Chapter 7 Exam Review Sheet
... What is the basic unit of life? Who was the first person to look at a cork cell and give it the name “cell”? What are the 3 statements made in the cell theory? What is the difference between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell? What is the function or job of the mitochondria? What is the function of t ...
... What is the basic unit of life? Who was the first person to look at a cork cell and give it the name “cell”? What are the 3 statements made in the cell theory? What is the difference between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell? What is the function or job of the mitochondria? What is the function of t ...
Eukaroytic Cells
... It is made of the polysaccharide cellulose, and can function as a carbohydrate store by varying the amount of cellulose it holds. The cell wall does not seal off a cell completely from its neighbors. There are pores within the walls called plasmodesmata. These connect two cells together by their cyt ...
... It is made of the polysaccharide cellulose, and can function as a carbohydrate store by varying the amount of cellulose it holds. The cell wall does not seal off a cell completely from its neighbors. There are pores within the walls called plasmodesmata. These connect two cells together by their cyt ...
A549/GFP Cell Line - Cell Biolabs, Inc.
... Note: For best results begin culture of cells immediately upon receipt. If this is not possible, store at -80ºC until first culture. Store subsequent cultured cells long term in liquid nitrogen. ...
... Note: For best results begin culture of cells immediately upon receipt. If this is not possible, store at -80ºC until first culture. Store subsequent cultured cells long term in liquid nitrogen. ...
Chapter 20
... 4) Several tissues are organized to form an organ (organ = group of tissues working together to perform a specific function(s)). a) Example: small intestines i) columnar epithelium – lines lumen, secretes mucous and digestive juices (enzymes) (1) villi – fingerlike projections – increase surface are ...
... 4) Several tissues are organized to form an organ (organ = group of tissues working together to perform a specific function(s)). a) Example: small intestines i) columnar epithelium – lines lumen, secretes mucous and digestive juices (enzymes) (1) villi – fingerlike projections – increase surface are ...
Chapter 12 – The Cell Cycle – Homework
... spindle fibers. What affect will this have on a cell undergoing mitosis? What will be the result? ...
... spindle fibers. What affect will this have on a cell undergoing mitosis? What will be the result? ...
L4-specialised-cells-cards
... are in our body to help us move. Muscle cells are adapted to their job as they are very flexible so when you use your muscles they can stretch without being broken. They also contain small organelles called mitochondria which can release energy from food for movement ...
... are in our body to help us move. Muscle cells are adapted to their job as they are very flexible so when you use your muscles they can stretch without being broken. They also contain small organelles called mitochondria which can release energy from food for movement ...
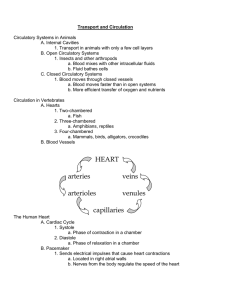
HEART arteries veins arterioles venules capillaries
... 2. Nerve signals can make arteries constrict or dilate B. Veins 1. Thinner, less elastic, less muscle than arteries 2. Lower pressure than arteries 3. Valves and gravity aid flow back to the heart C. Capillaries 1. One cell thick 2. Where transfer of gases and nutrients takes place Composition of Bl ...
... 2. Nerve signals can make arteries constrict or dilate B. Veins 1. Thinner, less elastic, less muscle than arteries 2. Lower pressure than arteries 3. Valves and gravity aid flow back to the heart C. Capillaries 1. One cell thick 2. Where transfer of gases and nutrients takes place Composition of Bl ...
Cells Chapter 1 Notes List the objectives for Section 1: Organization
... ● thought only plants had cells ...
... ● thought only plants had cells ...
ACHAEAN- One of two prokaryote domains that includes organisms
... ACHAEAN- One of two prokaryote domains that includes organisms with different plasma membranes and ribosomes than bacteria BACTERIA- One of two prokaryote domains that includes organisms with different plasma membranes and ribosomes than archaeans BIOLOGY- the study of life, living things, and the c ...
... ACHAEAN- One of two prokaryote domains that includes organisms with different plasma membranes and ribosomes than bacteria BACTERIA- One of two prokaryote domains that includes organisms with different plasma membranes and ribosomes than archaeans BIOLOGY- the study of life, living things, and the c ...
Biology 3B-1 - secondary
... If the concentration is equal the solutions are equal they are isotonic If they are not equal, the solution with the greater concentration is hypertonic and the solution with the lesser concentration is hypotonic ...
... If the concentration is equal the solutions are equal they are isotonic If they are not equal, the solution with the greater concentration is hypertonic and the solution with the lesser concentration is hypotonic ...
Cells File
... •Light microscope (which we will be using) – this uses light to illuminate the sample ...
... •Light microscope (which we will be using) – this uses light to illuminate the sample ...
Chapt 7 review worksheet answers
... separating two solutions. Assume that the water molecules can pass freely through the membrane but salt and starch molecules cannot. When equilibrium is reached, which side will contain the highest fluid level? ...
... separating two solutions. Assume that the water molecules can pass freely through the membrane but salt and starch molecules cannot. When equilibrium is reached, which side will contain the highest fluid level? ...
Cell Structure and Function
... function to rid the cell of toxic substances, in particular, hydrogen peroxide -- a common byproduct of cellular metabolism. ...
