Growth Control: A Saga of Cell Walls, ROS, and
... pollen tube is induced by ROS application and is required for ROS-induced bursting. It is intriguing in this context that rbohdeficient mutant pollen tubes (see below; Boisson-Dernier et al., 2013; Lassig et al., 2014) and root hairs (Duan et al., 2010) with low internal levels of ROS also display lo ...
... pollen tube is induced by ROS application and is required for ROS-induced bursting. It is intriguing in this context that rbohdeficient mutant pollen tubes (see below; Boisson-Dernier et al., 2013; Lassig et al., 2014) and root hairs (Duan et al., 2010) with low internal levels of ROS also display lo ...
Postmortem Diagnosis of Anaphylaxis
... principal lesions were found in the nervous system. In the first group, which includes prominent respiratory findings, the mechanism of death might have been a local reaction rather than a systemic shock. The group defined as anaphylaxis showed no specific anatomical lesions, and five of six individ ...
... principal lesions were found in the nervous system. In the first group, which includes prominent respiratory findings, the mechanism of death might have been a local reaction rather than a systemic shock. The group defined as anaphylaxis showed no specific anatomical lesions, and five of six individ ...
Effect of n-butanol and cold pretreatment on the cytoskeleton and
... vacuole is fragmented by cytoplasmic strands, creating the so-called star-like structure (reviewed by Touraev et al. 1997). This balanced distribution of cytoplasmic elements supports the symmetric division of the microspore, which is generally considered as a marker of embryogenic induction (Sorian ...
... vacuole is fragmented by cytoplasmic strands, creating the so-called star-like structure (reviewed by Touraev et al. 1997). This balanced distribution of cytoplasmic elements supports the symmetric division of the microspore, which is generally considered as a marker of embryogenic induction (Sorian ...
ECM and Drusen
... matrikines derived from collagen I, collagen IV, fibronectin, laminins, elastin, nidogen, and thrombospondin-1 and − 2 that exhibit chemotactic activity for inflammatory cells have been found in the sub-RPE deposits (Adair-Kirk and Senior 2008). There is evidence that MMPs can degrade these proteins ...
... matrikines derived from collagen I, collagen IV, fibronectin, laminins, elastin, nidogen, and thrombospondin-1 and − 2 that exhibit chemotactic activity for inflammatory cells have been found in the sub-RPE deposits (Adair-Kirk and Senior 2008). There is evidence that MMPs can degrade these proteins ...
Genetic Block of Outer Plaque Morphogenesis at the Second Meiotic
... non-sister spindle pole bodies entirely lacking outer plaque at the second meiotic division (Davidow et al., 1980). These phenotypes are similar to those of the hfdl-1 mutant. However, no prospore wall membrane was detected in AP-1 near the pole lacking the outer plaque (Davidow et al., 1980), while ...
... non-sister spindle pole bodies entirely lacking outer plaque at the second meiotic division (Davidow et al., 1980). These phenotypes are similar to those of the hfdl-1 mutant. However, no prospore wall membrane was detected in AP-1 near the pole lacking the outer plaque (Davidow et al., 1980), while ...
The Role of the Folate Coenzymes in Cellular Division A Review
... their DNA content (30, 67, 75, 92). Similarly, many authors have shown in viruses (53), tissue culture cells (14, 36, 70), bacteria (67, 92), yeast cells (92), and tissues of rats (30) or mice (75) treated with folie acid antagonists that the inhibi tion of nucleic acid synthesis is manifested by a ...
... their DNA content (30, 67, 75, 92). Similarly, many authors have shown in viruses (53), tissue culture cells (14, 36, 70), bacteria (67, 92), yeast cells (92), and tissues of rats (30) or mice (75) treated with folie acid antagonists that the inhibi tion of nucleic acid synthesis is manifested by a ...
MaterialsMetalsAlloys
... • Plastics are now used to __________ a variety of _________ materials, e.g. wood, metal and paper • Most plastics are (relatively) ________ to produce. This is one reason they are used to make _________ items, e.g. cutlery and cups. ...
... • Plastics are now used to __________ a variety of _________ materials, e.g. wood, metal and paper • Most plastics are (relatively) ________ to produce. This is one reason they are used to make _________ items, e.g. cutlery and cups. ...
Tetherin Inhibits HIV-1 Release by Directly Tethering Virions to Cells
... that are discontinuous with host cell membranes (Neil et al., 2006, 2007). While particles accumulate both in endosomes and at the plasma membrane, endosomal accumulation is the result of internalization of virions that were initially trapped at the cell surface and is not required for their retenti ...
