INTRODUCTION CELL BIOLOGY
... hydrogen, and nitrogen. They not only function as individual units, but also as a part of larger structures, namely tissues and organs, where they communicate with other cells, forming co-ordinated functional units. New cells are created by cell division. Once divided, they differentiate into cells ...
... hydrogen, and nitrogen. They not only function as individual units, but also as a part of larger structures, namely tissues and organs, where they communicate with other cells, forming co-ordinated functional units. New cells are created by cell division. Once divided, they differentiate into cells ...
Cytoplasmic Organelles
... Golgi apparatus, discovered by Camillo Golgi Proteins are first moved into the Golgi apparatus (Ga) Looks like a flattened stack of membranes piled one upon the other Proteins are often modified by special enzymes & attach carbohydrates and lipids to them After modifications in the Ga, the pro ...
... Golgi apparatus, discovered by Camillo Golgi Proteins are first moved into the Golgi apparatus (Ga) Looks like a flattened stack of membranes piled one upon the other Proteins are often modified by special enzymes & attach carbohydrates and lipids to them After modifications in the Ga, the pro ...
Cell Structure and Function 1 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v
... What was Robert Hooke observing when he coined the term cells? What is the cell theory? Cell Size… How big is an e-coli bacteria? Which is bigger the influenza virus or hepatitis? Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes What 4 structures are found in BOTH prokaryotes and eukaryotes? ...
... What was Robert Hooke observing when he coined the term cells? What is the cell theory? Cell Size… How big is an e-coli bacteria? Which is bigger the influenza virus or hepatitis? Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes What 4 structures are found in BOTH prokaryotes and eukaryotes? ...
Critical Thinking
... what it is made of. The function of a part is what that shape and material enable the part to do in the body. For example, alveoli are tiny sacs in the lungs that hold gases. They are made of a membrane that enables oxygen and carbon dioxide to pass in and out of the blood. Answers will vary. Sample ...
... what it is made of. The function of a part is what that shape and material enable the part to do in the body. For example, alveoli are tiny sacs in the lungs that hold gases. They are made of a membrane that enables oxygen and carbon dioxide to pass in and out of the blood. Answers will vary. Sample ...
chromosome aberrations induced by the Auger Emitter I
... Gy, followed by a plateau between 2 and 4.5 Gy. The data indicate that even the lowest dose of 0.2 Gy leads to significant damage in PBL and to a 4.5-fold increase of aberrations compared to the controls. Furthermore, a dose-dependent increase of cell death is observed. Conclusions: I-125-UdR has a ...
... Gy, followed by a plateau between 2 and 4.5 Gy. The data indicate that even the lowest dose of 0.2 Gy leads to significant damage in PBL and to a 4.5-fold increase of aberrations compared to the controls. Furthermore, a dose-dependent increase of cell death is observed. Conclusions: I-125-UdR has a ...
Unit 2 Exam Cell Cell organelles Plant and Animal Tissue
... They actually loose their nuclei, mitochondria, and ER’s because of needing room for carrying hemoglobin to bind oxygen. No function in metabolism ...
... They actually loose their nuclei, mitochondria, and ER’s because of needing room for carrying hemoglobin to bind oxygen. No function in metabolism ...
NAME DATE ______ PERIOD _____
... MULTIPLE CHOICE: Circle all that are TRUE. There may be MORE THAN ONE correct answer. 1. Which of the following is TRUE of a cell membranes? A. Cell membranes allow ALL substances to pass through easily B. It is selectively permeable so only certain molecules can pass through it. C. It acts more lik ...
... MULTIPLE CHOICE: Circle all that are TRUE. There may be MORE THAN ONE correct answer. 1. Which of the following is TRUE of a cell membranes? A. Cell membranes allow ALL substances to pass through easily B. It is selectively permeable so only certain molecules can pass through it. C. It acts more lik ...
Cell Specialization and Levels of Organization
... that are less than a week old • In the lab these totipotent stem cells are able to keep dividing for up to a year without differentiating – Can make any one of the 300 cell types found in an adult human ...
... that are less than a week old • In the lab these totipotent stem cells are able to keep dividing for up to a year without differentiating – Can make any one of the 300 cell types found in an adult human ...
Chapter 4 - Living Systems: Human Systems
... 7. Which of the following correctly lists the organizational hierarchy of organisms from simplest to most complex? A. cells, organs, tissues, organ systems, organisms B. cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organisms C. tissues, cells, organs, organ systems, organisms D. tissues, organs, cells, or ...
... 7. Which of the following correctly lists the organizational hierarchy of organisms from simplest to most complex? A. cells, organs, tissues, organ systems, organisms B. cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organisms C. tissues, cells, organs, organ systems, organisms D. tissues, organs, cells, or ...
CHAPTER 43—THE BODY S DEFENSES 1. What s the difference
... F. Suppressor T cells ______ Responsible for cell-mediated immunity; track down & attack bacteria, fungi, protozoa and foreign tissues that contain targeted antigen ______ Remain in reserve; differentiate into cytotoxic T cells with second exposure to antigen ______ Depress the action of other T cel ...
... F. Suppressor T cells ______ Responsible for cell-mediated immunity; track down & attack bacteria, fungi, protozoa and foreign tissues that contain targeted antigen ______ Remain in reserve; differentiate into cytotoxic T cells with second exposure to antigen ______ Depress the action of other T cel ...
Bio392-Chapter 10-1
... • Materials move through cells by diffusion. Oxygen and food move into cells, while waste products move out of cells. How does the size of a cell affect how efficiently materials get to all parts of a cell? • Work with a partner to complete this activity. 1. On a sheet of paper, make a drawing of a ...
