1. Define: Prokaryotic Cells without a nucleus. Very primitive
... Use your Nervous System Notes to answer the following questions. 22. What is a neuron? the basic unit of structure and function of the nervous system 23. Name the parts & function of the central nervous system. Parts – brain and spinal cord Function - relays messages, processes information and analy ...
... Use your Nervous System Notes to answer the following questions. 22. What is a neuron? the basic unit of structure and function of the nervous system 23. Name the parts & function of the central nervous system. Parts – brain and spinal cord Function - relays messages, processes information and analy ...
cell organelle WS 2014
... 13. Produces lipids and breaks down drug 14. Site where ribosomes are made 15. Composed of a phospholipid bilayer; controls what gets into and out of cell 16. Collection of DNA in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells 17. Longer whip-like structures used for movement 18. Small hair-like structures used fo ...
... 13. Produces lipids and breaks down drug 14. Site where ribosomes are made 15. Composed of a phospholipid bilayer; controls what gets into and out of cell 16. Collection of DNA in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells 17. Longer whip-like structures used for movement 18. Small hair-like structures used fo ...
Eukaryotes
... such as colonial environments where the metabolic specialties of one species could benefit others, organelles proved to be the most effective solution. Nucleus The nucleus was, for years, the criteria required for an organism to be a eukaryote. Much like the brain of humans, the nucleus represents t ...
... such as colonial environments where the metabolic specialties of one species could benefit others, organelles proved to be the most effective solution. Nucleus The nucleus was, for years, the criteria required for an organism to be a eukaryote. Much like the brain of humans, the nucleus represents t ...
Cells Check 2 (Solutions)
... proteins. Fat-soluble materials can pass through the lipid part of the membrane. Other materials can pass through protein channels. ...
... proteins. Fat-soluble materials can pass through the lipid part of the membrane. Other materials can pass through protein channels. ...
The importance of penicillin
... of the drug. Mass production was started immediately and as a result many people survived the final battles of the war. Fleming, Flory and Chain were awarded the 1945 Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine for their discoveries. ...
... of the drug. Mass production was started immediately and as a result many people survived the final battles of the war. Fleming, Flory and Chain were awarded the 1945 Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine for their discoveries. ...
If a cell makes a lot of protein, what organelle must it also have a lot
... support because it is very rigid? Cell wall ...
... support because it is very rigid? Cell wall ...
“differential reproductive advantage” within a population This is
... A person with type AB blood mates with a person with type O blood will produce these phenotypes in their offspring ...
... A person with type AB blood mates with a person with type O blood will produce these phenotypes in their offspring ...
Biology Benchmark Study Guide
... 13. What part of a plant cell provides support because it is very rigid? Cell wall 14. What property of the cell membrane describes its ability to move certain materials in and out of the cell? Selective permeability to allow only certain materials to pass through 15. What organelle stores water and ...
... 13. What part of a plant cell provides support because it is very rigid? Cell wall 14. What property of the cell membrane describes its ability to move certain materials in and out of the cell? Selective permeability to allow only certain materials to pass through 15. What organelle stores water and ...
Gene discovery shows how st
... Dr. Gabriel Ferguson, a postdoctoral fellow in Martinez-Agosto’s lab and first author of the study, built upon the lab’s previous research that utilized the blood system of the fruit fly species Drosophila to show that a specific set of signals must be received by progenitor cells to activate their ...
... Dr. Gabriel Ferguson, a postdoctoral fellow in Martinez-Agosto’s lab and first author of the study, built upon the lab’s previous research that utilized the blood system of the fruit fly species Drosophila to show that a specific set of signals must be received by progenitor cells to activate their ...
AP Biology Reading Questions
... AP Biology Reading Questions: Cells, Lesson 1- Overview and Endomembrane System 1. Explain how advances in microscopy led to advances in cytology. Provide two historical examples. 2. Why are certain cellular structures unable to be observed with a light microscope? 3. How does the ratio of a cell’s ...
... AP Biology Reading Questions: Cells, Lesson 1- Overview and Endomembrane System 1. Explain how advances in microscopy led to advances in cytology. Provide two historical examples. 2. Why are certain cellular structures unable to be observed with a light microscope? 3. How does the ratio of a cell’s ...
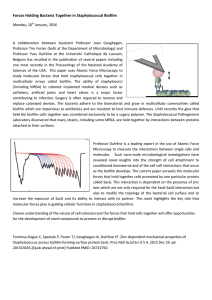
Forces Holding Bacteria Together in Staphylococcal Biofilm
... molecules. Such nano-scale microbiological investigations have revealed novel insights into the strength of cell attachment to conditioned biomaterial and of the cell-cell interactions that occur as the biofilm develops. The current paper unravels the molecular forces that hold together cells promot ...