... that are discontinuous with host cell membranes (Neil et al., 2006, 2007). While particles accumulate both in endosomes and at the plasma membrane, endosomal accumulation is the result of internalization of virions that were initially trapped at the cell surface and is not required for their retenti ...
I SEMESTER CYTOLOGY AND GENETICS
... Introduction to molecular biology: Molecular basis of life, Experimental Proof for DNA and RNA as genetic material. Unit II 11 hrs Nucleic Acids and Structure of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic gene: Structure and functions of DNA, Watson and Crick model of DNA, forms for DNA (A,B, C, D and Z DNA), physi ...
... Introduction to molecular biology: Molecular basis of life, Experimental Proof for DNA and RNA as genetic material. Unit II 11 hrs Nucleic Acids and Structure of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic gene: Structure and functions of DNA, Watson and Crick model of DNA, forms for DNA (A,B, C, D and Z DNA), physi ...
The Effect of Catalase on Recovery of Heat-injured
... were counted after 24 h incubation at 37 "C. Despite careful standardization of growth, harvesting and heating conditions, variations in survival curves were observed between replicate experiments, especially when these were done many months apart. The reason for this is not known but it may have be ...
... were counted after 24 h incubation at 37 "C. Despite careful standardization of growth, harvesting and heating conditions, variations in survival curves were observed between replicate experiments, especially when these were done many months apart. The reason for this is not known but it may have be ...
Breakdown of Tolerance to a Neo
... APC activity of B cells transgenically expressing HEL Abs When expressing specific Ab on their surface, B cells become exceedingly efficient APCs for the corresponding Ag (18, 19). Therefore, we hypothesized that the breakdown of tolerance in Dbl-Tg mice is due to the APC activity of B cells of thes ...
... APC activity of B cells transgenically expressing HEL Abs When expressing specific Ab on their surface, B cells become exceedingly efficient APCs for the corresponding Ag (18, 19). Therefore, we hypothesized that the breakdown of tolerance in Dbl-Tg mice is due to the APC activity of B cells of thes ...
as a PDF
... ent of results in cellular systems must take account of the relative imp.ermeability of the cell membrane to the highly charged (2.-5)A molecule, as well as its susceptibility to degradation by hydrolysis of the internucleotide linkages by phosphodiesterase(s), and of the terminal 5'-triphosph- ...
... ent of results in cellular systems must take account of the relative imp.ermeability of the cell membrane to the highly charged (2.-5)A molecule, as well as its susceptibility to degradation by hydrolysis of the internucleotide linkages by phosphodiesterase(s), and of the terminal 5'-triphosph- ...
An Equatorial Contractile Mechanism Drives Cell Elongation but not
... Sars International Centre for Marine Molecular Biology, University of Bergen, Bergen, Norway ...
... Sars International Centre for Marine Molecular Biology, University of Bergen, Bergen, Norway ...
plant cell biology in the new millennium: new tools and new
... Confocal microscopy—Confocal microscopy is proving to be one of the most exciting advances in optical microscopy of the last century. Although conventional wide-field epifluorescence microscopy has been a powerful tool for locating specific molecular components of the cell, it suffers from the probl ...
... Confocal microscopy—Confocal microscopy is proving to be one of the most exciting advances in optical microscopy of the last century. Although conventional wide-field epifluorescence microscopy has been a powerful tool for locating specific molecular components of the cell, it suffers from the probl ...
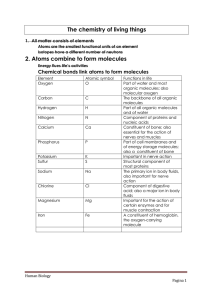
The chemistry of living things 2. Atoms combine to form molecules
... An important property of water is that it can absorb and hold a large amount of heat energy with only a modest increase in temperature. The ability of water to absorb and hold heat helps prevent rapid changes in body temperature when changes occur in metabolism or the environment. One way to lose he ...
... An important property of water is that it can absorb and hold a large amount of heat energy with only a modest increase in temperature. The ability of water to absorb and hold heat helps prevent rapid changes in body temperature when changes occur in metabolism or the environment. One way to lose he ...
Mediation of Clathrin-Dependent Trafficking during
... and division of the GMC facilitates the microscopy-based identification of nonlethal Arabidopsis mutants that disrupt cytokinesis, including cytokinesis defective1 (cyd1; Yang et al., 1999), stomatal cytokinesis defective1 (scd1; Falbel et al., 2003), and scd2 (see below). In the temperature-sensitiv ...
