Basic unit of all living things
... • process by which a green plant turns water and carbon dioxide into food when the plant is exposed to light ...
... • process by which a green plant turns water and carbon dioxide into food when the plant is exposed to light ...
Chap 19 - Iowa State University
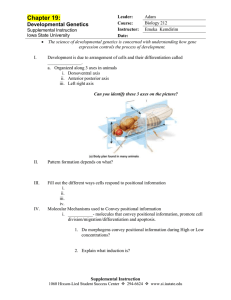
... Instructor: Emeka Kemdirim Supplemental Instruction Iowa State University Date: The science of developmental genetics is concerned with understanding how gene expression controls the process of development. ...
... Instructor: Emeka Kemdirim Supplemental Instruction Iowa State University Date: The science of developmental genetics is concerned with understanding how gene expression controls the process of development. ...
Overview of Kingdom Animalia
... form a zygote 2. Cell division: zygote divides through mitosis, forming an embryo, until a cell covered fluid filled ball is formed called a blastula (five days for humans) 3. Gastrulation: the cells on one side of the blastula move inward to form a gastrula, which is a structure made up of two laye ...
... form a zygote 2. Cell division: zygote divides through mitosis, forming an embryo, until a cell covered fluid filled ball is formed called a blastula (five days for humans) 3. Gastrulation: the cells on one side of the blastula move inward to form a gastrula, which is a structure made up of two laye ...
benchmark #1 study guide
... 10. What components make up the cell membrane? What is the function of the cell membrane? What does size of the molecule have to do with movement through the cell membrane? 11. What are the functions of the following cell organelles? a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. ...
... 10. What components make up the cell membrane? What is the function of the cell membrane? What does size of the molecule have to do with movement through the cell membrane? 11. What are the functions of the following cell organelles? a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. ...
The Cell Membrane
... a. The phospholipid bilayer is a double layer of lipids (fat). Each lipid has a phosphate molecule attached. The lipids are hydrophobic, which means that they repel water. The phosphate molecules are hydrophilic and attract water. This maintains the water inside the cell as well as sep ...
... a. The phospholipid bilayer is a double layer of lipids (fat). Each lipid has a phosphate molecule attached. The lipids are hydrophobic, which means that they repel water. The phosphate molecules are hydrophilic and attract water. This maintains the water inside the cell as well as sep ...
Cell Membrane, Photosynthesis and Respiration Name Date Word
... remove particles (in a vesicle) that are to large to fit through the cell membrane. ...
... remove particles (in a vesicle) that are to large to fit through the cell membrane. ...
Golgi apparatus
... Serves as a boundary of the cell, maintaining its integrity; protein molecules embedded in plasma membrane perform various functions. ...
... Serves as a boundary of the cell, maintaining its integrity; protein molecules embedded in plasma membrane perform various functions. ...
File
... Exist today only as bacteria Eukaryotic Cells Highly organized cells Have membrane bound nucleus and organelles Perform cellular functions Are found in animals, plants, protests, fungi Most are multi-cellular, but there are a limited number of unicellular eukaryotic organisms such as amoeb ...
... Exist today only as bacteria Eukaryotic Cells Highly organized cells Have membrane bound nucleus and organelles Perform cellular functions Are found in animals, plants, protests, fungi Most are multi-cellular, but there are a limited number of unicellular eukaryotic organisms such as amoeb ...
National 5: Multicellular Organisms Summary
... animals and have the potential to become different types of cell. Stem cells are involved in growth and repair. Meristems are the sites of production of non-specialised cells in plants and are the only sites for cell division in a plant. These cells have the potential to become any type of plant c ...
... animals and have the potential to become different types of cell. Stem cells are involved in growth and repair. Meristems are the sites of production of non-specialised cells in plants and are the only sites for cell division in a plant. These cells have the potential to become any type of plant c ...
Characteristics of Cancer Cells
... / or becomes disorganized • There is a shift in enzyme activity • Example • Reliance on glycolysis although oxygen is present ...
... / or becomes disorganized • There is a shift in enzyme activity • Example • Reliance on glycolysis although oxygen is present ...
4 A closer look at animal and plant cells KEY_2
... 1. How did scientists discover the common structure of cells? Scientists used microscope to observe many kids of cells 2. What are some of the common structures of a cell? Common cell structures include the cell membrane and cytoplasm. 3. Why is the nucleus an important part of most cells? The nucle ...
... 1. How did scientists discover the common structure of cells? Scientists used microscope to observe many kids of cells 2. What are some of the common structures of a cell? Common cell structures include the cell membrane and cytoplasm. 3. Why is the nucleus an important part of most cells? The nucle ...
