Module 45: Issues of Development
... What is Developmental Psych? • Basic question: What shapes the way we change over time? • Developmental Psychology - the study of how people change physically, mentally, and socially throughout the lifespan • At every age and stage of life, developmental psychologists investigate the influence of m ...
... What is Developmental Psych? • Basic question: What shapes the way we change over time? • Developmental Psychology - the study of how people change physically, mentally, and socially throughout the lifespan • At every age and stage of life, developmental psychologists investigate the influence of m ...
Review Unit 13 Treatment 2015-2016
... • 2. group-lets one see others have similar problems, cheaper • 3. family • 4. support group/self help groups (grew out of humanism) ...
... • 2. group-lets one see others have similar problems, cheaper • 3. family • 4. support group/self help groups (grew out of humanism) ...
Chapter 15 Therapies - Psychology Domain, an Introductory
... and is highly structured. It is based on the assumption that psychological symptoms are caused and maintained by interpersonal problems. Although originally conceived to be brief, it now may also be long term. • a. The therapist helps the person identify and understand his particular interpersonal p ...
... and is highly structured. It is based on the assumption that psychological symptoms are caused and maintained by interpersonal problems. Although originally conceived to be brief, it now may also be long term. • a. The therapist helps the person identify and understand his particular interpersonal p ...
EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY (7th Edition in
... Psychotherapy involves an emotionally charged, confiding interaction between a trained therapist and a mental patient. Biomedical therapy uses drugs or other procedures that act on the patient’s nervous system, treating his or her psychological disorders. An eclectic approach uses various forms of h ...
... Psychotherapy involves an emotionally charged, confiding interaction between a trained therapist and a mental patient. Biomedical therapy uses drugs or other procedures that act on the patient’s nervous system, treating his or her psychological disorders. An eclectic approach uses various forms of h ...
Memory
... system, treating his or her psychological disorders. An eclectic approach uses various forms of healing techniques depending upon the client’s unique problems. ...
... system, treating his or her psychological disorders. An eclectic approach uses various forms of healing techniques depending upon the client’s unique problems. ...
Humanism Handout
... attached. There is no evaluation, reservation or possessiveness by one person to another. Humanistic therapists accept a client without evaluations, reservations or conditions. For Rogers, unconditional positive regard is the ideal way in which others should interact with us, and how we should be wi ...
... attached. There is no evaluation, reservation or possessiveness by one person to another. Humanistic therapists accept a client without evaluations, reservations or conditions. For Rogers, unconditional positive regard is the ideal way in which others should interact with us, and how we should be wi ...
a PowerPoint presentation of Module 52
... and feelings which may be rooted in past relationships. In addition to insight, therapists suggest changes in patterns of thinking and relating to others. ...
... and feelings which may be rooted in past relationships. In addition to insight, therapists suggest changes in patterns of thinking and relating to others. ...
Normal Development: 9 Months Old
... Each child is unique. It is therefore difficult to describe exactly what should be expected at each stage of a child's development. While certain attitudes, behaviors, and physical milestones tend to occur at certain ages, a wide spectrum of growth and behavior for each age is normal. These guidelin ...
... Each child is unique. It is therefore difficult to describe exactly what should be expected at each stage of a child's development. While certain attitudes, behaviors, and physical milestones tend to occur at certain ages, a wide spectrum of growth and behavior for each age is normal. These guidelin ...
The Biomedical Therapies
... Family & Group Therapies treats the family or group as a system views an individual’s unwanted behaviors as influenced by or directed at other family members attempts to guide family members toward positive relationships and improved communication ...
... Family & Group Therapies treats the family or group as a system views an individual’s unwanted behaviors as influenced by or directed at other family members attempts to guide family members toward positive relationships and improved communication ...
Therapy and Treatment - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... Psychological Perspective: Understanding and Treating Abnormal Behavior in Terms of Psychological Events Humanistic Therapies: • Based on belief that humans are capable of controlling their actions and responsible for their behaviors. • Goal is to help an individual become more aware of him/herself, ...
... Psychological Perspective: Understanding and Treating Abnormal Behavior in Terms of Psychological Events Humanistic Therapies: • Based on belief that humans are capable of controlling their actions and responsible for their behaviors. • Goal is to help an individual become more aware of him/herself, ...
Module 14: Prenatal and Childhood Development
... •Children begin to think logically about abstract concepts and form strategies about things they may not have experienced ...
... •Children begin to think logically about abstract concepts and form strategies about things they may not have experienced ...
CHAPTER 19 METHODS OF THERAPY
... and then to say whatever comes to mind – taps into unconscious thoughts and feelings Dream Analysis – analyst interprets the content of clients’ dreams to unlock these unconscious thoughts and feelings Transference – the patient’s transfer of emotions associated with other relationships to the t ...
... and then to say whatever comes to mind – taps into unconscious thoughts and feelings Dream Analysis – analyst interprets the content of clients’ dreams to unlock these unconscious thoughts and feelings Transference – the patient’s transfer of emotions associated with other relationships to the t ...
Chapter 17 PowerPoint Notes
... We will look at four major forms of psychotherapies based on different theories of human nature: Psychoanalysis The first formal ___________________________ to emerge was psychoanalysis, developed by Sigmund Freud. Psychoanalysis: Aims - Since psychological problems originate from childhood ________ ...
