Involved in cell reproduction
... 20. Which of these supports the cell theory as it is stated today? F New cells are produced by division of existing cells. G All organisms are composed of more than one cell. H Cells must contain a nucleus. J Not all cells are alive 21. A student observes that a type of eubacteria contains chlorophy ...
... 20. Which of these supports the cell theory as it is stated today? F New cells are produced by division of existing cells. G All organisms are composed of more than one cell. H Cells must contain a nucleus. J Not all cells are alive 21. A student observes that a type of eubacteria contains chlorophy ...
Name_________________________________ Thompson 211
... 23. In the lymph there are T and B cells floating around and each is designed to kill a different invader. 24. Packed with dividing T cells the glands begin to swell. 25. She now has to cough to clear things out because the cilia cells have been damaged. 26. The body now starts to manufacture minute ...
... 23. In the lymph there are T and B cells floating around and each is designed to kill a different invader. 24. Packed with dividing T cells the glands begin to swell. 25. She now has to cough to clear things out because the cilia cells have been damaged. 26. The body now starts to manufacture minute ...
Cytotoxicity tests MEDETOX EN
... mechanism that occurs primarily at the cell surface. This bioreduction is largely dependent on the glycolytic production of NAD(P)H in viable cells. Therefore, the amount of formazan dye formed directly correlates to the number of metabolically active cells in the culture. Cells, grown in a 96-well ...
... mechanism that occurs primarily at the cell surface. This bioreduction is largely dependent on the glycolytic production of NAD(P)H in viable cells. Therefore, the amount of formazan dye formed directly correlates to the number of metabolically active cells in the culture. Cells, grown in a 96-well ...
MITOSIS
... 2. is the longest part of the cell cycle 3. has 4 parts a. “every day life”- when the cell is just doing its thing b. G1 phase- the cell begins to double in size c. S phase- DNA duplicates (go from 46 chromatids to 92 chromatids) d. G2 phase- cell is ready to start mitosis PROPHASE 1. is the first s ...
... 2. is the longest part of the cell cycle 3. has 4 parts a. “every day life”- when the cell is just doing its thing b. G1 phase- the cell begins to double in size c. S phase- DNA duplicates (go from 46 chromatids to 92 chromatids) d. G2 phase- cell is ready to start mitosis PROPHASE 1. is the first s ...
L4-specialised-cells-cards
... their job as they are very flexible so when you use your muscles they can stretch without being broken. They also contain small organelles called mitochondria which can release energy from food for ...
... their job as they are very flexible so when you use your muscles they can stretch without being broken. They also contain small organelles called mitochondria which can release energy from food for ...
Slide ()
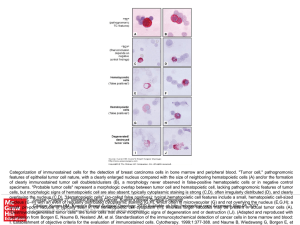
... Categorization of immunostained cells for the detection of breast carcinoma cells in bone marrow and peripheral blood. "Tumor cell," pathognomonic features of epithelial tumor cell nature, with a clearly enlarged nucleus compared with the size of neighboring hematopoietic cells (A) and/or the format ...
... Categorization of immunostained cells for the detection of breast carcinoma cells in bone marrow and peripheral blood. "Tumor cell," pathognomonic features of epithelial tumor cell nature, with a clearly enlarged nucleus compared with the size of neighboring hematopoietic cells (A) and/or the format ...
Investigating the Influence of Probiotics on Cell Proliferation
... through two pathways, the Intrinsic Pathway and the Extrinsic Pathway. The Intrinsic Pathway, also known as the Mitochondrial Pathway, is induced from inside the cell as a response to stress factors such as DNA damage and loss of cell-survival factors. In literature it can be observed that probiotic ...
... through two pathways, the Intrinsic Pathway and the Extrinsic Pathway. The Intrinsic Pathway, also known as the Mitochondrial Pathway, is induced from inside the cell as a response to stress factors such as DNA damage and loss of cell-survival factors. In literature it can be observed that probiotic ...
L*_*__*__dF - IES Alyanub
... biomolecule: smallest unit an organism can be divided into multicellular: containing more than one cell eukaryote: organism made of cells that have a nucleus heterotrophic: obtaining nutrition from compounds that already exist organelle: special compartment inside a eukaryotic cell that performs a s ...
... biomolecule: smallest unit an organism can be divided into multicellular: containing more than one cell eukaryote: organism made of cells that have a nucleus heterotrophic: obtaining nutrition from compounds that already exist organelle: special compartment inside a eukaryotic cell that performs a s ...
Chloroplasts
... In the beginning, there were Cells… • Bacteria are thought to be the earliest forms of life on the planet. • Simple life flourished in tidal pools near the sea. • Water was warm and full of nutrients. ...
... In the beginning, there were Cells… • Bacteria are thought to be the earliest forms of life on the planet. • Simple life flourished in tidal pools near the sea. • Water was warm and full of nutrients. ...
Two identical daughter cells are produced
... Two centrioles move to opposite ends of the cell and a spindle begins to develop between them. ...
... Two centrioles move to opposite ends of the cell and a spindle begins to develop between them. ...
