ELL Science Term 1 Exam 1 Study Guide
... Binomial nomenclature names organisms by ______________ and ______________. What is an enzyme? ...
... Binomial nomenclature names organisms by ______________ and ______________. What is an enzyme? ...
1.3 Cells from Cells
... So then what happens? Cell Division! It must produce smaller cells = more surface area. ...
... So then what happens? Cell Division! It must produce smaller cells = more surface area. ...
What are the two basic categories of cells and
... animal cells. These cells tend to be larger than the cells of bacteria, and have developed specialized packaging and transport mechanisms that may be necessary to support their larger size. Prokaryotic: These cells are simple in structure, with no recognizable organelles. The prokaryotes lack a nucl ...
... animal cells. These cells tend to be larger than the cells of bacteria, and have developed specialized packaging and transport mechanisms that may be necessary to support their larger size. Prokaryotic: These cells are simple in structure, with no recognizable organelles. The prokaryotes lack a nucl ...
DJ_Jeopardy
... This organelle functions in the collection, packaging, modification, and distribution of materials synthesized in the cell ...
... This organelle functions in the collection, packaging, modification, and distribution of materials synthesized in the cell ...
File
... 7. Storage sacs; plant cells have a single large one; animal cells have many small ones ...
... 7. Storage sacs; plant cells have a single large one; animal cells have many small ones ...
1.2 Plant and Animal Cells
... a) plant cells have one large vacuole and animal cells have many small vacuoles, if any b) plant cells have many small vacuoles, if any and animal cells have one large vacuole c) plant cells do no have vacuoles and animal cells have one large vacuole d) plant cells have many small vacuoles, if any a ...
... a) plant cells have one large vacuole and animal cells have many small vacuoles, if any b) plant cells have many small vacuoles, if any and animal cells have one large vacuole c) plant cells do no have vacuoles and animal cells have one large vacuole d) plant cells have many small vacuoles, if any a ...
Two Basic Cell Types: Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells
... • Perform the same basic functions • Surrounded by plasma membrane to control what enters and leaves the cell • “Filled” with cytoplasm • Contain ribosomes to make protein • Contain DNA to give the general instructions for the cell’s life ...
... • Perform the same basic functions • Surrounded by plasma membrane to control what enters and leaves the cell • “Filled” with cytoplasm • Contain ribosomes to make protein • Contain DNA to give the general instructions for the cell’s life ...
Powerpoint: Cell Membranes
... Analyze the results of the osmosis lab Explain how the structure of the cell membrane allows it to regulate ...
... Analyze the results of the osmosis lab Explain how the structure of the cell membrane allows it to regulate ...
PARTS OF THE CELL CELL ORGANELLES
... carbohydrates, & proteins into particles usable by rest of cell. b.) Also function to break down organelles that have outlived their usefulness. This helps prevent “junk” from cluttering up cell. ...
... carbohydrates, & proteins into particles usable by rest of cell. b.) Also function to break down organelles that have outlived their usefulness. This helps prevent “junk” from cluttering up cell. ...
Cells Review
... shape and support = cell wall 11. Destroys old cell parts = lysosomes 12. Packages materials = golgi bodies ...
... shape and support = cell wall 11. Destroys old cell parts = lysosomes 12. Packages materials = golgi bodies ...
Eukaryotic Cell Organelles
... production, processing and transport of proteins and in the production of lipids Rough ER – covered in ribosomes; packages proteins made by the ribosomes into vesicles (small sacs containing materials) that are transported to the golgi complex Smooth ER – no ribosomes; make lipids and break down tox ...
... production, processing and transport of proteins and in the production of lipids Rough ER – covered in ribosomes; packages proteins made by the ribosomes into vesicles (small sacs containing materials) that are transported to the golgi complex Smooth ER – no ribosomes; make lipids and break down tox ...
Role of mechanical tensile forces in cell fate acquisition Institute of
... cell via segregation of the endocytic protein Numb, a cell fate determinants that behaves as a tumour suppressor gene inhibiting the Notch signalling pathway. Thus, the acquisition of cell identity is controlled by the differential activation of Notch. Notch is activated by the ligand Delta present ...
