Assessment - mrsimonsclassroom
... _____ 28. An organism made of many cells that are permanently together and coordinate their activities is a a. unicellular organism. c. multicellular organism. b. colonial organism. _____ 29. Cells are arranged into tissues, organs, and organ systems in a a. unicellular organism. c. multicellular or ...
... _____ 28. An organism made of many cells that are permanently together and coordinate their activities is a a. unicellular organism. c. multicellular organism. b. colonial organism. _____ 29. Cells are arranged into tissues, organs, and organ systems in a a. unicellular organism. c. multicellular or ...
Cells - Petal School District
... 3. Large Vacuole 3. Smaller vacuoles ______________________________________________ ...
... 3. Large Vacuole 3. Smaller vacuoles ______________________________________________ ...
Multiple Choice
... ____ 8. The first set of reactions in cellular respiration is a. the Krebs cycle. b. electron transport. c. the Calvin cycle. d. glycolysis. ____ 9. What process releases energy from food molecules by producing ATP in the absence of oxygen? a. cellular respiration b. photosynthesis c. glycolysis d. ...
... ____ 8. The first set of reactions in cellular respiration is a. the Krebs cycle. b. electron transport. c. the Calvin cycle. d. glycolysis. ____ 9. What process releases energy from food molecules by producing ATP in the absence of oxygen? a. cellular respiration b. photosynthesis c. glycolysis d. ...
5.5 multicellular life outline
... 5.5 Mutlicellular Life Outline Multicellular organisms depend on interactions among different cell types. ...
... 5.5 Mutlicellular Life Outline Multicellular organisms depend on interactions among different cell types. ...
Animal Tissue
... • These cells function in involuntary movements and/or autonomic responses (such as breathing, secretion, ejaculation, birth, and certain reflexes). • spindle shaped cells that form masses. These fibers are components of structures in the digestive system, reproductive tract, and blood vessels. ...
... • These cells function in involuntary movements and/or autonomic responses (such as breathing, secretion, ejaculation, birth, and certain reflexes). • spindle shaped cells that form masses. These fibers are components of structures in the digestive system, reproductive tract, and blood vessels. ...
Name Period ______ Pre-AP Biology Cell Specialization Lab
... Using the following possible cell types given by your teacher. Predict the cell at each station. ...
... Using the following possible cell types given by your teacher. Predict the cell at each station. ...
the discovery of cells
... - Organisms with a cell that lacks internal structures surrounded by membranes - Most are single celled organisms Eukaryote/ Eukaryotic: - Organisms that have cells containing internal, membrane bound structures - Organelles = a structure that has a membrane surrounding it. - Organelles isolate the ...
... - Organisms with a cell that lacks internal structures surrounded by membranes - Most are single celled organisms Eukaryote/ Eukaryotic: - Organisms that have cells containing internal, membrane bound structures - Organelles = a structure that has a membrane surrounding it. - Organelles isolate the ...
Lesson 1 PP - Bridgend Moodle Site
... explaining the importance of the science behind the Project. ...
... explaining the importance of the science behind the Project. ...
Unicellular and Multicellular
... What are the characteristics of life? Microscope Handout (front and back) Cell Worksheet (front and back) Animal and Plant cell drawings with labels. ...
... What are the characteristics of life? Microscope Handout (front and back) Cell Worksheet (front and back) Animal and Plant cell drawings with labels. ...
Living Cells Part A Cell Structure and Function
... alcohol. The production of alcohol by yeast is also known as alcoholic fermentation. The concentration of alcohol that can be produced by yeast ...
... alcohol. The production of alcohol by yeast is also known as alcoholic fermentation. The concentration of alcohol that can be produced by yeast ...
Cell Structure and Function Guided Notes
... a. Robert Hooke stated that they looked like ______________________________________. b. Hooke is responsible for ___________________________________________. c. Hooke called them “CELLS” because they looked like the _________________________________ that monks lived in called cells 2. In 1673, _____ ...
... a. Robert Hooke stated that they looked like ______________________________________. b. Hooke is responsible for ___________________________________________. c. Hooke called them “CELLS” because they looked like the _________________________________ that monks lived in called cells 2. In 1673, _____ ...
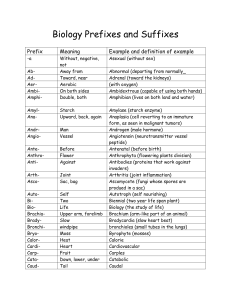
Biology Prefixes and Suffixes
... Erythrocyte (red blood cell) Eukaryote (Organism whose cells contains a “true” membrane bound nucleus) Exoskeleton (hard outer surface that provides support or protection for an organism) Extracellular (locating or occurring outside a cell) Gametes (egg or sperm that unite during sexual reproduction ...
