Multi-celled and Single-Celled Notes
... type of organism. Some get their food from the Sun’s energy, others get their food from eating living and nonliving materials *cocci bacteria-rod shaped, they are used in foods such as pickles and sauerkraut. They produce an acid that gives the food a distinctive flavor and helps preserve it. *bacil ...
... type of organism. Some get their food from the Sun’s energy, others get their food from eating living and nonliving materials *cocci bacteria-rod shaped, they are used in foods such as pickles and sauerkraut. They produce an acid that gives the food a distinctive flavor and helps preserve it. *bacil ...
Modeling the Phases of the Cell Cycle
... others, a root tip contains many cells at different phases of the cell cycle. This makes a root tip an excellent tissue in which to study the cell cycle. In this investigation, you will identify and describe the phases of the cell cycle in root tip cells. Problem: What do the phases of the cell cycl ...
... others, a root tip contains many cells at different phases of the cell cycle. This makes a root tip an excellent tissue in which to study the cell cycle. In this investigation, you will identify and describe the phases of the cell cycle in root tip cells. Problem: What do the phases of the cell cycl ...
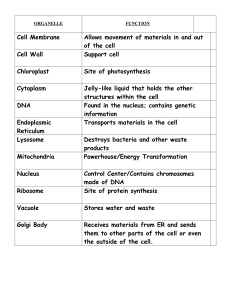
Organelle Function Matching
... Directions: Match the organelles with their functions. 1. A cell structure that controls which substances can enter and leave the cell. 2. A rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms. An organelle that helps to protect and support the cell. (not in ...
... Directions: Match the organelles with their functions. 1. A cell structure that controls which substances can enter and leave the cell. 2. A rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms. An organelle that helps to protect and support the cell. (not in ...
Slide 1
... Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine - 1974 For “the structure and functional organization of the cell” ...
... Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine - 1974 For “the structure and functional organization of the cell” ...
Ashleigh Sargent
... - Surgical removal of part of the gland or certain drugs can slow the production. - If not enough is produced, a condition called hypothyroidism occurs which is a low metabolic rates and body temperature lack of energy and weight gain. - In infancy, it can effect skeletal, muscular, and nervous syst ...
... - Surgical removal of part of the gland or certain drugs can slow the production. - If not enough is produced, a condition called hypothyroidism occurs which is a low metabolic rates and body temperature lack of energy and weight gain. - In infancy, it can effect skeletal, muscular, and nervous syst ...
Matthew Keirle Office: 25-115 Phone: 752
... • Every living organism is made of one or more cells • The smallest organisms are made of single cells while multicellular organisms are made of many cells • All cells arise from pre-existing cells ...
... • Every living organism is made of one or more cells • The smallest organisms are made of single cells while multicellular organisms are made of many cells • All cells arise from pre-existing cells ...
Topic Organizer # 3
... How are prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells alike? How are they different? ...
... How are prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells alike? How are they different? ...
Introduction to Cells
... with the study of cells in terms of structure, function and chemistry. – Cytopathology: the study of cellular disease and the use of cellular changes for the diagnosis of disease. – Cell Biology: the study of (normal) cellular anatomy, function and chemistry. ...
... with the study of cells in terms of structure, function and chemistry. – Cytopathology: the study of cellular disease and the use of cellular changes for the diagnosis of disease. – Cell Biology: the study of (normal) cellular anatomy, function and chemistry. ...
Introduction to Cells
... with the study of cells in terms of structure, function and chemistry. – Cytopathology: the study of cellular disease and the use of cellular changes for the diagnosis of disease. – Cell Biology: the study of (normal) cellular anatomy, function and chemistry. ...
... with the study of cells in terms of structure, function and chemistry. – Cytopathology: the study of cellular disease and the use of cellular changes for the diagnosis of disease. – Cell Biology: the study of (normal) cellular anatomy, function and chemistry. ...
Cells - edl.io
... • In 1674 Anton van Leeuwenhoek used a single lens microscope to observe pond water and other things. He saw a whole new world of tiny living organisms or microorganisms in which he called “animalcules”. ...
... • In 1674 Anton van Leeuwenhoek used a single lens microscope to observe pond water and other things. He saw a whole new world of tiny living organisms or microorganisms in which he called “animalcules”. ...
