* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name - TeacherWeb
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
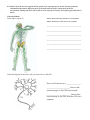
Name: _______________________________________ Block: ______ Date: __________________ MCAS Review: Human Body Broad Concept: There is a relationship between the organization of cells into tissues and the organization of tissues into organs. The structures and functions of organs determine their relationships within body systems of an organism. Homeostasis allows the body to perform its normal functions. 4.7 Recognize that the body’s systems interact to maintain homeostasis. Describe the basic function of a physiological feedback loop. Define the following terms: o Homeostasis - ______________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ o Physiological (or Negative) Feedback Loop - ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ State two ways in which the body maintains a constant internal body temperature. Mention one for lowering and one for raising body temperature. _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ Describe how the body responds when the concentration of glucose in the blood rises above normal. _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ 4.8 Recognize that communication between cells is required for coordination of body functions. The nerves communicate with electrochemical signals, hormones circulate through the blood, and some cells produce signals to communicate only with nearby cells. Complete the following table comparing the two systems in the human body that work together to coordination bodily activities. Nervous Endocrine Systems that Coordinate Bodily Functions Type of Transmission Method of Transmission Some cells produce chemical signals to communicate to nearby cells. What part of the cell recognizes these signals? _________________________________________________________ What is the function of the nervous system? _____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ What is the function of the endocrine system? ___________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ 4.4 Explain how the nervous system (brain, spinal cord, sensory neurons, motor neurons) mediates communication between different parts of the body and the body’s interactions with the environment. Identify the basic unit of the nervous system, the neuron, and explain generally how it works. Nervous System Label major organs (3). Name and state the function of the TWO major divisions of the nervous system: _______________________________________ _______________________________________ _______________________________________ _______________________________________ _______________________________________ _______________________________________ Label the diagram of the nerve cell (you don’t have to label D). Nerve cell is known as a _________________. __________________________-Nerves that send messages to the CNS from stimuli. ___________________________-Nerves that send message to the PNS from the CNS for a response. 4.2 Explain how the circulatory system (heart, arteries, veins, capillaries, red blood cells) transports nutrients and oxygen to cells and removes cell wastes. Describe how the kidneys and the liver are closely associated with the circulatory system as they perform the excretory function of removing waste from the blood. Recognize that kidneys remove nitrogenous wastes, and the liver removes many toxic compounds from blood. Functions of the circulatory system: ____________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ Complete the chart below for the three major types of blood vessels. Blood Vessel Direction of blood flow Function What Moves Blood Through Vessels artery capillary vein Label the diagram of the hear (left atrium, left ventricle, right atrium, right ventricle). Draw arrows to show direction of blood flow. The right side of the heart pumps blood to the ____________________________. This is referred to as the______________________ circuit. The left side of the heart pumps blood to the _____________________. This is referred to as the ______________________ circuit. Blood Cells Type of Blood Cell red (erythrocytes) white (leucocytes) platelets Function Made in the: Label the diagram of the excretory (urinary) system (4). The basic functioning unit of the kidney is the _______________________. What role does liver play in maintaining homeostasis in the body? _________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ 4.3 Explain how the respiratory system (nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, lungs, alveoli) provides exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Label the following parts of the respiratory system. Part Name A B C D E F G Where does gas exchange take place in lungs? _____________________________________ What 2 gases are exchanged? _____________________________________________________ 4.5 Explain how the muscular/skeletal system (skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscle, bones, cartilage, ligaments, tendons) works with other systems to support and allow for movement. Recognize that bones produce both red and white blood cells. Functions of the skeletal system: _______________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ The organs of the skeletal system are the ________________________. Where in the bones are blood cells produced? ___________________________________ What is the function of yellow marrow? _________________________________________ Complete the following table listing the three types of muscular tissue and their function. Types of Muscle Function Define: cartilage - ______________________________________________________________________________ tendon - _______________________________________________________________________________ ligament - ______________________________________________________________________________ What system signals muscles to contract? _____________________________________________________ 4.1 Explain generally how the digestive system (mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, rectum) converts macromolecules from food into smaller molecules that can be used by cells for energy and for repair and growth. Label the drawing of the digestive system with the following structures: esophagus, gall bladder, large intestine, liver, mouth, pancreas, pharynx, rectum, salivary glands, small intestine, stomach Complete the following chart telling the role of each organ in the digestive process. Organ Role in Digestion mouth esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine liver gall bladder pancreas salivary glands Complete the following table describing what each of the following organic molecules is broken down into and what parts of the digestive system are involved in this process. Organic Compound protein carbohydrate lipid Broken down into Organs involved in process