... function to rid the cell of toxic substances, in particular, hydrogen peroxide -- a common byproduct of cellular metabolism. ...
Document
... 3. Draw a red blood cell in an isotonic, hypertonic, and hypotonic solution. Draw dots to show the solute concentration and draw arrows to show which way the water would move. (Osmosis) ...
... 3. Draw a red blood cell in an isotonic, hypertonic, and hypotonic solution. Draw dots to show the solute concentration and draw arrows to show which way the water would move. (Osmosis) ...
Test 2 Study Guide
... Cotyledon- seed leaf; generally absorbs food in monocotyledons and stores food in other angiosperms Hypocotyl- provides root shoot access 3 types of tissues that form in the embryo: ▪ Epidermis- outermost layer of cells of the lead and young stems and roots ▪ Vascular tissue- any plant tissue ● Xyle ...
... Cotyledon- seed leaf; generally absorbs food in monocotyledons and stores food in other angiosperms Hypocotyl- provides root shoot access 3 types of tissues that form in the embryo: ▪ Epidermis- outermost layer of cells of the lead and young stems and roots ▪ Vascular tissue- any plant tissue ● Xyle ...
Cell Division
... Cell Growth • Organisms grow by producing more cells • Cell division occurs throughout an organisms life • Why do cells divide instead of just getting bigger? – Large cell = harder to move substances in and out – High Surface to Volume ratio ...
... Cell Growth • Organisms grow by producing more cells • Cell division occurs throughout an organisms life • Why do cells divide instead of just getting bigger? – Large cell = harder to move substances in and out – High Surface to Volume ratio ...
Cell Structure
... a. Cell Membrane: A double-layered membrane that separates the cell from its environment. It is selectively permeable meaning it can “select” the chemicals it lets in and out of the cell; it regulates the flow of traffic and provides mechanical strength to the cell. b. Cytoplasm: A semi fluid substa ...
... a. Cell Membrane: A double-layered membrane that separates the cell from its environment. It is selectively permeable meaning it can “select” the chemicals it lets in and out of the cell; it regulates the flow of traffic and provides mechanical strength to the cell. b. Cytoplasm: A semi fluid substa ...
Document
... __ 15.Chloroplasts are organelles that are found in the cells of a. animals b. mitochondria. c. plants and algae. cells. ...
... __ 15.Chloroplasts are organelles that are found in the cells of a. animals b. mitochondria. c. plants and algae. cells. ...
Beating disease with systems approaches and big data
... works on a molecular level throughout the organism, we might have the chance to cure those diseases,” says Giovanni Pauletti, Associate Professor of Biopharmaceutics & Pharmacokinetics at the University of Cincinnati, USA. The human body is a complex interconnected system. Isolated from one another, ...
... works on a molecular level throughout the organism, we might have the chance to cure those diseases,” says Giovanni Pauletti, Associate Professor of Biopharmaceutics & Pharmacokinetics at the University of Cincinnati, USA. The human body is a complex interconnected system. Isolated from one another, ...
Chapter 1: Vocabulary and Notes
... give off ____________ as a waste product. They make their ________ ____________. ...
... give off ____________ as a waste product. They make their ________ ____________. ...
ANIMAL FORM & FUNCTION
... Correlation between form & function Functions are properties that emerge from the specific shape & order of body parts Living things have the capacity to respond & adjust to environmental changes 1) over the long term by adaptation & natural selection 2) over the short term by physiologica ...
... Correlation between form & function Functions are properties that emerge from the specific shape & order of body parts Living things have the capacity to respond & adjust to environmental changes 1) over the long term by adaptation & natural selection 2) over the short term by physiologica ...
Chapter 1 Structure of Living Things
... C. 1670 – Anton Van Leeuwenhook G. Today, one angstrom microscopes D. 1860- 1890 staining cells 14.__ It is the process for making it easier to see and study cells under the microscope. 15.__ This microscope enabled scientists to see individual blood cells. 16.__ He studied slices of cork, see tiny ...
... C. 1670 – Anton Van Leeuwenhook G. Today, one angstrom microscopes D. 1860- 1890 staining cells 14.__ It is the process for making it easier to see and study cells under the microscope. 15.__ This microscope enabled scientists to see individual blood cells. 16.__ He studied slices of cork, see tiny ...
Supplementary Methods tolDC manufacture
... supplemented with human recombinant IL-4 (1000IU/ml; CellGenix) and human recombinant GM-CSF (1000IU/ml; Bayer, Seattle) to induce dendritic cell differentiation. After 3 days the culture volume was doubled by adding fresh pre-warmed CellGro DC® culture medium and replenishment of cytokines to a fin ...
... supplemented with human recombinant IL-4 (1000IU/ml; CellGenix) and human recombinant GM-CSF (1000IU/ml; Bayer, Seattle) to induce dendritic cell differentiation. After 3 days the culture volume was doubled by adding fresh pre-warmed CellGro DC® culture medium and replenishment of cytokines to a fin ...
Semester Study Guide
... Answer all the following questions for full credit. This assignment will help guide you as to what you need to know for the first semester final. If you complete these questions and study your answers, you should be very successful on the final exam! Good Luck! 1. List the six steps to the scienti ...
... Answer all the following questions for full credit. This assignment will help guide you as to what you need to know for the first semester final. If you complete these questions and study your answers, you should be very successful on the final exam! Good Luck! 1. List the six steps to the scienti ...