Hao Nguyen
... 2. A hypothetical cell expresses a mutated form of ras, which is constitutively (always) in the inactive form. Please, describe how this might affect the signal transduction pathway. NOTE: Be sure to name the specific pathway and all molecules that are directly affected. “The signal transduction pat ...
... 2. A hypothetical cell expresses a mutated form of ras, which is constitutively (always) in the inactive form. Please, describe how this might affect the signal transduction pathway. NOTE: Be sure to name the specific pathway and all molecules that are directly affected. “The signal transduction pat ...
Center for Eukaryotic Structural Genomics (CESG)
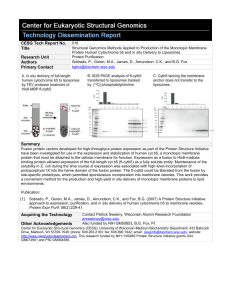
... Fusion protein vectors developed for high-throughput protein expression as part of the Protein Structure Initiative have been investigated for use in the expression and stabilization of human cyt b5, a monotopic membrane protein that must be attached to the cellular membrane for function. Expression ...
... Fusion protein vectors developed for high-throughput protein expression as part of the Protein Structure Initiative have been investigated for use in the expression and stabilization of human cyt b5, a monotopic membrane protein that must be attached to the cellular membrane for function. Expression ...
lesson 4 PC 2.3 Cell Structure & Keratinisation
... Matrix Layer • The germinal matrix layer is a special group of cells at the base of the follicle that are responsible for the reproduction of cells resulting in new hair growth. ...
... Matrix Layer • The germinal matrix layer is a special group of cells at the base of the follicle that are responsible for the reproduction of cells resulting in new hair growth. ...
CELLS: The Basic Units of Life
... Central Vacuole: single large vacuole for water storage and support Chloroplasts: site of photosynthesis; contains the pigment chlorophyll ● Plant cells lack centrioles & lysosomes ● They have all the other organelles found in animal cells ...
... Central Vacuole: single large vacuole for water storage and support Chloroplasts: site of photosynthesis; contains the pigment chlorophyll ● Plant cells lack centrioles & lysosomes ● They have all the other organelles found in animal cells ...
Chapter 3 Extended Chapter Outline
... b. The fluid outside the cell is extracellular fluid (ECF). II. The Cell Surface (pp. 91–100) A. Many physiological processes, including immune response, binding of egg and sperm, cell signaling, and detection of taste and smell, occur at the surface of the cell. (p. 91) B. The plasma membrane is th ...
... b. The fluid outside the cell is extracellular fluid (ECF). II. The Cell Surface (pp. 91–100) A. Many physiological processes, including immune response, binding of egg and sperm, cell signaling, and detection of taste and smell, occur at the surface of the cell. (p. 91) B. The plasma membrane is th ...
Cell Ball
... Plant cells have a central vacuole and animal cells have several small vacuoles to store food, water and waste. ...
... Plant cells have a central vacuole and animal cells have several small vacuoles to store food, water and waste. ...
CELLS songs and lyrics
... by They Might Be Giants Life is made out of cells – and cells make copies of themselves And they make copies of themselves – and they make copies of themselves Different cells have different jobs - but they all have one thing in common Inside of every cell is a twisted ladder – a recipe for life cal ...
... by They Might Be Giants Life is made out of cells – and cells make copies of themselves And they make copies of themselves – and they make copies of themselves Different cells have different jobs - but they all have one thing in common Inside of every cell is a twisted ladder – a recipe for life cal ...
Classification - SAVE MY EXAMS!
... Both the rough endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus are made up of membrane-bound sacs. (i) ...
... Both the rough endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus are made up of membrane-bound sacs. (i) ...
(DOCX, Unknown)
... A) Water will leave the cells, causing them to shrivel and collapse. B) NaCl will be exported from the red blood cells by facilitated diffusion. C) The blood cells will take up water, swell, and eventually burst. D) NaCl will passively diffuse into the red blood cells. E) The blood cells will expend ...
... A) Water will leave the cells, causing them to shrivel and collapse. B) NaCl will be exported from the red blood cells by facilitated diffusion. C) The blood cells will take up water, swell, and eventually burst. D) NaCl will passively diffuse into the red blood cells. E) The blood cells will expend ...
Instructions for Gram-LocEN Web-server
... experiments such as fluorescent microscopy imaging. Proteins with multiple locations play important roles in some metabolic processes taking place in more than one compartment. ...
... experiments such as fluorescent microscopy imaging. Proteins with multiple locations play important roles in some metabolic processes taking place in more than one compartment. ...
Chapter 3
... The following terms are freely used in your textbook. Make sure you know what they mean, how they are used, and how to use them. When an example is given, make sure you can describe and recall it. If a picture is provided, know what the structure looks like and where it is located. If a diagram desc ...
... The following terms are freely used in your textbook. Make sure you know what they mean, how they are used, and how to use them. When an example is given, make sure you can describe and recall it. If a picture is provided, know what the structure looks like and where it is located. If a diagram desc ...
File - Mastep4802
... (C) Water and oxygen 28. One of the principal chemical compounds that living things use to store energy is: (A) DNA (B)ATP (C) H2O (D) CO2 29. Information gathered from observing a plant that grows 3 cm over a two-week period results in: (A) Inferences (B) Variables (C) Hypotheses (D) Data 30. Scie ...
... (C) Water and oxygen 28. One of the principal chemical compounds that living things use to store energy is: (A) DNA (B)ATP (C) H2O (D) CO2 29. Information gathered from observing a plant that grows 3 cm over a two-week period results in: (A) Inferences (B) Variables (C) Hypotheses (D) Data 30. Scie ...
diffusion
... glucose and amino acids, cannot diffuse across the phospholipid bilayer. Also ions such as Na+ or Cl- cannot pass. ...