CELLS, CELLS and MORE CELLS I. Background In the very late
... Prokaryotes 1) No nucleus 2) No membrane bound or complex organelles 3) Simple, first to evolve and are VERY small 4) Example-bacteria Eukaryotes 1) *Have a nucleus* 2) Have membrane bound or COMPLEX organelles 3) Very complex, evolved after prokaryotes 4) Examples-plants & animals CELLULAR ORGANIZA ...
... Prokaryotes 1) No nucleus 2) No membrane bound or complex organelles 3) Simple, first to evolve and are VERY small 4) Example-bacteria Eukaryotes 1) *Have a nucleus* 2) Have membrane bound or COMPLEX organelles 3) Very complex, evolved after prokaryotes 4) Examples-plants & animals CELLULAR ORGANIZA ...
Lesson 04 Plant vs. Animal cells Lab Answers
... a. Specimen: _______Plant Stem Cell______________ b. Magnification of this view: ____400 power_____________ c. Field of View at this magnification: ___0.5 mm_____________ d. number of cells seen across the diameter ________24_____ e. approximate size of one cell, (c divided by d), __0.021mm__ ...
... a. Specimen: _______Plant Stem Cell______________ b. Magnification of this view: ____400 power_____________ c. Field of View at this magnification: ___0.5 mm_____________ d. number of cells seen across the diameter ________24_____ e. approximate size of one cell, (c divided by d), __0.021mm__ ...
CHAPTER 1: THE CELL 1.1 (p. 15) 1. Name four characteristics of
... 3. Describe the levels of organization in a tree. Photosynthetic plant leaf cells generate glucose which is transported by xylem and phloem tissue along with water for use throughout the tree. 4. In what way does a specialized cell in a multicellular organism differ from the cell of a unicellular or ...
... 3. Describe the levels of organization in a tree. Photosynthetic plant leaf cells generate glucose which is transported by xylem and phloem tissue along with water for use throughout the tree. 4. In what way does a specialized cell in a multicellular organism differ from the cell of a unicellular or ...
Introduction to Cells- the smallest unit of any living organism
... prokaryote is an organism made of a single prokaryotic cell. Bacteria are prokaryotes. They are very simple cells that do not have a nucleus. This means that their DNA is not enclosed in a membrane inside the cell. Instead, prokaryotes have a single loop DNA that floats in the cell’s cytoplasm. Like ...
... prokaryote is an organism made of a single prokaryotic cell. Bacteria are prokaryotes. They are very simple cells that do not have a nucleus. This means that their DNA is not enclosed in a membrane inside the cell. Instead, prokaryotes have a single loop DNA that floats in the cell’s cytoplasm. Like ...
biology – ecology
... Using a Circle Map, Identify the following o The importance of Enzymes to cell processes (Pg#159) o The significance of Temperature and pH for Enzyme action (Pg#160) o The chemical composition of Enzymes (Pg#159) Identify HOW an Enzyme works using a Flow Map Design (Pg#160, Figure 6.18) ...
... Using a Circle Map, Identify the following o The importance of Enzymes to cell processes (Pg#159) o The significance of Temperature and pH for Enzyme action (Pg#160) o The chemical composition of Enzymes (Pg#159) Identify HOW an Enzyme works using a Flow Map Design (Pg#160, Figure 6.18) ...
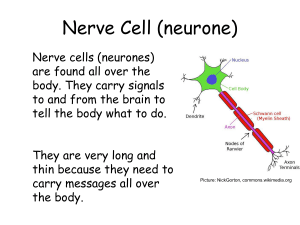
Nerve activates contraction
... Plant cells are encased by cell walls • The cell wall, found in prokaryotes, fungi, and some protists, has multiple functions. • In plants, the cell wall protects the cell, maintains its shape, and prevents excessive uptake of water. ...
... Plant cells are encased by cell walls • The cell wall, found in prokaryotes, fungi, and some protists, has multiple functions. • In plants, the cell wall protects the cell, maintains its shape, and prevents excessive uptake of water. ...
The Great Cell Scavenger Hunt You will visit the links to answer the
... Cells are small compartments that hold the biological equipment necessary to keep an organism alive and successful. Living things may be single-celled or they may be very complex such as a human being. ...
... Cells are small compartments that hold the biological equipment necessary to keep an organism alive and successful. Living things may be single-celled or they may be very complex such as a human being. ...
Compare the size of these organisms
... 4 small cells have more surface area than 1 big cell •More cell membrane – less cytoplasm ...
... 4 small cells have more surface area than 1 big cell •More cell membrane – less cytoplasm ...
Life Science Semester Review Part 2 NAME
... 26. Eglin AFB will soon be testing one of its newest airplanes. They will do this through models. The reason for using models is to _____. a. save time, money and lives, b. test predictions c. communicate 27. The correct hierarchy (order) for living things is _____. a. atoms, compounds, cells, organ ...
... 26. Eglin AFB will soon be testing one of its newest airplanes. They will do this through models. The reason for using models is to _____. a. save time, money and lives, b. test predictions c. communicate 27. The correct hierarchy (order) for living things is _____. a. atoms, compounds, cells, organ ...