Unit XIV: Excretion
... salts, urea = filtrate – 180 L per day - ___________ – filtrate passes into ___________ – reabsorb ______ by osmosis, reabsorb good substances (_______ and __________) by active transport - Left over fluid is ________ – some water, salts, and urea flows into the collecting duct ...
... salts, urea = filtrate – 180 L per day - ___________ – filtrate passes into ___________ – reabsorb ______ by osmosis, reabsorb good substances (_______ and __________) by active transport - Left over fluid is ________ – some water, salts, and urea flows into the collecting duct ...
Original
... *why do plants have different characteristics –cell wise? Well compare a human to a plant. Plants make their own carbon-containing molecules directly from the environment Through photosynthesis- they take carbon dioxide from the air and convert that from carbondioxide &water into sugars. ...
... *why do plants have different characteristics –cell wise? Well compare a human to a plant. Plants make their own carbon-containing molecules directly from the environment Through photosynthesis- they take carbon dioxide from the air and convert that from carbondioxide &water into sugars. ...
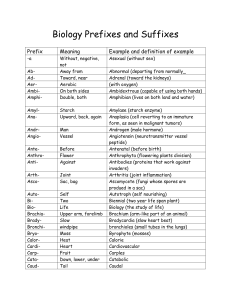
Biology Prefixes and Suffixes
... nutrients from dead or decaying matter) schizocarp (fruit that splits into several closed one-seeded portions upon maturation) ...
... nutrients from dead or decaying matter) schizocarp (fruit that splits into several closed one-seeded portions upon maturation) ...
Chapter 2-1 Vocabulary - Class Notes
... [All the stuff in the house - (Both plant and animal cells) Cytoplasm – The jellylike material that contains the organelles. [Air within the house] - (Both plant and animal cells) Nucleus –An organelle that directs and controls the activities of the cell. [Homeowner of the house] - (Both plant and a ...
... [All the stuff in the house - (Both plant and animal cells) Cytoplasm – The jellylike material that contains the organelles. [Air within the house] - (Both plant and animal cells) Nucleus –An organelle that directs and controls the activities of the cell. [Homeowner of the house] - (Both plant and a ...
The Diversity of Cells
... - Matthias Schleiden concluded that plant parts were composed of cells. - Thedor Schwann concluded that animal tissues were composed of cells. - Rudolf Virchow stated that cells could form only from other cells. - The Cell Theory was created by Schleiden, Schwann, & Virchow based off everyone’s obse ...
... - Matthias Schleiden concluded that plant parts were composed of cells. - Thedor Schwann concluded that animal tissues were composed of cells. - Rudolf Virchow stated that cells could form only from other cells. - The Cell Theory was created by Schleiden, Schwann, & Virchow based off everyone’s obse ...
Cell Structure and Function
... Cytoplasm-the region of the cell that is within the plasma membrane and that includes the fluid, the cytoskeleton, and all of the organelles except the nucleus. Control Center-area of the cell that carries DNA that codes for the cells ...
... Cytoplasm-the region of the cell that is within the plasma membrane and that includes the fluid, the cytoskeleton, and all of the organelles except the nucleus. Control Center-area of the cell that carries DNA that codes for the cells ...
Structure and Function of the Cell
... Ribosomes are the site of protein systhesis. Some ribosomes float freely in the cell and other attach themselves to the endoplasmic reticulum. 8. Vacuoles are fluid-filled sacs that store nutrients, water, and waste. 9. What is the function of the nucleus? Where DNA and RNA are made 10. Lysosomes ar ...
... Ribosomes are the site of protein systhesis. Some ribosomes float freely in the cell and other attach themselves to the endoplasmic reticulum. 8. Vacuoles are fluid-filled sacs that store nutrients, water, and waste. 9. What is the function of the nucleus? Where DNA and RNA are made 10. Lysosomes ar ...
2. atomic. Formed by atoms. The atoms that can be found in living
... Leewenhoek used a simple microscope to observe tiny unicellular organisms. The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665. He examined (under a compound microscope) very thin slices of cork and saw a multitude of tiny pores that he remarked looked like the walled compartments a monk would live in. ...
... Leewenhoek used a simple microscope to observe tiny unicellular organisms. The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665. He examined (under a compound microscope) very thin slices of cork and saw a multitude of tiny pores that he remarked looked like the walled compartments a monk would live in. ...
Microorganisms as Cells
... from its environment and incorporating them into its own fabric. At the same time, it discards waste products into its environment. A cell is thus an open system, forever changing yet generally remaining the same. Where did the first cells come from? In some way the first cell must have come from a ...
... from its environment and incorporating them into its own fabric. At the same time, it discards waste products into its environment. A cell is thus an open system, forever changing yet generally remaining the same. Where did the first cells come from? In some way the first cell must have come from a ...
Science Background Living Systems: Cells and the Five Kingdoms
... Within each kingdom, organisms are divided into smaller groups. Animals are classified as vertebrates if they have a backbone (dogs, fish, people, snakes) and invertebrates if they don’t (snails, insects, worms, crabs). Plants are classified as vascular if they suck up water through roots and pump i ...
... Within each kingdom, organisms are divided into smaller groups. Animals are classified as vertebrates if they have a backbone (dogs, fish, people, snakes) and invertebrates if they don’t (snails, insects, worms, crabs). Plants are classified as vascular if they suck up water through roots and pump i ...
Cell Biology Study Guide - Westerville City Schools
... Many are multi-cellular such as Plants and animals (among others). ...
... Many are multi-cellular such as Plants and animals (among others). ...
