Cell Organelles
... Cell Membrane Nucleus Cytoplasm Mitochondria Golgi Complex Ribosomes Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Cell Wall Chloroplast Central Vacuole Lysosome ...
... Cell Membrane Nucleus Cytoplasm Mitochondria Golgi Complex Ribosomes Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Cell Wall Chloroplast Central Vacuole Lysosome ...
Biology Semester 1 Review
... What is the difference between passive and active transport? What is diffusion? Is osmosis the same thing as diffusion? Explain. Name and describe 3 types of passive transport. What role do transport proteins play in facilitated diffusion? What role do transport proteins play in active transport? If ...
... What is the difference between passive and active transport? What is diffusion? Is osmosis the same thing as diffusion? Explain. Name and describe 3 types of passive transport. What role do transport proteins play in facilitated diffusion? What role do transport proteins play in active transport? If ...
EOC Review 2015 answer key A
... a. Nucleus- directs all of the cell’s activities and is where the genetic information is stored. b. Mitochondria – the “powerhouses” of the cell that convert energy in food molecules to energy the cell can use (respiration) to carry out its functions c. Cell membrane –the next barrier within the cel ...
... a. Nucleus- directs all of the cell’s activities and is where the genetic information is stored. b. Mitochondria – the “powerhouses” of the cell that convert energy in food molecules to energy the cell can use (respiration) to carry out its functions c. Cell membrane –the next barrier within the cel ...
Rev. 1/06 1 LECTURE 3 Cell Structure and Cell Division I. The cell
... 1. Rigid cell wall. This protects and supports the cell, and ultimately, the whole plant. a. The cell wall consists of up to 4 layers of fibrous material (cellulose) each laid down over the next, the fibers facing a different direction. 2. Large spaces are vacuoles. They may contain any number of su ...
... 1. Rigid cell wall. This protects and supports the cell, and ultimately, the whole plant. a. The cell wall consists of up to 4 layers of fibrous material (cellulose) each laid down over the next, the fibers facing a different direction. 2. Large spaces are vacuoles. They may contain any number of su ...
Cell Organelle Reading
... Even with a powerful microscope, it’s difficult to see organelles other than the nucleus. Many discoveries about organelles were made using an electron microscope. This type of microscope uses tiny particles called electrons, instead of reflected light, to form images. The mitochondria provide all o ...
... Even with a powerful microscope, it’s difficult to see organelles other than the nucleus. Many discoveries about organelles were made using an electron microscope. This type of microscope uses tiny particles called electrons, instead of reflected light, to form images. The mitochondria provide all o ...
The Discovery of Cells
... A cell’s outer wall (surface area) needs to be able to accommodate its inner activities (volume). ...
... A cell’s outer wall (surface area) needs to be able to accommodate its inner activities (volume). ...
Biology Study Guide 2nd Semester Exam
... 6. The population of small, photosynthetic organisms found near the surface of the ocean is called ______________________________. 7. All fungi _______________ their food. 8. A mushroom is a fungal _______________ _______________. 9. Fungi that absorb food from decaying organic matter are called ___ ...
... 6. The population of small, photosynthetic organisms found near the surface of the ocean is called ______________________________. 7. All fungi _______________ their food. 8. A mushroom is a fungal _______________ _______________. 9. Fungi that absorb food from decaying organic matter are called ___ ...
Name - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... of the proper procedures for completing a drawing! Label any organelles that are visible (cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, etc.). For organelles that can be seen but are too small to be identified, label them as “unknown organelles”. 5. Add a drop of iodine solution to one side of the cover slip. Usin ...
... of the proper procedures for completing a drawing! Label any organelles that are visible (cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, etc.). For organelles that can be seen but are too small to be identified, label them as “unknown organelles”. 5. Add a drop of iodine solution to one side of the cover slip. Usin ...
Cell Structure and Function 1 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v
... Feel free to pause the video whenever you need to and remember to write down any questions you have and ASK them when you get to class. All questions should be answered in your bill book. What was Robert Hooke observing when he coined the term cells? What is the cell theory? Cell Size… How big is an ...
... Feel free to pause the video whenever you need to and remember to write down any questions you have and ASK them when you get to class. All questions should be answered in your bill book. What was Robert Hooke observing when he coined the term cells? What is the cell theory? Cell Size… How big is an ...
Cell City - TeacherWeb
... Mitochondria Centrioles Vacuole Cytoplasm Written portion completed _________(15) Each structure in your cell city is compared with a cell structure and a reason why it is a good representation of that structure. (Example: The water tower is like the vacuole because it stores water.) This is to be w ...
... Mitochondria Centrioles Vacuole Cytoplasm Written portion completed _________(15) Each structure in your cell city is compared with a cell structure and a reason why it is a good representation of that structure. (Example: The water tower is like the vacuole because it stores water.) This is to be w ...
cell-organils - WordPress.com
... Similarly we will be studying about cells is this course and therefore you need to know about its parts and their functions. ...
... Similarly we will be studying about cells is this course and therefore you need to know about its parts and their functions. ...
Excretion - BellaireAPBio
... produces filtrate Reabsorption – reclaims valuable substances by active transport Secretion – extraction of toxins & excess ions from blood Excretion – removal from body ...
... produces filtrate Reabsorption – reclaims valuable substances by active transport Secretion – extraction of toxins & excess ions from blood Excretion – removal from body ...
