Cell Structure and Function
... 5. Return to the Generalized Cell homepage and click secretory vesicle or golgi complex.. a. ...
... 5. Return to the Generalized Cell homepage and click secretory vesicle or golgi complex.. a. ...
Biology Reporting Category 1: Cell Structure and Function
... Controls what molecules are allowed in and out of the cell. Made of a double layer of phospholipid molecules that form semi-permeable membrane around cell. Help with cell division in animal cells The solution that fills the cell. Contains lots of proteins and dissolved ions that are involved in many ...
... Controls what molecules are allowed in and out of the cell. Made of a double layer of phospholipid molecules that form semi-permeable membrane around cell. Help with cell division in animal cells The solution that fills the cell. Contains lots of proteins and dissolved ions that are involved in many ...
Cheek Cell Lab - Helena High School
... 1. Make a wet mount slide and examine the onion cells on 4X (low/scanning power), using the coarse adjustment knob. Then rotate the microscope nosepiece to put the 10X objective in place. Focus clearly on 10X, using the fine adjustment knob! Go to the 40X objective and take a look-see. 2. Some cell ...
... 1. Make a wet mount slide and examine the onion cells on 4X (low/scanning power), using the coarse adjustment knob. Then rotate the microscope nosepiece to put the 10X objective in place. Focus clearly on 10X, using the fine adjustment knob! Go to the 40X objective and take a look-see. 2. Some cell ...
Name: How I`ll Show What I Know about Cells: Due Wednesday, Oct
... How I’ll Show What I Know about Cells: Due Wednesday, Oct. 6th (no late projects accepted) To show what I’ve learned about eukaryotic cell parts, I will make a cell part analogy poster. In the center of the poster, I will draw and label a plant or animal cell. I will use colorful pictures from the i ...
... How I’ll Show What I Know about Cells: Due Wednesday, Oct. 6th (no late projects accepted) To show what I’ve learned about eukaryotic cell parts, I will make a cell part analogy poster. In the center of the poster, I will draw and label a plant or animal cell. I will use colorful pictures from the i ...
Endocytosis 2 Types: 1. Phagocytosis 2. Pinocytosis
... ingestion of solid particles by the cell. The materials fuse with the lysosome and is then digested. The engulfed material is digested or degraded and then released by exocytosis. Also called “cell eating” ...
... ingestion of solid particles by the cell. The materials fuse with the lysosome and is then digested. The engulfed material is digested or degraded and then released by exocytosis. Also called “cell eating” ...
Reperfusion injury
... It has been noted that many of the effects of ischemic injury seem to occur not only during the ischemic episode itself but also when perfusion (blood flow) is reestablished to an area of tissue that has been ischemic. The re-flowed blood encounters cells with already disrupted membranes from the in ...
... It has been noted that many of the effects of ischemic injury seem to occur not only during the ischemic episode itself but also when perfusion (blood flow) is reestablished to an area of tissue that has been ischemic. The re-flowed blood encounters cells with already disrupted membranes from the in ...
Introduction
... • Recently, evidence is accumulating that the cytoskeleton may transmit mechanical signals that rearrange the nucleoli and other structures. • There are three main types of fibers in the cytoskeleton: microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments. ...
... • Recently, evidence is accumulating that the cytoskeleton may transmit mechanical signals that rearrange the nucleoli and other structures. • There are three main types of fibers in the cytoskeleton: microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments. ...
Chapter 15 - Evolution
... Ribosomes are made in the nucleolus, once they leave the nucleus where do they end up? A. cytoplasm B. rough ER C. both a & b D. neither a & b ...
... Ribosomes are made in the nucleolus, once they leave the nucleus where do they end up? A. cytoplasm B. rough ER C. both a & b D. neither a & b ...
Science Lesson Plan Biology 111/112 Unit 1 – The Cell Cell
... Move the class toward a discussion of organic molecules. During warm-up, we saw organic molecules which spontaneously arranged themselves around a molecule of dirt. These amphiphilic molecules could also form a membrane spontaneously. The membrane is made primarily of phospholipids, which have a hyd ...
... Move the class toward a discussion of organic molecules. During warm-up, we saw organic molecules which spontaneously arranged themselves around a molecule of dirt. These amphiphilic molecules could also form a membrane spontaneously. The membrane is made primarily of phospholipids, which have a hyd ...
Tour of Cell Organelles
... organelles that do this work… cell membrane lysosomes vacuoles & vesicles mitochondria ...
... organelles that do this work… cell membrane lysosomes vacuoles & vesicles mitochondria ...
A cell-cell communication code reveals the fitness of a cell to
... furthers our understanding of the developmental process of "cell competition" and may provide some insight into pathological conditions that involve imbalances in cell fitness, such as cancer. Christa Rhiner, Jesús M. López-Gay, Davide Soldini, Sergio Casas-Tinto, Francisco A. MartIn, and Luis Lomba ...
... furthers our understanding of the developmental process of "cell competition" and may provide some insight into pathological conditions that involve imbalances in cell fitness, such as cancer. Christa Rhiner, Jesús M. López-Gay, Davide Soldini, Sergio Casas-Tinto, Francisco A. MartIn, and Luis Lomba ...