... We will look at four major forms of psychotherapies based on different theories of human nature: Psychoanalysis The first formal ___________________________ to emerge was psychoanalysis, developed by Sigmund Freud. Psychoanalysis: Aims - Since psychological problems originate from childhood ________ ...
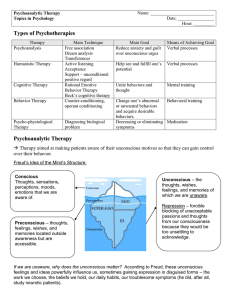
Psychoanalytic Therapy Notes
... The process, experienced by the patient, of feeling toward an analyst or therapist the way he or she feels or felt toward some other important figure in his or her life. Projective Tests – personality tests to uncover hidden emotions. Therapist presents vague stimuli and the patient “projects” hidde ...
... The process, experienced by the patient, of feeling toward an analyst or therapist the way he or she feels or felt toward some other important figure in his or her life. Projective Tests – personality tests to uncover hidden emotions. Therapist presents vague stimuli and the patient “projects” hidde ...
CHAPTER OBJECTIVES 17
... Give some reasons why clinicians tend to overestimate the effectiveness of psychotherapy, and describe two phenomena that contribute to clients’ and clinicians’ misperceptions in this area. ...
... Give some reasons why clinicians tend to overestimate the effectiveness of psychotherapy, and describe two phenomena that contribute to clients’ and clinicians’ misperceptions in this area. ...
CARFLEOPCarney
... denominator? I am increasingly convinced that underlying (it all) is a singular condition. Like the immune system dysfunction that underlies a myriad of medical symptoms, syndromes, and sicknesses, there is also a psychological condition that underlies a diverse array of learning and ...
... denominator? I am increasingly convinced that underlying (it all) is a singular condition. Like the immune system dysfunction that underlies a myriad of medical symptoms, syndromes, and sicknesses, there is also a psychological condition that underlies a diverse array of learning and ...
File
... Having children with an innate push to form attachments will also ensure the protection of the child (along with the gene). This is suggesting that attachments are inherited from parents and expressed regardless of the environment. ...
... Having children with an innate push to form attachments will also ensure the protection of the child (along with the gene). This is suggesting that attachments are inherited from parents and expressed regardless of the environment. ...
Chapter 14
... problems, such as bed-wetting, phobias, compulsions, marital problems, and sexual disorders. • Studies confirm that Cognitive Therapy is effective in coping with depression and reducing suicidal risks • Biomedical Therapy – is particularly essential for the treatment of the positive symptoms of ...
... problems, such as bed-wetting, phobias, compulsions, marital problems, and sexual disorders. • Studies confirm that Cognitive Therapy is effective in coping with depression and reducing suicidal risks • Biomedical Therapy – is particularly essential for the treatment of the positive symptoms of ...
Treatment of Abnormal Behavior
... a. Describe the central characteristics of psychotherapeutic intervention. b. Describe major treatment orientations used in therapy (e.g., behavioral, cognitive, humanistic) and how those orientations influence therapeutic planning. c. Compare and contrast different treatment formats (e.g., individu ...
... a. Describe the central characteristics of psychotherapeutic intervention. b. Describe major treatment orientations used in therapy (e.g., behavioral, cognitive, humanistic) and how those orientations influence therapeutic planning. c. Compare and contrast different treatment formats (e.g., individu ...
adolescence notes
... • The fear of strangers an infant displays around 8 months of age Lasts until approx. ...
... • The fear of strangers an infant displays around 8 months of age Lasts until approx. ...
Step Up To: Psychology
... • C) helping client learn how to test the reality of their automatic thoughts • D) creating a therapeutic climate of collaboration ...
... • C) helping client learn how to test the reality of their automatic thoughts • D) creating a therapeutic climate of collaboration ...
Chapter 4 Developmental
... Infancy/Childhood—brain development; maturation and motor development Cognitive development—Piaget and 4 stages of cognitive development—basic info Social development—Harlow’s theory, describe attachment theory and types of attachment, temperament and attachment Deprivation of attachment Erikson sta ...
... Infancy/Childhood—brain development; maturation and motor development Cognitive development—Piaget and 4 stages of cognitive development—basic info Social development—Harlow’s theory, describe attachment theory and types of attachment, temperament and attachment Deprivation of attachment Erikson sta ...
Ch 4 part 3 - My Teacher Pages
... Language Development • A Critical Period is a limited time in which an event can occur, usually to result in some kind of transformation. • If the organism does not receive the appropriate stimulus during this "critical period", it may be difficult, ultimately less successful, or even impossible, t ...
... Language Development • A Critical Period is a limited time in which an event can occur, usually to result in some kind of transformation. • If the organism does not receive the appropriate stimulus during this "critical period", it may be difficult, ultimately less successful, or even impossible, t ...
1 - NewarkPsychology
... Psychotherapy: (Talking) Emotionally charged interaction between a therapist and person with psychological difficulties Eclectic Approach: Therapeutic approach that uses techniques from multiple forms of therapy Psychoanalysis: Freudian use of free associations, dreams, projective tests to help subj ...
... Psychotherapy: (Talking) Emotionally charged interaction between a therapist and person with psychological difficulties Eclectic Approach: Therapeutic approach that uses techniques from multiple forms of therapy Psychoanalysis: Freudian use of free associations, dreams, projective tests to help subj ...