carbs and lipids 2
... Know the structural and energy storing polysaccharides a. Structural: Cellulose and Chitin; why are they structural, general structure information, why can’t humans use cellulose or chitin as energy stores b. Energy storing: Glycogen and Starch; what makes these energy storing, how do enzymes re ...
... Know the structural and energy storing polysaccharides a. Structural: Cellulose and Chitin; why are they structural, general structure information, why can’t humans use cellulose or chitin as energy stores b. Energy storing: Glycogen and Starch; what makes these energy storing, how do enzymes re ...
Nerve activates contraction
... Objective 4: TSWBAT identify the components of the fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane. Objective 5: TSWBAT describe the roles of the various proteins found in and on the cell membrane. ...
... Objective 4: TSWBAT identify the components of the fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane. Objective 5: TSWBAT describe the roles of the various proteins found in and on the cell membrane. ...
macromolecule_sheets
... Critical Thinking: Cellulose is very hard to digest, yet cows are able to eat and digest these polysaccharides. Explain why. ...
... Critical Thinking: Cellulose is very hard to digest, yet cows are able to eat and digest these polysaccharides. Explain why. ...
Cell City Analogy Directions: Match the important parts of the city
... Descriptions of important parts of the Cell City: A. City Limits/Police Department -‐ control what goes in and out of the city B. City Wall—a brick wall that protects the inside of the city. C. Road ...
... Descriptions of important parts of the Cell City: A. City Limits/Police Department -‐ control what goes in and out of the city B. City Wall—a brick wall that protects the inside of the city. C. Road ...
Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells
... -‐Be able to label at least 10 organelles in a Eukaryotic cell -‐Know how eukaryotic cells obtain energy -‐Be able to compare and contrast Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells (size, age, complexity, struc ...
... -‐Be able to label at least 10 organelles in a Eukaryotic cell -‐Know how eukaryotic cells obtain energy -‐Be able to compare and contrast Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells (size, age, complexity, struc ...
Answers to exam questions on Chloroplasts and
... glucose. Oxygen is produced as a waste product. Relation to other cell organelles (mitochondria) = The glucose produced by the chloroplasts is used by mitochondria in the process of respiration, which produces ATP. Overall functioning of the cell = Other organelles use this ATP to carry out cell act ...
... glucose. Oxygen is produced as a waste product. Relation to other cell organelles (mitochondria) = The glucose produced by the chloroplasts is used by mitochondria in the process of respiration, which produces ATP. Overall functioning of the cell = Other organelles use this ATP to carry out cell act ...
AntimicrobialCopper[1]
... After punching holes, how do copper ions further damage the cell? Now that the cells main defense (its outer envelope) has been breached, there is an unopposed stream of copper ions entering the cell. This puts several vital processes inside the cell in danger. Copper literally overwhelms the insid ...
... After punching holes, how do copper ions further damage the cell? Now that the cells main defense (its outer envelope) has been breached, there is an unopposed stream of copper ions entering the cell. This puts several vital processes inside the cell in danger. Copper literally overwhelms the insid ...
Study Guide for Exam I-DOC
... The plasma membrane is semi-permeable. What is semi-permeable mean? What is cytoskeleton? What is the fluid matrix that organelles are embedded in and what is it composed of? What is the nucleus and what is its function? What is ER and what is the difference between the two types? What is the functi ...
... The plasma membrane is semi-permeable. What is semi-permeable mean? What is cytoskeleton? What is the fluid matrix that organelles are embedded in and what is it composed of? What is the nucleus and what is its function? What is ER and what is the difference between the two types? What is the functi ...
(B2) Checklist
... The cells of multicellular organisms may differentiate and become adapted for specific functions. Tissues are aggregations of similar cells; organs are aggregations of tissues performing specific physiological functions. Organs are organised into organ systems, which work together to form organisms. ...
... The cells of multicellular organisms may differentiate and become adapted for specific functions. Tissues are aggregations of similar cells; organs are aggregations of tissues performing specific physiological functions. Organs are organised into organ systems, which work together to form organisms. ...
PPT
... allow cilia and flagella to move. Flagella are much larger than cilia. Cilia are more numerous on a cell than flagella. A cell will have either cilia or flagella but not both. The contractile proteins of cilia and flagella form a characteristic arrangement. They come in ...
... allow cilia and flagella to move. Flagella are much larger than cilia. Cilia are more numerous on a cell than flagella. A cell will have either cilia or flagella but not both. The contractile proteins of cilia and flagella form a characteristic arrangement. They come in ...
The muscular system
... • Proteinassisted diffusion – Transporters or carriers • Amino acids, glucose ...
... • Proteinassisted diffusion – Transporters or carriers • Amino acids, glucose ...
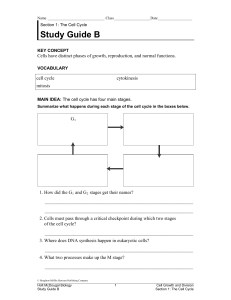
Study Guide B
... 5. Among different types of cells, which stage of the cell cycle varies most in length? _______________________________________________________________ 6. Why does a skin cell divide more often than a liver cell? _______________________________________________________________ 7. What is G 0 ? ______ ...
