Linköping University Post Print Histone Variants and Their Post-Translational
... from either purified nuclei or intact cells. Direct acid extraction of whole adipocytes was more efficient, yielding about 100 mg of protein with histone content of 60% –70% from 10 mL of fat cells. Differential proteolysis of the protein extracts by trypsin or ArgC-protease followed by nanoLC/MS/MS ...
... from either purified nuclei or intact cells. Direct acid extraction of whole adipocytes was more efficient, yielding about 100 mg of protein with histone content of 60% –70% from 10 mL of fat cells. Differential proteolysis of the protein extracts by trypsin or ArgC-protease followed by nanoLC/MS/MS ...
Biochemistry of Fruits and Vegetables
... or with machinery. This ruptures cells, increases respiration, causes ...
... or with machinery. This ruptures cells, increases respiration, causes ...
Role of CD26-adenosine deaminase interaction in T cell
... Glu206, Tyr547 and His750. The highly conserved Glu205Glu206 motif interacts with the free amino terminus of the P2-residue, thus determining the dipeptidyl «amino»peptidase activity of the enzyme, and the point mutations Glu205Lys and/or Glu206Leu abolish enzyme activity(13,22). The Tyr547, which m ...
... Glu206, Tyr547 and His750. The highly conserved Glu205Glu206 motif interacts with the free amino terminus of the P2-residue, thus determining the dipeptidyl «amino»peptidase activity of the enzyme, and the point mutations Glu205Lys and/or Glu206Leu abolish enzyme activity(13,22). The Tyr547, which m ...
Isolated Osteoclasts Resorb the Organic and Inorganic Components
... electron microscopy, these cells were seen to have the abundant mitochondria and the extensive membrane ruffling characteristic of osteoclasts (Fig. 2). Binding of osteoclast-specific antibody confirmed that the cells were osteoclasts (Fig. 3). Isolated osteoclasts, incubated with 45Ca o r L-[5-aH]p ...
... electron microscopy, these cells were seen to have the abundant mitochondria and the extensive membrane ruffling characteristic of osteoclasts (Fig. 2). Binding of osteoclast-specific antibody confirmed that the cells were osteoclasts (Fig. 3). Isolated osteoclasts, incubated with 45Ca o r L-[5-aH]p ...
Basic Amino Acid Inhibition of Cell Division and
... ornithine as sole nitrogen source; growth on proline was normal. The cells were shown to be devoid of ornithine transaminase activity using the method of Jenkins & Tsai (1970). Strain ~ 5 is8a diploid organism defective in the arginine catabolic enzyme arginase (Whitney & Magasanik, 1973). Culture c ...
... ornithine as sole nitrogen source; growth on proline was normal. The cells were shown to be devoid of ornithine transaminase activity using the method of Jenkins & Tsai (1970). Strain ~ 5 is8a diploid organism defective in the arginine catabolic enzyme arginase (Whitney & Magasanik, 1973). Culture c ...
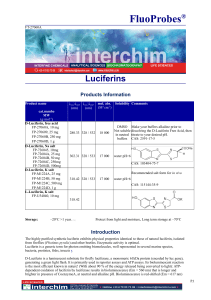
FluoProbes Luciferin substrates
... *Adjust to pH 7.8 Protect from light, may store at –70º C Apply Firefly Luciferase immediately before measurement starts All liquids that used for in vivo tests and experiments, we recommended make a sterile filtration, please filtrate through 0.25 µm filter. Other protocol may found in the literatu ...
... *Adjust to pH 7.8 Protect from light, may store at –70º C Apply Firefly Luciferase immediately before measurement starts All liquids that used for in vivo tests and experiments, we recommended make a sterile filtration, please filtrate through 0.25 µm filter. Other protocol may found in the literatu ...
Chapter 17. Cytoskeleton Chapter 17. Cytoskeleton Chapter 17
... Chapter 17. Cytoskeleton • Cells are not “bags of enzymes”, but rather organized in three dimensions. • This organization is carried out by the cytoskeleton, the “bones and muscles” (and more) of cells. • Cells are thousands of times larger than a typical molecule. Therefore the cytoskeleton must lo ...
... Chapter 17. Cytoskeleton • Cells are not “bags of enzymes”, but rather organized in three dimensions. • This organization is carried out by the cytoskeleton, the “bones and muscles” (and more) of cells. • Cells are thousands of times larger than a typical molecule. Therefore the cytoskeleton must lo ...