... and division of the GMC facilitates the microscopy-based identification of nonlethal Arabidopsis mutants that disrupt cytokinesis, including cytokinesis defective1 (cyd1; Yang et al., 1999), stomatal cytokinesis defective1 (scd1; Falbel et al., 2003), and scd2 (see below). In the temperature-sensitiv ...
Mark scheme
... All Examiners are instructed that alternative correct answers and unexpected approaches in candidates’ scripts must be given marks that fairly reflect the relevant knowledge and skills ...
... All Examiners are instructed that alternative correct answers and unexpected approaches in candidates’ scripts must be given marks that fairly reflect the relevant knowledge and skills ...
Dual mode of paraxial mesoderm formation during chick gastrulation
... streak mostly gave rise to cells in medial somites from the anterior level of the somitic region to the tail bud (SI Table 1; Fig. 1 e, g, and j). In contrast, grafts of more posterior regions of the primitive streak (70–80% level) essentially produced descendants in the lateral part of the somites ...
... streak mostly gave rise to cells in medial somites from the anterior level of the somitic region to the tail bud (SI Table 1; Fig. 1 e, g, and j). In contrast, grafts of more posterior regions of the primitive streak (70–80% level) essentially produced descendants in the lateral part of the somites ...
Inhibition of Protein Synthesis by Vaccinia Virus. II. Studies on the
... is not synthesized in substantial amounts under conditions where inhibition of protein synthesis may be observed. The inhibition of protein synthesis by dsRNA has been shown to be mediated by phosphorylation of initiation factor IF-3 (eIF-2) (Kaempfer & Kaufman, I973). We have examined the phosphory ...
... is not synthesized in substantial amounts under conditions where inhibition of protein synthesis may be observed. The inhibition of protein synthesis by dsRNA has been shown to be mediated by phosphorylation of initiation factor IF-3 (eIF-2) (Kaempfer & Kaufman, I973). We have examined the phosphory ...
Microtubule
... switch between two states. (Figure 2A) The switch from growth to shrinkage is called a catastrophe, and the switch from shrinkage to growth is called a rescue. Dynamic instability is due to the structural differences between the growing and the shrinking ends. If the nucleotide hydrolysis proceeds m ...
... switch between two states. (Figure 2A) The switch from growth to shrinkage is called a catastrophe, and the switch from shrinkage to growth is called a rescue. Dynamic instability is due to the structural differences between the growing and the shrinking ends. If the nucleotide hydrolysis proceeds m ...
Glucose-transport-def icient mutants of
... wild-type cells; open symbols, YGS-B22 cells; circles, D-glucose; triangles, D-fructose; squares, 2DG. Downloaded from www.microbiologyresearch.org by IP: 88.99.165.207 On: Thu, 03 Aug 2017 07:29:58 ...
... wild-type cells; open symbols, YGS-B22 cells; circles, D-glucose; triangles, D-fructose; squares, 2DG. Downloaded from www.microbiologyresearch.org by IP: 88.99.165.207 On: Thu, 03 Aug 2017 07:29:58 ...
Differential role played by the MEK/ERK/EGR
... (green fluorescent protein) chimaera [33] and CPV strain BR (Brighton Red) were propagated into Vero cells and were highly purified by sucrose gradient sedimentation as described in [34]. There are two infective forms of VV/CPV, the IMV (intracellular mature virus) and the EEV (extracellular envelop ...
... (green fluorescent protein) chimaera [33] and CPV strain BR (Brighton Red) were propagated into Vero cells and were highly purified by sucrose gradient sedimentation as described in [34]. There are two infective forms of VV/CPV, the IMV (intracellular mature virus) and the EEV (extracellular envelop ...
ISG15, a ubiquitin-like interferon
... (pegylated IFN-a/ribavirin). This study assessed the effect of ISG15 on HCV production in vitro. The levels of ISG15 and of its conjugation to target proteins (ISGylation) were increased by plasmid transfection, but ISGylation was inhibited by small interfering RNA directed against the E1 activating ...
... (pegylated IFN-a/ribavirin). This study assessed the effect of ISG15 on HCV production in vitro. The levels of ISG15 and of its conjugation to target proteins (ISGylation) were increased by plasmid transfection, but ISGylation was inhibited by small interfering RNA directed against the E1 activating ...
Involvement of retinoic acid-inducible gene- BEAS-2B cells
... Part of this study was supported by the Fund for Medical Research of the Aomori Bank (Aomori, Japan). ...
... Part of this study was supported by the Fund for Medical Research of the Aomori Bank (Aomori, Japan). ...