proteins made in the Rough E.R. 2. Manufacture Lipid components of the cell membrane c. There are 2 forms of ER: a. ...
Classification notes
... 1) _______________________ – Study of evolutionary relationships. 2) Members of the same species share a recent _____________________ ______________________ ...
... 1) _______________________ – Study of evolutionary relationships. 2) Members of the same species share a recent _____________________ ______________________ ...
permeability of cell membrane (red blood cell
... Every cell of the body is bathed in a watery fluid that contains a mixture of molecules that are essential to its survival. This fluid may be the plasma of blood or the tissue fluid in the interstitial spaces. In either case, these molecules, whether water, nutrients, gases, or ions, pass in and out ...
... Every cell of the body is bathed in a watery fluid that contains a mixture of molecules that are essential to its survival. This fluid may be the plasma of blood or the tissue fluid in the interstitial spaces. In either case, these molecules, whether water, nutrients, gases, or ions, pass in and out ...
me239 mechanics of the cell 1.2 introduction to the cell 1.2
... production site to their working site? how do cells interact with their environment? what are the cell's mechanisms to sense environmental changes and to respond to them? ...
... production site to their working site? how do cells interact with their environment? what are the cell's mechanisms to sense environmental changes and to respond to them? ...
Cell Membrane Proteins.
... processed in the Golgi apparatus to form lysosomes, secretory vesicles, and other cytoplasmic components Lysosomes:, are vesicular organelles that form by breaking off from the Golgi apparatus and then dispersing throughout the cytoplasm. The lysosomes provide an intracellular digestive system that ...
... processed in the Golgi apparatus to form lysosomes, secretory vesicles, and other cytoplasmic components Lysosomes:, are vesicular organelles that form by breaking off from the Golgi apparatus and then dispersing throughout the cytoplasm. The lysosomes provide an intracellular digestive system that ...
Cell Organelle Review Game
... It is your job as the teacher to set up the main objective of the game before it is played. This game can be modified to fit your needs. You want to highlight what you feel that the students need the most help in. For example, if you are just covering the basic cell organelles and their roles in pla ...
... It is your job as the teacher to set up the main objective of the game before it is played. This game can be modified to fit your needs. You want to highlight what you feel that the students need the most help in. For example, if you are just covering the basic cell organelles and their roles in pla ...
Section 1 Chemistry of Life A. Everything around you is
... a. Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose molecules. b. Each glucose molecule is broken down into two simpler molecules, releasing energy. 2. Respiration moves into the mitochondria. a. The two simpler molecules are broken down again, releasing much more energy. b. This process uses oxygen and p ...
... a. Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose molecules. b. Each glucose molecule is broken down into two simpler molecules, releasing energy. 2. Respiration moves into the mitochondria. a. The two simpler molecules are broken down again, releasing much more energy. b. This process uses oxygen and p ...
Topic: Types of Cells and Membranes
... Contains arrangement of atoms attached to glycerol including phosphate group ...
... Contains arrangement of atoms attached to glycerol including phosphate group ...
Transport across cell membranes
... • Factors that affect rate of diffusion: – Molecule size: larger molecules = slower rate of diffusion – Molecule polarity: polar molecules = slower rate of diffusion – Molecule or ion charge: charged molecules and ions cannot freely diffuse across a cell membrane ...
... • Factors that affect rate of diffusion: – Molecule size: larger molecules = slower rate of diffusion – Molecule polarity: polar molecules = slower rate of diffusion – Molecule or ion charge: charged molecules and ions cannot freely diffuse across a cell membrane ...
7.3 ANIMAL and PLANT CELL STRUCTURE HO
... cytoplasm of the cell and carry out the activities that keep the cell alive. Plant and animal cells have many of the same organelles, but they also have some major differences. These different cellular structures have a huge impact on how these different living things go about the business of life. ...
... cytoplasm of the cell and carry out the activities that keep the cell alive. Plant and animal cells have many of the same organelles, but they also have some major differences. These different cellular structures have a huge impact on how these different living things go about the business of life. ...