Evolution and Diversity of Plant Cell Walls: From Algae to Flowering
... All photosynthetic multicellular Eukaryotes, including land plants and algae, have cells that are surrounded by a dynamic, complex, carbohydrate-rich cell wall. The cell wall exerts considerable biological and biomechanical control over individual cells and organisms, thus playing a key role in thei ...
... All photosynthetic multicellular Eukaryotes, including land plants and algae, have cells that are surrounded by a dynamic, complex, carbohydrate-rich cell wall. The cell wall exerts considerable biological and biomechanical control over individual cells and organisms, thus playing a key role in thei ...
Isolation, engineering, and characterization of intracellular
... development of the disease is the propensity of an N-terminal proteolytic htt fragment containing the glutamine-expanded region to misfold and adopt a conformation which is prone to aggregation. Intracellular antibodies (intrabodies) against htt have been shown to reduce htt aggregation by binding t ...
... development of the disease is the propensity of an N-terminal proteolytic htt fragment containing the glutamine-expanded region to misfold and adopt a conformation which is prone to aggregation. Intracellular antibodies (intrabodies) against htt have been shown to reduce htt aggregation by binding t ...
Cellular function and pathological role of ATP13A2 and related P
... with sybII whereas its N-terminal membrane-associated region is an inducible amphipathic α-helix that obtains its structure only after contact with the membrane (Auluck et al., 2010; Bendor et al., 2013). The amphipathic helix does not enter the membrane bilayer, but aligns itself parallel to the bi ...
... with sybII whereas its N-terminal membrane-associated region is an inducible amphipathic α-helix that obtains its structure only after contact with the membrane (Auluck et al., 2010; Bendor et al., 2013). The amphipathic helix does not enter the membrane bilayer, but aligns itself parallel to the bi ...
Hepatocyte Growth Factor Induces Wnt
... affect of Met activation in response to HGF on the Wnt pathway components with emphasis on membrane-associated -catenin in hepatocytes. HGF/scatter factor, a known mitogen, motogen, and morphogen for liver and other tissues, signals through membrane-associated Met, a tyrosine kinase receptor (18, 2 ...
... affect of Met activation in response to HGF on the Wnt pathway components with emphasis on membrane-associated -catenin in hepatocytes. HGF/scatter factor, a known mitogen, motogen, and morphogen for liver and other tissues, signals through membrane-associated Met, a tyrosine kinase receptor (18, 2 ...
Evolution and Diversity of Plant Cell Walls: From Algae to Flowering
... All photosynthetic multicellular Eukaryotes, including land plants and algae, have cells that are surrounded by a dynamic, complex, carbohydrate-rich cell wall. The cell wall exerts considerable biological and biomechanical control over individual cells and organisms, thus playing a key role in thei ...
... All photosynthetic multicellular Eukaryotes, including land plants and algae, have cells that are surrounded by a dynamic, complex, carbohydrate-rich cell wall. The cell wall exerts considerable biological and biomechanical control over individual cells and organisms, thus playing a key role in thei ...
Assessing the effect of different shapes of glyco
... transmission electron microscopy (TEM).10 Moreover, they are less toxic compared to quantum dots. Penadés and co-workers used AuNPs to decorate more than one sugar to target HIV, bacteria, modulation of immune responses, and CPIs.11 Similarly, enormous effort has been expended by the group of Lin, W ...
... transmission electron microscopy (TEM).10 Moreover, they are less toxic compared to quantum dots. Penadés and co-workers used AuNPs to decorate more than one sugar to target HIV, bacteria, modulation of immune responses, and CPIs.11 Similarly, enormous effort has been expended by the group of Lin, W ...
3.1 How does the body heal?
... process merging with the next phase. In fact, one wound may be in more than one phase at one time. ...
... process merging with the next phase. In fact, one wound may be in more than one phase at one time. ...
Assessing the effect of different shapes of glyco
... transmission electron microscopy (TEM).10 Moreover, they are less toxic compared to quantum dots. Penadés and co-workers used AuNPs to decorate more than one sugar to target HIV, bacteria, modulation of immune responses, and CPIs.11 Similarly, enormous effort has been expended by the group of Lin, W ...
... transmission electron microscopy (TEM).10 Moreover, they are less toxic compared to quantum dots. Penadés and co-workers used AuNPs to decorate more than one sugar to target HIV, bacteria, modulation of immune responses, and CPIs.11 Similarly, enormous effort has been expended by the group of Lin, W ...
Effects of Lignification, Cellulose Crystallinity and Enzyme
... Phenoli c acids may limit cell wall carbohydrate degradation by s t eric hindrance of the fihrolytic e n zyme, which could affect both rate and exten t of degradation, and by their potentially toxic effects on microbes. Crystalline cellulose, occurring in secondary cell walls, may be degraded at a s ...