... 5. Among different types of cells, which stage of the cell cycle varies most in length? _______________________________________________________________ 6. Why does a skin cell divide more often than a liver cell? _______________________________________________________________ 7. What is G 0 ? ______ ...
Biochemistry/Scientific Method Test Review Guide
... 1. What are lipids? 2. What is the function of a lipid? 3. What elements make up lipids? 4. What are 3 examples of a lipid? 5. What lipid is found in cell membranes? 6. Draw what a cell membrane looks like. Proteins 1. What are the functions of a protein? 2. What are the building blocks of a protein ...
... 1. What are lipids? 2. What is the function of a lipid? 3. What elements make up lipids? 4. What are 3 examples of a lipid? 5. What lipid is found in cell membranes? 6. Draw what a cell membrane looks like. Proteins 1. What are the functions of a protein? 2. What are the building blocks of a protein ...
Plant Parts and Cells Plants are living things that are made of many
... those in an animal’s cells. Third and most important, plant cells have organelles called chloroplasts. These are filled with chlorophyll and are where photosynthesis occurs. Just as in animal cells, plant cells replicate through mitosis. However, after the chromosomes split to go into two separate c ...
... those in an animal’s cells. Third and most important, plant cells have organelles called chloroplasts. These are filled with chlorophyll and are where photosynthesis occurs. Just as in animal cells, plant cells replicate through mitosis. However, after the chromosomes split to go into two separate c ...
Facebook Organelle
... B. Incorporate the following components into your Facebook page: 1. Organelle Name 2. Location of Organelle in the cell 3. Type of cell your organelle is found in (plants, animals, or bacteria?) (Is your part modified in some way in different kinds of cells?) 4. Colorful pictures of the organelle an ...
... B. Incorporate the following components into your Facebook page: 1. Organelle Name 2. Location of Organelle in the cell 3. Type of cell your organelle is found in (plants, animals, or bacteria?) (Is your part modified in some way in different kinds of cells?) 4. Colorful pictures of the organelle an ...
Bio 2.1.2 * Analyze how various organisms accomplish
... Transport and Excretion – how different organisms get what they need to cells; how they move waste from cells to organs of excretion. Focus is on maintaining balance in pH, salt, and water. Include plants - vascular and nonvascular. Respiration – how different organisms take in and release gases (ca ...
... Transport and Excretion – how different organisms get what they need to cells; how they move waste from cells to organs of excretion. Focus is on maintaining balance in pH, salt, and water. Include plants - vascular and nonvascular. Respiration – how different organisms take in and release gases (ca ...
Chapter 20 Power Point File - York College Course and Testing
... Chromatin – uncondensed, stringy DNA Chromosomes – condensed DNA ...
... Chromatin – uncondensed, stringy DNA Chromosomes – condensed DNA ...
Plant Cells: Comparing Plant Cells with Animal Cells
... 2. Captures sunlight for photosynthesis (makes glucose) ...
... 2. Captures sunlight for photosynthesis (makes glucose) ...
all living things are composed of cells
... carbohydrates and lipids to proteins – go to outside of cell Lysosome – small organelles filled with enzymes. Break down lipids, carbohydrates and proteins from foods into particles used by rest of cell Vacuoles – sac like structures that store materials such as water, salt, proteins and carbohydrat ...
... carbohydrates and lipids to proteins – go to outside of cell Lysosome – small organelles filled with enzymes. Break down lipids, carbohydrates and proteins from foods into particles used by rest of cell Vacuoles – sac like structures that store materials such as water, salt, proteins and carbohydrat ...
Possible Next Steps –S1 Cells
... second and third trimesters. During the time of development, the fertilised egg becomes an ________ in the first trimester, then a_________, then finally becoming a ______ at birth. Know that the _________ becomes fully developed in the first trimester of pregnancy. The placenta is an organ attached ...
... second and third trimesters. During the time of development, the fertilised egg becomes an ________ in the first trimester, then a_________, then finally becoming a ______ at birth. Know that the _________ becomes fully developed in the first trimester of pregnancy. The placenta is an organ attached ...
Parts of a Cell Adapted
... out all life functions of the organism, such as making new materials and removing energy from food. Cells contain many parts with special jobs that work together to carry out these life functions. Organelles are small structures inside of cells that carry out specialized jobs. In this activity, you ...
... out all life functions of the organism, such as making new materials and removing energy from food. Cells contain many parts with special jobs that work together to carry out these life functions. Organelles are small structures inside of cells that carry out specialized jobs. In this activity, you ...
Chapter 31: Page 304
... in both plant and animal cells: the nucleus, ribosomes, “ER”, and mitochondria. Every eukaryotic cell uses these small structures to stay alive. But there are many more for you to study... In this chapter, you are going to look at three more organelles that can be found in both plant and animal cell ...
... in both plant and animal cells: the nucleus, ribosomes, “ER”, and mitochondria. Every eukaryotic cell uses these small structures to stay alive. But there are many more for you to study... In this chapter, you are going to look at three more organelles that can be found in both plant and animal cell ...







![AntimicrobialCopper[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006183415_1-46f42e14087e0060861546e4331c0742-300x300.png)