* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Points of Interaction between Body Systems
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic resistance to malaria wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Animal nutrition wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
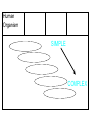
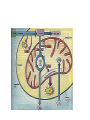
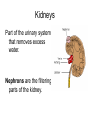
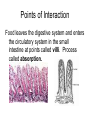
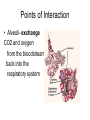
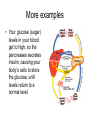
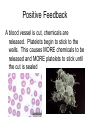
Points of Interaction between Body Systems Human Organism SIMPLE Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism COMPLEX Things your Cell needs to get daily From your digestive From your respiratory system: system: Oxygen Nutrients Minerals Enzymes: are Lipids proteins that help Carbohydrates speed up Protiens chemical Water reactions and help your body get these things. Cellular Respiration Chemical reaction that occurs in the cells once the cell gets nutrients, water, enzymes (proteins) and oxygen causing energy to be released. Chemical ReactionNutrients + oxygen -- energy + water + CO2 Then the Cell needs to get rid of… C02 using the respiratory system. Extra water, minerals, and other cellular waste though the excretory system. This process is called EXCRETION. Kidneys Part of the urinary system that removes excess water. Nephrons are the filtering parts of the kidney. Points of Interaction Food leaves the digestive system and enters the circulatory system in the small intestine at points called villi. Process called absorption. Points of Interaction • Alveoli- exchange CO2 and oxygen from the bloodstream back into the respiratory system Homeostasis • Homeostasis- Process by which the body maintains a stable internal environment How do you return to homeostasis? Negative Feedback • when a change in the normal state occurs a negative feedback mechanism causes the body to return to the normal state. Most common way for the body to return to homeostasis. Examples: • You get overheated, so your body starts to sweat, and you cool back off Negative Feedback • Blood pressure gets too high, so your heart beats slower, and blood pressure returns to normal. More examples • Your glucose (sugar) levels in your blood get to high, so the pancreases secretes insulin, causing your body’s cells to store the glucose, until levels return to a normal level. Positive Feedback Positive Feedback- when a change in the normal state occurs the positive feedback mechanism causes an even greater change. -rare in normal healthy bodies. . Positive Feedback A blood vessel is cut, chemicals are released. Platelets begin to stick to the walls. This causes MORE chemicals to be released and MORE platelets to stick until the cut is sealed Positive Feedback The uterus starts contacting causing the baby to enter the birth canal. When the brain notices this change it causes the uterus to contract MORE until the baby is pushed out.