Pasteur: Ummm, I don`t think so!!!
... Cells are the building blocks of life The average human being is composed of around 100 Trillion individual cells!!! It would take as many as 50 cells to cover the area of a dot on the letter “i” ...
... Cells are the building blocks of life The average human being is composed of around 100 Trillion individual cells!!! It would take as many as 50 cells to cover the area of a dot on the letter “i” ...
Name: Date: Period: Discovering the Cell Video Worksheet
... 7. Electron microscopes allow you to see tremendous _______________, but only in cells that have been ____________________. 8. The confocal laser scanning microscope provides us with _________ images that enable us to see the shape of cells. 9. Antoni von Leeuwenhoke saw the __________ _____________ ...
... 7. Electron microscopes allow you to see tremendous _______________, but only in cells that have been ____________________. 8. The confocal laser scanning microscope provides us with _________ images that enable us to see the shape of cells. 9. Antoni von Leeuwenhoke saw the __________ _____________ ...
Virtual Lab: The Cell Cycle and Cancer
... 3. How long did normal cells and cancer cells spend in interphase? What does this data mean to the overall number of new cells created in a given period of time? ...
... 3. How long did normal cells and cancer cells spend in interphase? What does this data mean to the overall number of new cells created in a given period of time? ...
Day 5, Cell Unit Test
... A Make proteins, can be located in cytoplasm or on the endoplasmic reticulum B Directs all cellular functions, separated from cytoplasm by membrane H Makes food in plant cells ...
... A Make proteins, can be located in cytoplasm or on the endoplasmic reticulum B Directs all cellular functions, separated from cytoplasm by membrane H Makes food in plant cells ...
Mitosis PowerPoint
... daughter cells are formed and the cells begin to separate. This stage is indicated by the formation of a cell plate in plant cells and a cleavage furrow in animal cells. ...
... daughter cells are formed and the cells begin to separate. This stage is indicated by the formation of a cell plate in plant cells and a cleavage furrow in animal cells. ...
The Discovery of Cells
... 3 main ideas of the Cell Theory 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Singular cell organisms and Multicellular organisms. 2. The cell is the basic structure and organization of organisms. No matter how large an organism, it is made up of cells. 3. All cells come from preexisting cells ...
... 3 main ideas of the Cell Theory 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Singular cell organisms and Multicellular organisms. 2. The cell is the basic structure and organization of organisms. No matter how large an organism, it is made up of cells. 3. All cells come from preexisting cells ...
Name Due Date Cell Specialization Station 1
... 3. There are two main types of cells. What type are bacteria? 4. What is a structure you will never see in a bacteria cell? 5. What are two good things bacteria do for humans? ...
... 3. There are two main types of cells. What type are bacteria? 4. What is a structure you will never see in a bacteria cell? 5. What are two good things bacteria do for humans? ...
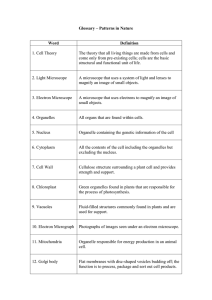
Glossary – Patterns in Nature
... Vascular tissue in plants that transports organic molecules (food) up and down the plant. ...
... Vascular tissue in plants that transports organic molecules (food) up and down the plant. ...
Glossary – Patterns in Nature
... Fluid-filled sacs containing enzymes to break down worn out cell organelles. ...
... Fluid-filled sacs containing enzymes to break down worn out cell organelles. ...
Mitosis Notes - Roslyn Public Schools
... o Purpose: occurs in somatic (body) cells for growth and repair of tissue (ex. Growing, or healing an injury). Occurs in both plants and animals: asexual reproduction, (starting a new plant from a stem/leaf of another one) o Method: mitosis involves one duplication of nuclear material, and one divis ...
... o Purpose: occurs in somatic (body) cells for growth and repair of tissue (ex. Growing, or healing an injury). Occurs in both plants and animals: asexual reproduction, (starting a new plant from a stem/leaf of another one) o Method: mitosis involves one duplication of nuclear material, and one divis ...
2.1Cell Theory AT
... Anton van Leeuwenhoek documented unicellular organisms based on observations of protozoa [1673] and bacteria [1683] ...
... Anton van Leeuwenhoek documented unicellular organisms based on observations of protozoa [1673] and bacteria [1683] ...
What is the Chapter 4 Test Like
... 1. Activity: Why Don’t Cells Grow Indefinitely? AND Review Worksheet: Cell Growth o How do you calculate surface area to volume ratios? o What is the significance of surface area to volume ratios? o Is a small cell or a large cell more efficient? 2. Activity: The Cell Theory o What were the contribu ...
... 1. Activity: Why Don’t Cells Grow Indefinitely? AND Review Worksheet: Cell Growth o How do you calculate surface area to volume ratios? o What is the significance of surface area to volume ratios? o Is a small cell or a large cell more efficient? 2. Activity: The Cell Theory o What were the contribu ...