... • Materials move through cells by diffusion. Oxygen and food move into cells, while waste products move out of cells. How does the size of a cell affect how efficiently materials get to all parts of a cell? • Work with a partner to complete this activity. 1. On a sheet of paper, make a drawing of a ...
CELL PROCESSES A selectively permeable cell membrane allows
... into usable, soluble particles that can be used by different cells. There are two types of digestion: mechanical - involving the physical breakdown of food into useable pieces and chemical - breaking down with enzymes the smaller pieces into usable nutrients. ...
... into usable, soluble particles that can be used by different cells. There are two types of digestion: mechanical - involving the physical breakdown of food into useable pieces and chemical - breaking down with enzymes the smaller pieces into usable nutrients. ...
Unit 3 (ch 4)
... The Nucleus is the genetic control center of a eukaryotic cell. Nuclear DNA is in very long fibers called chromatin Each fiber of chromatin is a chromosome During cell division, chromatin condenses so it is visible ...
... The Nucleus is the genetic control center of a eukaryotic cell. Nuclear DNA is in very long fibers called chromatin Each fiber of chromatin is a chromosome During cell division, chromatin condenses so it is visible ...
Organelles for support and locomotion
... They anchor and support many organelles They provide a “highway” system through with materials move within the cell. ...
... They anchor and support many organelles They provide a “highway” system through with materials move within the cell. ...
Jan. 9th, 2012 Warm Up
... • For cells with cell walls,the cell membrane is inside the cell wall • Allows food, oxygen, & water into the cell & waste products out of the cell. ...
... • For cells with cell walls,the cell membrane is inside the cell wall • Allows food, oxygen, & water into the cell & waste products out of the cell. ...
Cell Biology Unit - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... years of research, a drug made from this protein was tested and found to bring the blood count to normal in several AIDS patients and those being treated for cancer. The researchers patented the cells. The man who unknowingly donated the spleen to research now states that the doctor owes him money f ...
... years of research, a drug made from this protein was tested and found to bring the blood count to normal in several AIDS patients and those being treated for cancer. The researchers patented the cells. The man who unknowingly donated the spleen to research now states that the doctor owes him money f ...
Cells
... 3. Theodor Schwann – studied animal cells- concluded all animals were made up of cells 4. Rudolf Virchow – hypothesized that new cells don’t form on their own. Cells divide to form new cells 5. Anton van Leeuwenhoek – used simple microscopes to observe tiny animalculeslater named bacteria ...
... 3. Theodor Schwann – studied animal cells- concluded all animals were made up of cells 4. Rudolf Virchow – hypothesized that new cells don’t form on their own. Cells divide to form new cells 5. Anton van Leeuwenhoek – used simple microscopes to observe tiny animalculeslater named bacteria ...
The Cell wall
... The Wall described in the plant cell as a wall dead have features a cellulose devoid of them non-plant cells, and it's form as a result of the activity of protoplasm where evolve into cellular plate and as soon as they met the walls of the cell mother turns into what is known as Middle Lamella, and ...
... The Wall described in the plant cell as a wall dead have features a cellulose devoid of them non-plant cells, and it's form as a result of the activity of protoplasm where evolve into cellular plate and as soon as they met the walls of the cell mother turns into what is known as Middle Lamella, and ...
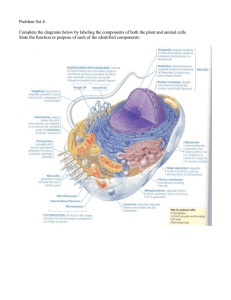
Problem Set 4:
... Complete the diagrams below by labeling the components of both the plant and animal cells. State the function or purpose of each of the identified components: ...
... Complete the diagrams below by labeling the components of both the plant and animal cells. State the function or purpose of each of the identified components: ...
CARCINOGENESIS - UCSD Pharmacology
... carcinogens. This causal process is called carcinogenesis. In humans, it is generally accepted that most epithelial cancers are caused by environmental exposure to certain kinds of chemicals. However, carcinogenesis is clearly influenced by large numbers of genes and non-carcinogenic environmental f ...
... carcinogens. This causal process is called carcinogenesis. In humans, it is generally accepted that most epithelial cancers are caused by environmental exposure to certain kinds of chemicals. However, carcinogenesis is clearly influenced by large numbers of genes and non-carcinogenic environmental f ...
exam2review - HCC Learning Web
... 3. Intercellular connections: tight junction, gap junction and desmosomes. What are CAMs? 4. Distinguish between endocrine and exocrine glands. Explain the 3 modes of secretion and give an example of a gland for each (page 118). 5. Describe the basement membrane. (where found, chemical ingredients). ...
... 3. Intercellular connections: tight junction, gap junction and desmosomes. What are CAMs? 4. Distinguish between endocrine and exocrine glands. Explain the 3 modes of secretion and give an example of a gland for each (page 118). 5. Describe the basement membrane. (where found, chemical ingredients). ...
Name: Period________ General Biology First Semester Study
... 79. Name, in order, the phases of mitosis AND briefly tell what happens to the CHROMOSOMES in each: ...
... 79. Name, in order, the phases of mitosis AND briefly tell what happens to the CHROMOSOMES in each: ...
1 - Schoolwires.net
... 9. What part of the microscope should not be used when looking at specimens under high power? Coarse adjustment knob ...
... 9. What part of the microscope should not be used when looking at specimens under high power? Coarse adjustment knob ...