Sinerik Ayrapetyan “Cell Hydration Variation is a Primary
... special water channels (aqua pores) in PM, the water transports through the membrane take place much faster than predicted by simple osmotic diffusion. The transient water fluxes through PM have strong modulation effects on membrane conductive function and changing intracellular collective water dyn ...
... special water channels (aqua pores) in PM, the water transports through the membrane take place much faster than predicted by simple osmotic diffusion. The transient water fluxes through PM have strong modulation effects on membrane conductive function and changing intracellular collective water dyn ...
Dentistry college - first class Medical biology
... The shape of the cells are highly variable , the bacterial cell could be rod , cocci or spiral shape ,the different cells in multicellular organisms are flat or sequamous as in endothelium of the artery ,cuboidal as in kidney tubules or bile ducts of the liver , columnar as in mucosa of the alimenta ...
... The shape of the cells are highly variable , the bacterial cell could be rod , cocci or spiral shape ,the different cells in multicellular organisms are flat or sequamous as in endothelium of the artery ,cuboidal as in kidney tubules or bile ducts of the liver , columnar as in mucosa of the alimenta ...
Development - Cal State LA
... gastrulation + organ formation All three steps will make use of mitosis to produce new cells ...
... gastrulation + organ formation All three steps will make use of mitosis to produce new cells ...
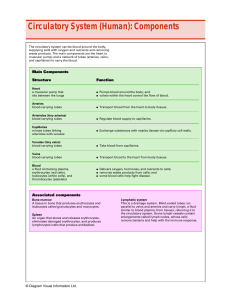
Circulatory System (Human): Components
... The circulatory system carries blood around the body, supplying cells with oxygen and nutrients and removing waste products. The main components are the heart (a muscular pump) and a network of tubes (arteries, veins, and capillaries) to carry the blood. ...
... The circulatory system carries blood around the body, supplying cells with oxygen and nutrients and removing waste products. The main components are the heart (a muscular pump) and a network of tubes (arteries, veins, and capillaries) to carry the blood. ...
Excretion - Mocks.ie
... Name this hormone and the endocrine gland from which it is secreted. (iii) Give a precise target area for this hormone. How does the hormone reach the target area? (iv) Explain the role of the hormone at its target area, when the water content of the blood is low. ...
... Name this hormone and the endocrine gland from which it is secreted. (iii) Give a precise target area for this hormone. How does the hormone reach the target area? (iv) Explain the role of the hormone at its target area, when the water content of the blood is low. ...
1. Which of the following carries nerve impulses from pressure
... B assisting in the transport of nutrients in the bloodstream C carrying the signal for a nerve impulse from one neuron to the next D facilitating diffusion of amino acids across the plasma membrane of cells 6. Degenerative nerve diseases destroy nerve cells. These diseases can lead to paralysis by i ...
... B assisting in the transport of nutrients in the bloodstream C carrying the signal for a nerve impulse from one neuron to the next D facilitating diffusion of amino acids across the plasma membrane of cells 6. Degenerative nerve diseases destroy nerve cells. These diseases can lead to paralysis by i ...
Chapter 7
... 14. What does photosynthesis accomplish? 15. What is cellular respiration? 16. What general function do the chloroplast and mitochondria have in common? How are their functions different? ...
... 14. What does photosynthesis accomplish? 15. What is cellular respiration? 16. What general function do the chloroplast and mitochondria have in common? How are their functions different? ...
Bone Formation Cell Lines
... To generate large numbers of osteocyte-like cells in order to produce sufficient quantities of osteocytes for study. To generate large numbers of cells of a homogeneous stage of osteogenic differentiation. To study osteocyte secretion of sclerostin, such as screening for sclerostin antagonists. To i ...
... To generate large numbers of osteocyte-like cells in order to produce sufficient quantities of osteocytes for study. To generate large numbers of cells of a homogeneous stage of osteogenic differentiation. To study osteocyte secretion of sclerostin, such as screening for sclerostin antagonists. To i ...
1 - OG-Science
... theory by Robert Hooke, Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann, and Rudolf Virchow. ...
... theory by Robert Hooke, Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann, and Rudolf Virchow. ...
Cells Alive- Internet Lesson
... URL: www.cellsalive.com Objective: You will look at computer models of cells; learn the functions and the descriptions of the cells and their components. ...
... URL: www.cellsalive.com Objective: You will look at computer models of cells; learn the functions and the descriptions of the cells and their components. ...
Test Review Notes
... 3 major components of cell theory All living organisms are composed of cells. The cell is the basic unit of life Cells arise from pre-existing cells. Scientists who contributed to cell theory Hans and Zacharias Janssen-1590 inventors of 1st compound microscope Robert Hooke-1665 used the word “cell” ...
... 3 major components of cell theory All living organisms are composed of cells. The cell is the basic unit of life Cells arise from pre-existing cells. Scientists who contributed to cell theory Hans and Zacharias Janssen-1590 inventors of 1st compound microscope Robert Hooke-1665 used the word “cell” ...