MICROSCOPE - Use the cards to help identify the parts of the
... of transport goes down the concentration gradient. Types includes diffusion (the movement of particles from high concentration to low concentration), osmosis (the movement of water from areas of low solute concentration to areas of high solute concentration), and facilitated diffusion (diffusion of ...
... of transport goes down the concentration gradient. Types includes diffusion (the movement of particles from high concentration to low concentration), osmosis (the movement of water from areas of low solute concentration to areas of high solute concentration), and facilitated diffusion (diffusion of ...
MSSE470S-Lesson2F
... nature of structure and function. Important levels of organization for structure and function include cells, organs, tissues, organ systems, whole organisms, and ecosystems. All organisms are composed of cells—the fundamental unit of life. Most organisms are single cells; other organisms, including ...
... nature of structure and function. Important levels of organization for structure and function include cells, organs, tissues, organ systems, whole organisms, and ecosystems. All organisms are composed of cells—the fundamental unit of life. Most organisms are single cells; other organisms, including ...
Good Cells Gone Bad
... In cancer cells: • Proteins or “worker molecules” can be missing or present in unnecessary amounts. Proteins may not be able to function normally to stop cell growth or they may make the cell grow faster. • Cells do not need signals to keep growing • Energy is made without oxygen • Growth is not reg ...
... In cancer cells: • Proteins or “worker molecules” can be missing or present in unnecessary amounts. Proteins may not be able to function normally to stop cell growth or they may make the cell grow faster. • Cells do not need signals to keep growing • Energy is made without oxygen • Growth is not reg ...
Calling All Cells
... Why Should we study cells? We should study cells because we should know what is in our bodies and how the cells work and each part. Another reason why we would study cells is to know the difference between plant cell and animal cell. Because its important to know how to identify the to cells. ...
... Why Should we study cells? We should study cells because we should know what is in our bodies and how the cells work and each part. Another reason why we would study cells is to know the difference between plant cell and animal cell. Because its important to know how to identify the to cells. ...
Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Review Questions
... d. They contain enzymes that break down lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins. 17. What are vacuoles? __________________________________________________________ 18. What is the role of the vacuole in plants? _______________________________________ 19. True or False: Both chloroplasts and mitochondria ...
... d. They contain enzymes that break down lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins. 17. What are vacuoles? __________________________________________________________ 18. What is the role of the vacuole in plants? _______________________________________ 19. True or False: Both chloroplasts and mitochondria ...
Ashley Ajayi
... separate its contents from the cytoplasm. It is perforates by pores and in continuous with the Endoplasmic Reticulum. A Nucleolus is a nonmembranous organelle, located in the nucleus, involved in the synthesis of ribosomal DNA and production of ribosomes. A nucleus has one or more nucleoli depending ...
... separate its contents from the cytoplasm. It is perforates by pores and in continuous with the Endoplasmic Reticulum. A Nucleolus is a nonmembranous organelle, located in the nucleus, involved in the synthesis of ribosomal DNA and production of ribosomes. A nucleus has one or more nucleoli depending ...
A cell is like a car - Monroe County Schools
... • A plant cell has cell walls to support it but an animal cell has a cytoskeleton to support it. • A plant cell uses photosynthesis and respiration to breath but an animal cell only uses respiration to breath • Plant cells have a chloroplast to absorb energy while an animal cell has no chloroplast • ...
... • A plant cell has cell walls to support it but an animal cell has a cytoskeleton to support it. • A plant cell uses photosynthesis and respiration to breath but an animal cell only uses respiration to breath • Plant cells have a chloroplast to absorb energy while an animal cell has no chloroplast • ...
Bellwork 11-18-14
... B the ribosomes packages proteins and sends them to their final destination. C the nucleus packages proteins and sends them to their final destination. D the golgi apparatus packages proteins and sends them to their final destination. ...
... B the ribosomes packages proteins and sends them to their final destination. C the nucleus packages proteins and sends them to their final destination. D the golgi apparatus packages proteins and sends them to their final destination. ...
Name______ -HOME Test Period______ Eukaryotic Cell Structure
... compounds D. An internal membrane system in which components of cell membrane and some proteins are constructed E. Sac-like structure that stores materials ...
... compounds D. An internal membrane system in which components of cell membrane and some proteins are constructed E. Sac-like structure that stores materials ...
Unit 3 Cells Review Name ____ Learning target 1: I can describe
... 12. Define homeostasis & describe how a membrane can help maintain it. Learning Target 4. I can analyze the similarities and differences between eukaryotic & prokaryotic cells 13. Distinguish between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell. What similarities do they have? Learning Target 5. I can a ...
... 12. Define homeostasis & describe how a membrane can help maintain it. Learning Target 4. I can analyze the similarities and differences between eukaryotic & prokaryotic cells 13. Distinguish between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell. What similarities do they have? Learning Target 5. I can a ...
March 21,200O Food and Drug Administration
... in the lungs and other organs. Selem~“is *ar%s’sem%ltrace mmeral that works to prevent oxidative cell damage,a major contributor to cellular destruction. The body needs Selenium to produce glutathione peroxidase,a critical enzyme which is necessaryfor the antioxidant protection of red blood cells an ...
... in the lungs and other organs. Selem~“is *ar%s’sem%ltrace mmeral that works to prevent oxidative cell damage,a major contributor to cellular destruction. The body needs Selenium to produce glutathione peroxidase,a critical enzyme which is necessaryfor the antioxidant protection of red blood cells an ...
THE CELL
... Takes proteins from the ER and changes them Packages them into vesicles to be released outside the cells ...
... Takes proteins from the ER and changes them Packages them into vesicles to be released outside the cells ...