Cell Structure & Function
... •All living things are composed of cells •Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things ...
... •All living things are composed of cells •Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things ...
Synthesis, Targeting and Sorting STF - 1
... 7. (26 pts) The cells lining the digestive system of cnidarians (hydra, jellyfish, corals and their relatives) directly ingest and then internally digest unicellular prey. Curiously, some cnidaria (or coelenterata as they used to be called) have evolved mechanisms for forming a commensal relationshi ...
... 7. (26 pts) The cells lining the digestive system of cnidarians (hydra, jellyfish, corals and their relatives) directly ingest and then internally digest unicellular prey. Curiously, some cnidaria (or coelenterata as they used to be called) have evolved mechanisms for forming a commensal relationshi ...
The human kinome and all its associated signaling proteins
... kinases involved largely in cell cycle control in fungi, mammals and other eukaryotes. hNek5 is a new member of the human Nek family of yet unknown function. Analysis of RT-PCR products showed that hNek5 mRNA was expressed in asynchronous HeLa cells, but, the expression was strongly regulated during ...
... kinases involved largely in cell cycle control in fungi, mammals and other eukaryotes. hNek5 is a new member of the human Nek family of yet unknown function. Analysis of RT-PCR products showed that hNek5 mRNA was expressed in asynchronous HeLa cells, but, the expression was strongly regulated during ...
SPECIALIZED CELLS
... – Muscle cells make specialized tissue that can contract. – Muscle tissue contains the specialized proteins actin and myosin that slide past one another. ...
... – Muscle cells make specialized tissue that can contract. – Muscle tissue contains the specialized proteins actin and myosin that slide past one another. ...
Cell Growth and Division
... – chromatids are pulled apart to separate ends – membrane begins to pinch off in the middle ...
... – chromatids are pulled apart to separate ends – membrane begins to pinch off in the middle ...
Cell Definitions
... Organ Structure, such as the heart, made up of different types of tissues that all work together By health.howstuffworks.com ...
... Organ Structure, such as the heart, made up of different types of tissues that all work together By health.howstuffworks.com ...
UNICELLULAR MULTICELLULAR
... MADE OF CELL(S) Ingest-surrounds and engulfs other organisms and moves them into the REPRODUCE vacuoles Digest-enzymes move into the GROW AND REPAIR vacuole in order to break down food into nutrients that can be used INGEST by the cell Reproduce-binary fission-divides DIGEST into two cells that are ...
... MADE OF CELL(S) Ingest-surrounds and engulfs other organisms and moves them into the REPRODUCE vacuoles Digest-enzymes move into the GROW AND REPAIR vacuole in order to break down food into nutrients that can be used INGEST by the cell Reproduce-binary fission-divides DIGEST into two cells that are ...
3.1 Study Guide KEY
... the bottom of the Y shape beloq write the characteristics that both kinds of cells have in common, Then lightly cross out those characteristics at the top of the Y. ...
... the bottom of the Y shape beloq write the characteristics that both kinds of cells have in common, Then lightly cross out those characteristics at the top of the Y. ...
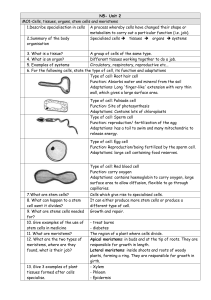
N5- Unit 2 MO1-Cells, tissues, organs, stem cells and meristems 1
... Cells which give rise to specialised cells. It can either produce more stem cells or produce a different type of cell. Growth and repair. - treat burns - diabetes The region of a plant where cells divide. Apical meristems: in buds and at the tip of roots. They are responsible for growth in length. L ...
... Cells which give rise to specialised cells. It can either produce more stem cells or produce a different type of cell. Growth and repair. - treat burns - diabetes The region of a plant where cells divide. Apical meristems: in buds and at the tip of roots. They are responsible for growth in length. L ...
CELL CYCLE TEST REVIEW PAP Biology 1. List the three parts of a
... List the three parts of a nucleotide (the monomer of DNA). Which two parts make up the backbone of DNA? What are the base pairing rules for the nitrogen bases? What type of bond holds the N-bases together? What is helicase? What is DNA polymerase? When and why does DNA replication occur in the cell ...
... List the three parts of a nucleotide (the monomer of DNA). Which two parts make up the backbone of DNA? What are the base pairing rules for the nitrogen bases? What type of bond holds the N-bases together? What is helicase? What is DNA polymerase? When and why does DNA replication occur in the cell ...
Cells - Baldwin Schools Teachers
... and systems. Cells are small compartments that hold all of the biological equipment necessary to keep an organism alive and successful on Earth. ...
... and systems. Cells are small compartments that hold all of the biological equipment necessary to keep an organism alive and successful on Earth. ...