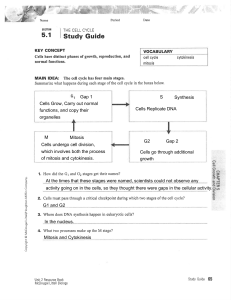
5.1 Study Guide KEY
... The rate of cell division is linked to the body's need for that type of cell. Skin cells are typically exposed to more damaging conditions and must be replaced more often than liver cells. ...
... The rate of cell division is linked to the body's need for that type of cell. Skin cells are typically exposed to more damaging conditions and must be replaced more often than liver cells. ...
Name Date ____ Period ___ #____ Parts of Prokaryotic
... RNA & protein FUNCTION: construction site for proteins CELL MEMBRANE or PLASMA MEMBRANE Made mainly of phosphate and lipids HYDROPHOBIC “tails” of phospholipids make molecules line up as a LIPID bilayer with POLAR heads facing out and NON-POLAR tails facing in Proteins attached to surface (inside or ...
... RNA & protein FUNCTION: construction site for proteins CELL MEMBRANE or PLASMA MEMBRANE Made mainly of phosphate and lipids HYDROPHOBIC “tails” of phospholipids make molecules line up as a LIPID bilayer with POLAR heads facing out and NON-POLAR tails facing in Proteins attached to surface (inside or ...
Understanding by Design Unit Plan
... 7.3.1: What makes something living vs. non-living? 7.3.1: What are the most basic needs for an organism to survive? 7.3.1: What is a cell? 7.3.1: What are the 5 building blocks of a cell? B.2.2: What are the parts of the cell and what is its purpose? 7.3.3: How does the structure of a cell affect it ...
... 7.3.1: What makes something living vs. non-living? 7.3.1: What are the most basic needs for an organism to survive? 7.3.1: What is a cell? 7.3.1: What are the 5 building blocks of a cell? B.2.2: What are the parts of the cell and what is its purpose? 7.3.3: How does the structure of a cell affect it ...
CLOZE EVALUATION QUESTIONS
... DIRECTIONS: Select the answer, from the four choices given, by circling the correct letter. ...
... DIRECTIONS: Select the answer, from the four choices given, by circling the correct letter. ...
Basic Cell Structure
... Nutrients from capillaries in underlying connective tissue Nerves pass through Easily regenerates E.g. skin, lining of gut, mucous membranes ...
... Nutrients from capillaries in underlying connective tissue Nerves pass through Easily regenerates E.g. skin, lining of gut, mucous membranes ...
Cells - Biology Junction
... 15. double layer surrounding the nucleus 17. energy molecule made inside the mitochondria 18. short hair-like structures made of microtubules that help move cells 19. a constant internal environment maintained by cells 20. made of similar cells working together to do a job such as muscle 22. long wh ...
... 15. double layer surrounding the nucleus 17. energy molecule made inside the mitochondria 18. short hair-like structures made of microtubules that help move cells 19. a constant internal environment maintained by cells 20. made of similar cells working together to do a job such as muscle 22. long wh ...
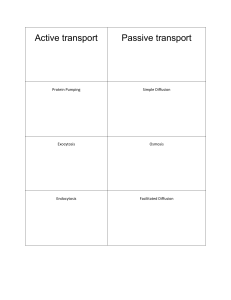
passive active transport word sort
... out of the cell From hypertonic To hypotonic This is why desalination uses so much electricity to remove salt from ...
... out of the cell From hypertonic To hypotonic This is why desalination uses so much electricity to remove salt from ...
Crucial step in cell division discovered
... genetic information during division. So understanding the details of how normal cells divide could help researchers explain how this process goes awry in cancer cells and develop Provided by Cancer Research UK drugs to control the problem. Dr Mark Petronczki, lead author based at Cancer Research UK' ...
... genetic information during division. So understanding the details of how normal cells divide could help researchers explain how this process goes awry in cancer cells and develop Provided by Cancer Research UK drugs to control the problem. Dr Mark Petronczki, lead author based at Cancer Research UK' ...
Document
... Cells are very similar to factories. To stay alive and function properly, cells have a division of labor similar to that found in factories. ...
... Cells are very similar to factories. To stay alive and function properly, cells have a division of labor similar to that found in factories. ...
Cell Wall (Plants Only) Chloroplasts (Plants Only)
... share many of the same structures. Some of the structures may look slightly different (for example, the size of the vacuole may differ), or they may not be as obvious (for example, the cell membrane in plant cells is often hidden by the cell wall). ...
... share many of the same structures. Some of the structures may look slightly different (for example, the size of the vacuole may differ), or they may not be as obvious (for example, the cell membrane in plant cells is often hidden by the cell wall). ...
The Process of Cell Division
... Name the main events of the cell cycle. Describe what happens during the four stages of mitosis. Describe the process of cytokinesis. ...
... Name the main events of the cell cycle. Describe what happens during the four stages of mitosis. Describe the process of cytokinesis. ...