AJP - Cell Physiology - American Journal of Physiology
... Regulation of ERK1/2 by ouabain and Na-K-ATPase-dependent energy utilization and AMPK activation in parotid acinar cells S. P. Soltoff and L. Hedden ...
... Regulation of ERK1/2 by ouabain and Na-K-ATPase-dependent energy utilization and AMPK activation in parotid acinar cells S. P. Soltoff and L. Hedden ...
CELLS - Clever Teach
... The rigid cell wall in plant cells is made of cellulose and gives the cell membrane and contents extra support It gives plants their rigidity - their stable 3D structure. ...
... The rigid cell wall in plant cells is made of cellulose and gives the cell membrane and contents extra support It gives plants their rigidity - their stable 3D structure. ...
Name - TeacherWeb
... MCAS Review: Human Body Broad Concept: There is a relationship between the organization of cells into tissues and the organization of tissues into organs. The structures and functions of organs determine their relationships within body systems of an organism. Homeostasis allows the body to perform i ...
... MCAS Review: Human Body Broad Concept: There is a relationship between the organization of cells into tissues and the organization of tissues into organs. The structures and functions of organs determine their relationships within body systems of an organism. Homeostasis allows the body to perform i ...
Review Module Macromolecules, Cell Theory, Organelles, Cell
... 20. Plasmolysis is seen in animal cells when they take on too much water and burst. 21. Crenation is caused by the movement of water out of a cell by osmosis. 22. Isotonic solutions on either side of the membrane are equal and cells show no net change. 23. A dialysis tube is filled with water and su ...
... 20. Plasmolysis is seen in animal cells when they take on too much water and burst. 21. Crenation is caused by the movement of water out of a cell by osmosis. 22. Isotonic solutions on either side of the membrane are equal and cells show no net change. 23. A dialysis tube is filled with water and su ...
SIA Worksheet
... 2. In order to maintain homeostasis, the systems of the human body work together to keep a constant internal temperature. Which of the following statements describes how the human body responds in a cold environment? a. The nervous system moves the jawbones and causes the chattering of teeth. b. The ...
... 2. In order to maintain homeostasis, the systems of the human body work together to keep a constant internal temperature. Which of the following statements describes how the human body responds in a cold environment? a. The nervous system moves the jawbones and causes the chattering of teeth. b. The ...
6th Grade
... Name: Anne Bell Class: 6th Grade Science (Level Red) Chapter/Unit Name: Chapter 16: Cells: The Units of Life-p. 474/Unit 5: Life’s Diversity April 15-April 19, 2013 Monday ...
... Name: Anne Bell Class: 6th Grade Science (Level Red) Chapter/Unit Name: Chapter 16: Cells: The Units of Life-p. 474/Unit 5: Life’s Diversity April 15-April 19, 2013 Monday ...
Unit 3 Review Study Guide
... Background Information: There are many different types of cells in the human body. None of these cells function on their own well. These cells are part of the larger organism that is called – human. Cells work together to form tissues. There are four main types of tissues: muscle tissue, nervous tis ...
... Background Information: There are many different types of cells in the human body. None of these cells function on their own well. These cells are part of the larger organism that is called – human. Cells work together to form tissues. There are four main types of tissues: muscle tissue, nervous tis ...
MP2 QUARTERLY EXAM STUDY GUIDE
... Unicellular organisms are made up of one cell. Multicellular organisms are two or more cells and the cells are arranged in the levels of organization (tissues, organs, organ systems). ...
... Unicellular organisms are made up of one cell. Multicellular organisms are two or more cells and the cells are arranged in the levels of organization (tissues, organs, organ systems). ...
Endosymbiotic Theory
... National Institutes of Health There are many theories as to how the first life on Earth came to be, including the hydrothermal vents and Panspermia theories. While those explain how the most primitive types of cells came into existence, another theory is needed to describe how those primitive cells ...
... National Institutes of Health There are many theories as to how the first life on Earth came to be, including the hydrothermal vents and Panspermia theories. While those explain how the most primitive types of cells came into existence, another theory is needed to describe how those primitive cells ...
midterm 16 review
... Cells The basic unit of structure and function in all living things (organisms) ...
... Cells The basic unit of structure and function in all living things (organisms) ...