Cell Reproduction Notes
... In addition, the cell has more trouble moving enough ____________________ and __________ across its cell membrane – Activity Surface Area to volume ratio ...
... In addition, the cell has more trouble moving enough ____________________ and __________ across its cell membrane – Activity Surface Area to volume ratio ...
Name Date____________ Block ___ Movement of Materials
... across a membrane depends on the permeability of the membrane to that substance as well as the concentration of the substance on either side of the membrane. Osmosis is the diffusion of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane. Facilitated diffusion is the process in which carrier pr ...
... across a membrane depends on the permeability of the membrane to that substance as well as the concentration of the substance on either side of the membrane. Osmosis is the diffusion of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane. Facilitated diffusion is the process in which carrier pr ...
facts - KScience
... part of the kidney tubule that builds up a low water potential in the kidney medulla ...
... part of the kidney tubule that builds up a low water potential in the kidney medulla ...
Role of tumor suppressor WOX1 in breast cancer cell migration
... TGF-induced metastasis by forming mutant-p53/Smad complex. In addition, TGF-mediated TIAF1 (TGF1-induced antiapoptoic factor 1) self-aggregation is prevented by the binding of Smad4. These studies indicate that WOX1 may regulate cell migration through coordination with molecules such as p53 and T ...
... TGF-induced metastasis by forming mutant-p53/Smad complex. In addition, TGF-mediated TIAF1 (TGF1-induced antiapoptoic factor 1) self-aggregation is prevented by the binding of Smad4. These studies indicate that WOX1 may regulate cell migration through coordination with molecules such as p53 and T ...
Osmosis in Plants
... plant like young __________ and leaves, and holds the stems _____________ so the leaves can carry on _________________ properly. If a plant loses too much water from its cells so that they become ___________, this makes the plant _________. You can see this in a pot plant which has been left for too ...
... plant like young __________ and leaves, and holds the stems _____________ so the leaves can carry on _________________ properly. If a plant loses too much water from its cells so that they become ___________, this makes the plant _________. You can see this in a pot plant which has been left for too ...
Chapter 7 Test
... • You can discuss each answer with your table partner. • Together, you will turn in one set of answers. • Discuss each answer before writing! • During the discussion, decide which concepts from the notes to include in your answer. • Remember to underline each concept. ...
... • You can discuss each answer with your table partner. • Together, you will turn in one set of answers. • Discuss each answer before writing! • During the discussion, decide which concepts from the notes to include in your answer. • Remember to underline each concept. ...
Cell Organelles - Cloudfront.net
... Cell Membrane Nucleus Cytoplasm Mitochondria Golgi Complex Ribosomes Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Cell Wall Chloroplast Central Vacuole Lysosome ...
... Cell Membrane Nucleus Cytoplasm Mitochondria Golgi Complex Ribosomes Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Cell Wall Chloroplast Central Vacuole Lysosome ...
Points of Interaction between Body Systems
... Oxygen Nutrients Minerals Enzymes: are Lipids proteins that help Carbohydrates speed up Protiens chemical Water reactions and help your body get these things. ...
... Oxygen Nutrients Minerals Enzymes: are Lipids proteins that help Carbohydrates speed up Protiens chemical Water reactions and help your body get these things. ...
Biology - Central Lyon CSD
... Introduction: In chapter 4 we learned about the outer shell or plasma membrane of a cell. We investigated how particles move in and out of a cell by osmosis, facilitated diffusion and active transport. Now we are ready to investigate the organelles (inside structures of a cell) and how each of them ...
... Introduction: In chapter 4 we learned about the outer shell or plasma membrane of a cell. We investigated how particles move in and out of a cell by osmosis, facilitated diffusion and active transport. Now we are ready to investigate the organelles (inside structures of a cell) and how each of them ...
Cell Structure Answers Worksheet
... 19. Cell differentiation is the development of different cells with specific functions in a multicellular organism, from a single cell. For example, each human began as a singlecelled zygote, but it developed into a many-celled organism with 230 different cell types such as nerve cells, muscle cell ...
... 19. Cell differentiation is the development of different cells with specific functions in a multicellular organism, from a single cell. For example, each human began as a singlecelled zygote, but it developed into a many-celled organism with 230 different cell types such as nerve cells, muscle cell ...
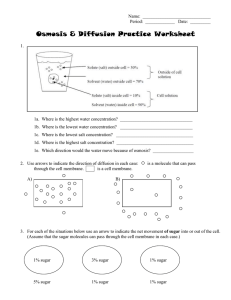
Diffusion, Osmosis, and Active Transport
... 1e. Which direction would the water move because of osmosis? __________________ 2. Use arrows to indicate the direction of diffusion in each case: through the cell membrane. is a cell membrane. A) ...
... 1e. Which direction would the water move because of osmosis? __________________ 2. Use arrows to indicate the direction of diffusion in each case: through the cell membrane. is a cell membrane. A) ...
CELL_PARTS
... • Holds contents of cell inside (like skin) • Keeps harmful substances out • Controls what enters and leaves • Water, oxygen, and nutrients are allowed to enter • Waste products are allowed to exit ...
... • Holds contents of cell inside (like skin) • Keeps harmful substances out • Controls what enters and leaves • Water, oxygen, and nutrients are allowed to enter • Waste products are allowed to exit ...