... cell via segregation of the endocytic protein Numb, a cell fate determinants that behaves as a tumour suppressor gene inhibiting the Notch signalling pathway. Thus, the acquisition of cell identity is controlled by the differential activation of Notch. Notch is activated by the ligand Delta present ...
Cells!
... Objective: Upon completion of this activity, you should be able to describe the cell and identify its parts (organelles). You should be able to distinguish between plant and animal cells. PART I Go to: www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=AP11604 Click “Next” to begin the activity. Answer ...
... Objective: Upon completion of this activity, you should be able to describe the cell and identify its parts (organelles). You should be able to distinguish between plant and animal cells. PART I Go to: www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=AP11604 Click “Next” to begin the activity. Answer ...
File
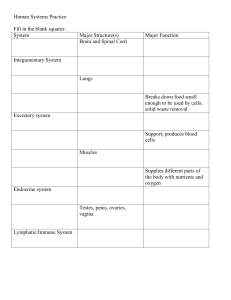
... Directions: Match the system to its primary functions and also to the organs found in that system. Write the correct letter(s) under the system name. Place the value (number found next to the letter(s)) next to the letters. The numbers will add up to a 100 when all the correct answers are put togeth ...
... Directions: Match the system to its primary functions and also to the organs found in that system. Write the correct letter(s) under the system name. Place the value (number found next to the letter(s)) next to the letters. The numbers will add up to a 100 when all the correct answers are put togeth ...
chapter 12.rtf - HCC Learning Web
... MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) If cells in the process of dividing are subjected to colchicine, a drug that interferes with the formation of the spindle apparatus, at which stage will mitosis be arrested? A) anaphase B) inter ...
... MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) If cells in the process of dividing are subjected to colchicine, a drug that interferes with the formation of the spindle apparatus, at which stage will mitosis be arrested? A) anaphase B) inter ...
Cells
... to float in the cytoplasm. • Prokaryotes usually made of only ONE CELL. • Have a cell membrane, cell wall, and an outer layer called a capsule. • Also have cilia & flagella ...
... to float in the cytoplasm. • Prokaryotes usually made of only ONE CELL. • Have a cell membrane, cell wall, and an outer layer called a capsule. • Also have cilia & flagella ...
The Basic Units of Life
... B) Plants, animals and _____________ have got a nucleus in their cells. Around the nucleus there is a _________________ membrane. ...
... B) Plants, animals and _____________ have got a nucleus in their cells. Around the nucleus there is a _________________ membrane. ...
Plant and Animal Cells Study Guide
... Match the vocabulary word to the correct definition. 1. cells ...
... Match the vocabulary word to the correct definition. 1. cells ...
Cells - BrainPOP
... a. They help cells think b. Cells could not function without them c. They require a lot of blood to operate properly d. They are located at the top of the cell 8. How are eukaryotic cells different from prokaryotic cells? a. Eukaryotic cells have nuclei; prokaryotic cells don't b. Eukaryotic cells h ...
... a. They help cells think b. Cells could not function without them c. They require a lot of blood to operate properly d. They are located at the top of the cell 8. How are eukaryotic cells different from prokaryotic cells? a. Eukaryotic cells have nuclei; prokaryotic cells don't b. Eukaryotic cells h ...
Excretory System: Practice Questions #1
... The diagram represents a microscopic view of a functional unit of a kidney. In a kidney, which blood component would not usually pass through the membranes from region A to region B? A. B. C. D. ...
... The diagram represents a microscopic view of a functional unit of a kidney. In a kidney, which blood component would not usually pass through the membranes from region A to region B? A. B. C. D. ...
Cell membrane
... Cell membrane All cells are surrounded by a membrane. Function: It separates the inside of the cell from its environment and controls what goes in and out of the cell. Look at the amoeba below: ...
... Cell membrane All cells are surrounded by a membrane. Function: It separates the inside of the cell from its environment and controls what goes in and out of the cell. Look at the amoeba below: ...