... Erythrocyte (red blood cell) Eukaryote (Organism whose cells contains a “true” membrane bound nucleus) Exoskeleton (hard outer surface that provides support or protection for an organism) Extracellular (locating or occurring outside a cell) Gametes (egg or sperm that unite during sexual reproduction ...
Open File
... Like animal cells, plant cells are surrounded by a cell membrane Outside the cell membrane is another layer made of cellulose to protect and support the cell Many of the organelles in the cytoplasm of a plant cell are very similar to those of an animal cells Vacuoles in a plant cell tend to be much ...
... Like animal cells, plant cells are surrounded by a cell membrane Outside the cell membrane is another layer made of cellulose to protect and support the cell Many of the organelles in the cytoplasm of a plant cell are very similar to those of an animal cells Vacuoles in a plant cell tend to be much ...
Cells and Basketball
... Cells can be specialized in their shape and the organelles that they have within them. Organelles are small parts of a cell that perform certain jobs with in the cell. For example one organelle, mitochondria, is often called the powerhouse of the cell because it produces energy for the cell to do it ...
... Cells can be specialized in their shape and the organelles that they have within them. Organelles are small parts of a cell that perform certain jobs with in the cell. For example one organelle, mitochondria, is often called the powerhouse of the cell because it produces energy for the cell to do it ...
Cell Study Guide
... 1. Cells are basic units of all livings things, including humans. 2. Cell shape and structure are not exactly the same but are similar in plants and animals. 3. Cells are shaped differently because of where they are located and their specific job. 4. New cells are made from pre-existing cells (other ...
... 1. Cells are basic units of all livings things, including humans. 2. Cell shape and structure are not exactly the same but are similar in plants and animals. 3. Cells are shaped differently because of where they are located and their specific job. 4. New cells are made from pre-existing cells (other ...
Name
... Introduction: Living things are made of cells. All cells have parts that do certain jobs. Cells have an outer covering called the cell (plasma) membrane. The cell membrane controls what enter/exits a cell. The clear jellylike material inside the cell is the cytoplasm. The nucleus is the control cent ...
... Introduction: Living things are made of cells. All cells have parts that do certain jobs. Cells have an outer covering called the cell (plasma) membrane. The cell membrane controls what enter/exits a cell. The clear jellylike material inside the cell is the cytoplasm. The nucleus is the control cent ...
Cell Quiz/Test
... 1. The process when cells don’t have to use energy to transport materials across the membrane. 2. Large organic molecule that includes all of the fats and oils in the body. 3. Chemical reaction in plant cells that creates glucose (sugar) 4. Diffusion of water through a membrane (ex. Egg lab) 5. This ...
... 1. The process when cells don’t have to use energy to transport materials across the membrane. 2. Large organic molecule that includes all of the fats and oils in the body. 3. Chemical reaction in plant cells that creates glucose (sugar) 4. Diffusion of water through a membrane (ex. Egg lab) 5. This ...
Imaging live cells by X-ray laser diffraction - SPring-8
... with a width and length of ~194 nm and ~570 nm, respectively. The lower part of the cell image contains a dumbbell-shaped high image-intensity region, indicative of a nucleoid, a DNA-rich structure in prokaryotic cells. In fact, the image intensity difference between the upper and lower regions of t ...
... with a width and length of ~194 nm and ~570 nm, respectively. The lower part of the cell image contains a dumbbell-shaped high image-intensity region, indicative of a nucleoid, a DNA-rich structure in prokaryotic cells. In fact, the image intensity difference between the upper and lower regions of t ...
Honors Anatomy, Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Part 1: Cells Anatomy
... _____________________ split Sister chromatids _______________ to opposite poles _____________________: new ________________ form Cytokinesis Cleavage furrow ________________ cytoplasm in half Protein Synthesis Genes: The Blueprint for Protein Structure 19. Define gene. DNA segment carrying the instr ...
... _____________________ split Sister chromatids _______________ to opposite poles _____________________: new ________________ form Cytokinesis Cleavage furrow ________________ cytoplasm in half Protein Synthesis Genes: The Blueprint for Protein Structure 19. Define gene. DNA segment carrying the instr ...
Chapter 8: Cell Reproduction
... all the time? • Because it is easier to copy (transcribe) in its chromatin form, which happens before division occurs ...
... all the time? • Because it is easier to copy (transcribe) in its chromatin form, which happens before division occurs ...