... Phenoli c acids may limit cell wall carbohydrate degradation by s t eric hindrance of the fihrolytic e n zyme, which could affect both rate and exten t of degradation, and by their potentially toxic effects on microbes. Crystalline cellulose, occurring in secondary cell walls, may be degraded at a s ...
Redox States of Plastids and Mitochondria
... to specifically alter the redox state of chloroplasts or mitochondria and then determined their impact on PD-mediated intercellular transport. Paraquat (also called methyl viologen dichloride) is a herbicide that primarily affects plants by acting as a terminal oxidant for PSI and by direct oxidatio ...
... to specifically alter the redox state of chloroplasts or mitochondria and then determined their impact on PD-mediated intercellular transport. Paraquat (also called methyl viologen dichloride) is a herbicide that primarily affects plants by acting as a terminal oxidant for PSI and by direct oxidatio ...
infected nodule cells
... the root primordia following infection threads and are released into plant cells in an endocytic-like process (Catalano et al., 2006). Within these cells, rhizobia will differentiate into bacteroids surrounded by the plasmalemma-derived symbiosome membrane, and are then able to convert, fix, N2 into ...
... the root primordia following infection threads and are released into plant cells in an endocytic-like process (Catalano et al., 2006). Within these cells, rhizobia will differentiate into bacteroids surrounded by the plasmalemma-derived symbiosome membrane, and are then able to convert, fix, N2 into ...
Changes in DNA and microtubules during loss and re
... microtubular cytoskeleton, which is markedly sensitive to desiccation stress (Sargent et al., 1981). Microtubules (MTs) are elongated tubular structures, made of a and b-tubulin, which in plant cells play an important part in cell elongation, determination of the division site, chromosome separation ...
... microtubular cytoskeleton, which is markedly sensitive to desiccation stress (Sargent et al., 1981). Microtubules (MTs) are elongated tubular structures, made of a and b-tubulin, which in plant cells play an important part in cell elongation, determination of the division site, chromosome separation ...
DORSAL-VENTRAL PATTERNING AND NEURAL INDUCTION IN
... twisted gastrulation (dTsg, a BMP-binding protein that functions as a cofactor of ...
... twisted gastrulation (dTsg, a BMP-binding protein that functions as a cofactor of ...
A Phosphorylation State-specific Antibody Recognizes Hsp27, a
... PKD,1 originally cloned and termed PKC! and identified as a PKC (protein kinase C) family member, comprises a family of three closely related isoforms, PKD1, PKD2, and PKD3/PKC". Based on sequence similarities, PKDs are now grouped into the CAMK (calcium and calmodulin-dependent kinases) family of k ...
... PKD,1 originally cloned and termed PKC! and identified as a PKC (protein kinase C) family member, comprises a family of three closely related isoforms, PKD1, PKD2, and PKD3/PKC". Based on sequence similarities, PKDs are now grouped into the CAMK (calcium and calmodulin-dependent kinases) family of k ...
The Amino-terminal Domain of the Golgi Protein Giantin Interacts
... restriction site. We cloned this fragment in pcDNA3.1(!), BamHIEcoRI. We then inserted the myc tag sequence between KpnI and BamHI to obtain pGL142. To express Gtn1967–2541 we made pGL141. We used Pfu turbo DNA polymerase to amplify a "1.7-kb fragment from pGCP364/pSG5 using primers GL37, 5#-CCGAGCT ...
... restriction site. We cloned this fragment in pcDNA3.1(!), BamHIEcoRI. We then inserted the myc tag sequence between KpnI and BamHI to obtain pGL142. To express Gtn1967–2541 we made pGL141. We used Pfu turbo DNA polymerase to amplify a "1.7-kb fragment from pGCP364/pSG5 using primers GL37, 5#-CCGAGCT ...
Distinct High-Performance Liquid
... absence of EGF; and 0-TGFs, which do not bind to EGF recep tors and must act in synergy with either EGF or a-TGFs to promote anchorage-independent growth (1, 3, 20). Like EGF, aTGFs will catalyze phosphorylation of tyrosine moieties in the EGF receptor (17, 28). TGF activity has been identified in t ...
... absence of EGF; and 0-TGFs, which do not bind to EGF recep tors and must act in synergy with either EGF or a-TGFs to promote anchorage-independent growth (1, 3, 20). Like EGF, aTGFs will catalyze phosphorylation of tyrosine moieties in the EGF receptor (17, 28). TGF activity has been identified in t ...