S8 Text. The effects of the parameters on the model In our
... due to our mRNA-inherited noise (e.g., by setting of these components = 0 or 1)
result in some cells that execute the wrong sequence of the normal cell cycle. This is
because cell cycle events in our model, such as relicensing of origins of replication, bud
formation, and spindle assembly, ...
... due to our mRNA-inherited noise (e.g., by setting
Cell theory worksheet - science-teachers
... Although Robert Hooke had discovered ‘cells’ in 1665, he did not understand the importance of his discovery. At that time, scientists knew that organisms were made of tissues and organs but they thought that these were not living. It was believed that only a whole organism was living, and that the p ...
... Although Robert Hooke had discovered ‘cells’ in 1665, he did not understand the importance of his discovery. At that time, scientists knew that organisms were made of tissues and organs but they thought that these were not living. It was believed that only a whole organism was living, and that the p ...
Specialised Cells
... and animals consist of many cells and so are known as multicellular They contain many different types of cells. Each type of cell is designed to carry out a particular job or function. This is known as cell specialism Not all cells look the same. Some cells have a special shape and feature ...
... and animals consist of many cells and so are known as multicellular They contain many different types of cells. Each type of cell is designed to carry out a particular job or function. This is known as cell specialism Not all cells look the same. Some cells have a special shape and feature ...
Specialised Cells
... and animals consist of many cells and so are known as multicellular They contain many different types of cells. Each type of cell is designed to carry out a particular job or function. This is known as cell specialism Not all cells look the same. Some cells have a special shape and feature ...
... and animals consist of many cells and so are known as multicellular They contain many different types of cells. Each type of cell is designed to carry out a particular job or function. This is known as cell specialism Not all cells look the same. Some cells have a special shape and feature ...
Hierarchy of Life
... A cell is the smallest functional unit that can perform all of life’s tasks. A living organism may consist of a single cell or a huge number of cells. In multicellular organisms, cells are specialized and depend on other cells to maintain life. The specialization and interdependence of cells contrib ...
... A cell is the smallest functional unit that can perform all of life’s tasks. A living organism may consist of a single cell or a huge number of cells. In multicellular organisms, cells are specialized and depend on other cells to maintain life. The specialization and interdependence of cells contrib ...
The purpose of digestion is to do what? Break down large molecules
... when they are outside of the space shuttle and wearing their space suits? Because there is no air in space in which sound waves to travel. ...
... when they are outside of the space shuttle and wearing their space suits? Because there is no air in space in which sound waves to travel. ...
RESPONSE OF HUMAN CANCER CELLS TO IONIZING RADIATION
... radiotherapy efficiency. Besides, a cross-resistance of tumor cells to anti-cancer drugs and ionizing radiation may also exist. The mechanisms of such cross-resistance are poorly studied. The aim of the study was to compare the effect of X-irradiation on growth and apoptosis of cancer cells of diffe ...
... radiotherapy efficiency. Besides, a cross-resistance of tumor cells to anti-cancer drugs and ionizing radiation may also exist. The mechanisms of such cross-resistance are poorly studied. The aim of the study was to compare the effect of X-irradiation on growth and apoptosis of cancer cells of diffe ...
Access the Student Journal for Activity 2
... never seen before. When you examine them closely, you see that they are made up of cells, but not human cells. These creatures have cells with structures very different from human cells even though they complete some of the same functions as human cells. 1. Imagine the kinds of structures the Martia ...
... never seen before. When you examine them closely, you see that they are made up of cells, but not human cells. These creatures have cells with structures very different from human cells even though they complete some of the same functions as human cells. 1. Imagine the kinds of structures the Martia ...
Topic 1 and 2 vocab practice - wths
... __ Macromolecule E. This is a molecule that contains both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. They are the building blocks of protein. __ Nitrogenous ...
... __ Macromolecule E. This is a molecule that contains both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. They are the building blocks of protein. __ Nitrogenous ...
HOMEOSTASIS AND CELL TRANSPORT NOTES SOLUTIONS
... A _____________________ gradient is caused by the concentration of molecules inside the cell being ________________ from the outside of the cell or just different concentrations ______________________. ...
... A _____________________ gradient is caused by the concentration of molecules inside the cell being ________________ from the outside of the cell or just different concentrations ______________________. ...
Ch6 Cell homework
... e. Composed of 9 cylinders of microtubules ______________________ f. Sends secretory vesicles to the plasma membrane for exocytosis _____________ g. Site of chromosomes ______________________ h. Engages in autophagy ______________________ i. Site of cellular respiration/ATP production_______________ ...
... e. Composed of 9 cylinders of microtubules ______________________ f. Sends secretory vesicles to the plasma membrane for exocytosis _____________ g. Site of chromosomes ______________________ h. Engages in autophagy ______________________ i. Site of cellular respiration/ATP production_______________ ...