... glucose and amino acids, cannot diffuse across the phospholipid bilayer. Also ions such as Na+ or Cl- cannot pass. ...
THE HISTORY OF CELL BIOLOGY
... nucleus, the endoplasmic reticulum, and lysosomes. nucleus, the endoplasmic reticulum, and chloroplasts. nucleus and mitochondria. endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus. Modern Biology Study Guide ...
... nucleus, the endoplasmic reticulum, and lysosomes. nucleus, the endoplasmic reticulum, and chloroplasts. nucleus and mitochondria. endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus. Modern Biology Study Guide ...
Skin and Body Membranes Chapter 4
... Lucidum: dead, clear cells found only on hands/feet Granulosum: still living cells Spinosum:living cells Basale: absorb nutrients from the dermis to keep them alive, and “float” up to form the above 4 layers ...
... Lucidum: dead, clear cells found only on hands/feet Granulosum: still living cells Spinosum:living cells Basale: absorb nutrients from the dermis to keep them alive, and “float” up to form the above 4 layers ...
File
... inside and outside of the cell, with a water-hating inner layer of fats. Where it is found: Surrounding the cell When it is used: Always Why/ its function: To protect the cell, contain the cell, and filter what enters/leaves the cell. How it works: The chemical structure of the cell membrane and emb ...
... inside and outside of the cell, with a water-hating inner layer of fats. Where it is found: Surrounding the cell When it is used: Always Why/ its function: To protect the cell, contain the cell, and filter what enters/leaves the cell. How it works: The chemical structure of the cell membrane and emb ...
Membrane Transport Study Guide
... 21. Give an example of a solute molecule that is transported via simple diffusion. 22. Explain why simple diffusion is considered a form of passive transport. 23. Describe the state of equilibrium. Use the word “concentration” in your answer. 24. Describe the movement of solute particles once equili ...
... 21. Give an example of a solute molecule that is transported via simple diffusion. 22. Explain why simple diffusion is considered a form of passive transport. 23. Describe the state of equilibrium. Use the word “concentration” in your answer. 24. Describe the movement of solute particles once equili ...
Cell Shapes
... through membrane in bubblelike vesicles of plasma membrane, uses ATP • Exocytosis – vesicular transport out of cell • Endocytosis – vesicular transport into cell – phagocytosis – engulfing large particles by pseudopods – pinocytosis – taking in fluid droplets – receptor mediated endocytosis – taking ...
... through membrane in bubblelike vesicles of plasma membrane, uses ATP • Exocytosis – vesicular transport out of cell • Endocytosis – vesicular transport into cell – phagocytosis – engulfing large particles by pseudopods – pinocytosis – taking in fluid droplets – receptor mediated endocytosis – taking ...
Chapter 7 Section 2: Cell organelles Quiz
... Which of the following structures serves as the cell’s outer boundary and regulates what goes in & out of the cell? a. mitochondrion b. cell membrane c. chloroplast d. channel proteins ...
... Which of the following structures serves as the cell’s outer boundary and regulates what goes in & out of the cell? a. mitochondrion b. cell membrane c. chloroplast d. channel proteins ...
Review Packet 1
... b. Prophase c. Metaphase d. Anaphase 46. Which stage is the shortest a. interphase b. prophase c. metaphase d. anaphase 47. The percentage of cells in anaphase is about a. 3 b. 4 c. 5 d. 6 48. The length of time spent in anaphase is about a. 13 minutes b. 1 hour c. 1.3 hours d. 3.2 hours 49. The len ...
... b. Prophase c. Metaphase d. Anaphase 46. Which stage is the shortest a. interphase b. prophase c. metaphase d. anaphase 47. The percentage of cells in anaphase is about a. 3 b. 4 c. 5 d. 6 48. The length of time spent in anaphase is about a. 13 minutes b. 1 hour c. 1.3 hours d. 3.2 hours 49. The len ...
biology list of practicals
... Recording the heights of class fellows to predict which kind of variation is it and presentation of the data of class fellows’ heights in graphical form (either histogram or ...
... Recording the heights of class fellows to predict which kind of variation is it and presentation of the data of class fellows’ heights in graphical form (either histogram or ...
Ch. 3 Cells Power Point
... Types of Active Transport • Endocytosis- the movement of a substance into the cell by a vesicle. A vesicle is a form of packaging that is used by cells. – Phagocytosis- cytoplasm of cell surrounds and engulfs particle--ex. ameba and white blood cell – Pinocytosis- plasma membrane "pinches in" to p ...
... Types of Active Transport • Endocytosis- the movement of a substance into the cell by a vesicle. A vesicle is a form of packaging that is used by cells. – Phagocytosis- cytoplasm of cell surrounds and engulfs particle--ex. ameba and white blood cell – Pinocytosis- plasma membrane "pinches in" to p ...
Lecture 013--Organelles 4 (Cytoskeleton)
... network of fibers extending throughout cytoplasm 3 main protein fibers ...
... network of fibers extending throughout cytoplasm 3 main protein fibers ...
Cell (biology)
... and made via messenger RNA intermediates and ribosomes. Metabolism, including taking in raw materials, building cell components, converting energy, molecules and releasing byproducts. The functioning of a cell depends upon its ability to extract and use chemical energy stored in organic molecules. T ...
... and made via messenger RNA intermediates and ribosomes. Metabolism, including taking in raw materials, building cell components, converting energy, molecules and releasing byproducts. The functioning of a cell depends upon its ability to extract and use chemical energy stored in organic molecules. T ...