Cell Full Notes
... Vacuoles • Membrane-bound sacs for storage, digestion, and waste removal • Contains water solution • Help plants maintain shape ...
... Vacuoles • Membrane-bound sacs for storage, digestion, and waste removal • Contains water solution • Help plants maintain shape ...
cell theory
... – Cells are small because a large surface-to-volume ratio allows them to easily exchange food and wastes. ...
... – Cells are small because a large surface-to-volume ratio allows them to easily exchange food and wastes. ...
Ans. - Testlabz.com
... As plasma membrane acts as the mechanical barrier, if it ruptures or breaks down, the cell can not differentiate ...
... As plasma membrane acts as the mechanical barrier, if it ruptures or breaks down, the cell can not differentiate ...
Clusterin as a novel Bcl-2 Homology 3 (BH3)
... ethanol-induced nuclear overexpression of clusterin does not protect cells, but rather leads to cell death. Clusterin (Clu) is ubiquitously expressed and implicated in diverse, yet contrasting, cellular processes such as apoptosis and anti-apoptosis1,2. Whereas Clu is known to inhibit the proapoptot ...
... ethanol-induced nuclear overexpression of clusterin does not protect cells, but rather leads to cell death. Clusterin (Clu) is ubiquitously expressed and implicated in diverse, yet contrasting, cellular processes such as apoptosis and anti-apoptosis1,2. Whereas Clu is known to inhibit the proapoptot ...
Section 9.2 * Mitosis and Cytokinesis
... material separates and the cell prepares to split into two cells • This allows the cell’s genetic material to pass into the new cells – The resulting daughter cells are genetically identical!! ...
... material separates and the cell prepares to split into two cells • This allows the cell’s genetic material to pass into the new cells – The resulting daughter cells are genetically identical!! ...
PDF
... nuclear Dorsal concentrations change continuously during interphase and that the Dorsal gradient breaks down and reforms with every mitotic division. Dorsal, they report, constantly shuttles in and out of the nuclei during interphase. Furthermore, its diffusion is partly constrained to cytoplasmic d ...
... nuclear Dorsal concentrations change continuously during interphase and that the Dorsal gradient breaks down and reforms with every mitotic division. Dorsal, they report, constantly shuttles in and out of the nuclei during interphase. Furthermore, its diffusion is partly constrained to cytoplasmic d ...
PDF
... nuclear Dorsal concentrations change continuously during interphase and that the Dorsal gradient breaks down and reforms with every mitotic division. Dorsal, they report, constantly shuttles in and out of the nuclei during interphase. Furthermore, its diffusion is partly constrained to cytoplasmic d ...
... nuclear Dorsal concentrations change continuously during interphase and that the Dorsal gradient breaks down and reforms with every mitotic division. Dorsal, they report, constantly shuttles in and out of the nuclei during interphase. Furthermore, its diffusion is partly constrained to cytoplasmic d ...
Name Date Ch 4 reading guide – Biology in Focus
... Concept 4.1 Biologists Use Microscopes and the Tools of Biochemistry to Study Cells 1. The development of electron microscopes has further opened our window on the cell and its organelles. What is considered a major disadvantage of the electron microscopes? ...
... Concept 4.1 Biologists Use Microscopes and the Tools of Biochemistry to Study Cells 1. The development of electron microscopes has further opened our window on the cell and its organelles. What is considered a major disadvantage of the electron microscopes? ...
Structures and Functions of Living Things
... 7. cytoplasm – the region between the cell membrane and the nucleus; in organisms without a nucleus, the region located inside the cell membrane. 8. nucleus – a cell structure that contains nucleic acids, the chemical instructions that direct all the cell’s activities. 9. chromatin – material in cel ...
... 7. cytoplasm – the region between the cell membrane and the nucleus; in organisms without a nucleus, the region located inside the cell membrane. 8. nucleus – a cell structure that contains nucleic acids, the chemical instructions that direct all the cell’s activities. 9. chromatin – material in cel ...
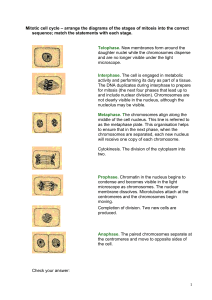
Mitotic cell cycle – arrange the diagrams of the stages of mitosis into
... activity and performing its duty as part of a tissue. The DNA duplicates during interphase to prepare for mitosis (the next four phases that lead up to and include nuclear division). Chromosomes are not clearly visible in the nucleus, although the nucleolus may be visible. Metaphase. The chromosomes ...
... activity and performing its duty as part of a tissue. The DNA duplicates during interphase to prepare for mitosis (the next four phases that lead up to and include nuclear division). Chromosomes are not clearly visible in the nucleus, although the nucleolus may be visible. Metaphase. The chromosomes ...
Cell transport ppt. - student notes
... Endocytosis A process in which cells surround and engulf substances that are TOO BIG to enter the cell. The cell uses its own membrane to engulf the substance into a vesicle and bring it in. ...
... Endocytosis A process in which cells surround and engulf substances that are TOO BIG to enter the cell. The cell uses its own membrane to engulf the substance into a vesicle and bring it in. ...