... molecules. Such nano-scale microbiological investigations have revealed novel insights into the strength of cell attachment to conditioned biomaterial and of the cell-cell interactions that occur as the biofilm develops. The current paper unravels the molecular forces that hold together cells promot ...
Cell Structure and Function Note Guide
... All living things are made up of one or more _____________. Single celled or _________________ organisms do many of the same things as multicellular organisms. Describe the two basic types of cells: Prokaryotes: Eukaryotes: List the structures that help single-celled organisms move: ...
... All living things are made up of one or more _____________. Single celled or _________________ organisms do many of the same things as multicellular organisms. Describe the two basic types of cells: Prokaryotes: Eukaryotes: List the structures that help single-celled organisms move: ...
Chapter 7: A tour of the cell
... Familiarize yourself with the diagrams of a representative animal cell (page 114) and a representative plant cell (page 115) The nucleus and ribosomes The nucleus contains a eukaryotic cells genetic library Nucleus Contains MOST of the genes (excludes mitochondrial and chloroplastic DNA) Nuclear mem ...
... Familiarize yourself with the diagrams of a representative animal cell (page 114) and a representative plant cell (page 115) The nucleus and ribosomes The nucleus contains a eukaryotic cells genetic library Nucleus Contains MOST of the genes (excludes mitochondrial and chloroplastic DNA) Nuclear mem ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... • Intermediate in size between actin filaments and microtubules • Functions: – Support nuclear envelope – Cell-cell junctions, such as those holding skin cells tightly together ...
... • Intermediate in size between actin filaments and microtubules • Functions: – Support nuclear envelope – Cell-cell junctions, such as those holding skin cells tightly together ...
Cell organelle card sort vacuole Where proteins are synthesised
... of the chemical reactions take place. ...
... of the chemical reactions take place. ...
Download PDF
... constructed and cloned a stress-reporting cell line. Results obtained with this platform indicate that both high field strengths and low-frequency fields adversely affect cell physiology. KEYWORDS: Dielectrophoresis, stress, physiology, high-content screening. INTRODUCTION Dielectrophoresis (DEP) is ...
... constructed and cloned a stress-reporting cell line. Results obtained with this platform indicate that both high field strengths and low-frequency fields adversely affect cell physiology. KEYWORDS: Dielectrophoresis, stress, physiology, high-content screening. INTRODUCTION Dielectrophoresis (DEP) is ...
Lesson 2: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells (1
... simplistic and primitive cells. For this reasons, these cells are thought to be the first cells to appear on earth. ...
... simplistic and primitive cells. For this reasons, these cells are thought to be the first cells to appear on earth. ...
Document
... Where energy is produced for the cell. The “powerhouse” of the cell. Golgi Body Controls what goes in and out of the nucleus Stores water for the cell. Is also the largest organelle in a plant cell. ...
... Where energy is produced for the cell. The “powerhouse” of the cell. Golgi Body Controls what goes in and out of the nucleus Stores water for the cell. Is also the largest organelle in a plant cell. ...
Exercicis danglès 2
... • This is the action of introducing an antigen within the cell envelope it to nourish itself. 17. True or false 1. Lysosomes can be called "suicide sacs" T 2. Red blood cells have a life span of about 500 days F 18. What type of blood cells make up the majority of human blood? ...
... • This is the action of introducing an antigen within the cell envelope it to nourish itself. 17. True or false 1. Lysosomes can be called "suicide sacs" T 2. Red blood cells have a life span of about 500 days F 18. What type of blood cells make up the majority of human blood? ...
Plant Cell
... Nucleus The nucleus directs all of the cell‘s activities, including reproduction. Endoplasmic Reticulum This network of passageways carries materials from one part of the cell to another. ...
... Nucleus The nucleus directs all of the cell‘s activities, including reproduction. Endoplasmic Reticulum This network of passageways carries materials from one part of the cell to another. ...
Nerve activates contraction
... Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
cell structure &function-2
... mitochondria come from the cytoplasm of the ovum, or egg cell. • In plants, chloroplasts are the organelles that capture the energy from the sunlight and convert it into chemical energy in a process called photosynthesis. ...
... mitochondria come from the cytoplasm of the ovum, or egg cell. • In plants, chloroplasts are the organelles that capture the energy from the sunlight and convert it into chemical energy in a process called photosynthesis. ...
Proteins - Houston ISD
... mitochondria come from the cytoplasm of the ovum, or egg cell. • In plants, chloroplasts are the organelles that capture the energy from the sunlight and convert it into chemical energy in a process called photosynthesis. ...
... mitochondria come from the cytoplasm of the ovum, or egg cell. • In plants, chloroplasts are the organelles that capture the energy from the sunlight and convert it into chemical energy in a process called photosynthesis. ...