5 Early Atomic Theory and Structure Chapter Outline Early Theories
... 3. Atoms of different elements differ in their mass and size. 4. Compounds are formed by combining two or more atoms of different elements. 5. Atoms combine to form compounds in simple whole number ratios. ...
... 3. Atoms of different elements differ in their mass and size. 4. Compounds are formed by combining two or more atoms of different elements. 5. Atoms combine to form compounds in simple whole number ratios. ...
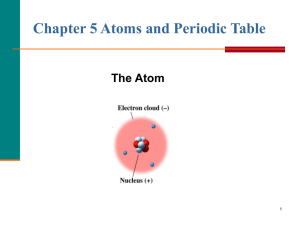
Chapter 4 Atoms and Elements
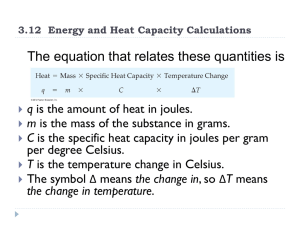
... the final temperature of the water? The specific heat of water is 4.184J Heat is transferred from the 90g of hot water to the 10g of cold water. Since the same amount of heat is transferred in both cases we can set the two q=mc(Tf-Ti) equations equal. ...
... the final temperature of the water? The specific heat of water is 4.184J Heat is transferred from the 90g of hot water to the 10g of cold water. Since the same amount of heat is transferred in both cases we can set the two q=mc(Tf-Ti) equations equal. ...
Isotopes of Hydrogen
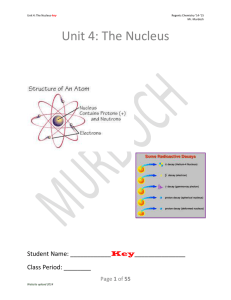
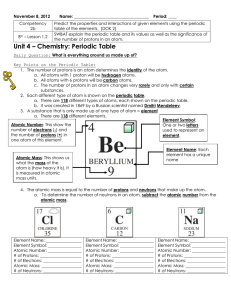
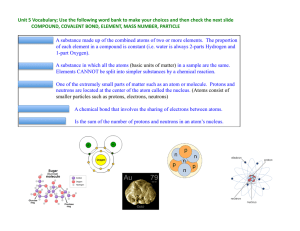
... Isotopes are atoms of the same elements that have different masses. The isotopes of a particular element all have the same number of protons and electrons but different numbers of neutrons. SECTION 3-3 OBJECTIVE 2 Define atomic number and mass number, and describe how they apply to isotopes. The Ato ...
... Isotopes are atoms of the same elements that have different masses. The isotopes of a particular element all have the same number of protons and electrons but different numbers of neutrons. SECTION 3-3 OBJECTIVE 2 Define atomic number and mass number, and describe how they apply to isotopes. The Ato ...
Chapter 3 Atoms and Elements
... Isotopes of Some Elements and Their Atomic Mass Most elements have two or more isotopes that contribute to the atomic mass of that element. ...
... Isotopes of Some Elements and Their Atomic Mass Most elements have two or more isotopes that contribute to the atomic mass of that element. ...
Historical Development of the Periodic Table
... increasing atomic mass. • This is known as his Periodic Law. Nevertheless he placed greater importance on properties than on atomic mass values. • He was able to predict, with great accuracy, the properties of the elements that should fit into the gaps he had left. ...
... increasing atomic mass. • This is known as his Periodic Law. Nevertheless he placed greater importance on properties than on atomic mass values. • He was able to predict, with great accuracy, the properties of the elements that should fit into the gaps he had left. ...
Historical Development of the Periodic Table Periodic Table of the
... increasing atomic mass. • This is known as his Periodic Law. Nevertheless he placed greater importance on properties than on atomic mass values. • He was able to predict, with great accuracy, the properties of the elements that should fit into the gaps he had left. ...
... increasing atomic mass. • This is known as his Periodic Law. Nevertheless he placed greater importance on properties than on atomic mass values. • He was able to predict, with great accuracy, the properties of the elements that should fit into the gaps he had left. ...
Units and Unit Conversions 6. Define the problem: If the nucleus
... Check your answers: Pounds and kilograms are both larger units than grams, so it makes sense that the number of kilograms and the number of pounds would be smaller than the number of grams. 32. Define the problem: Given the identity of an element (cobalt) and the atom’s mass number (60), find the nu ...
... Check your answers: Pounds and kilograms are both larger units than grams, so it makes sense that the number of kilograms and the number of pounds would be smaller than the number of grams. 32. Define the problem: Given the identity of an element (cobalt) and the atom’s mass number (60), find the nu ...
Isotopes
... all of the atoms of a given element were identical. This idea persisted for over 100 years, until James Chadwick discovered that the nuclei of most atoms contain neutrons as well as protons. (This is a good example of how a theory changes as new observations are made.) After the discovery of the neu ...
... all of the atoms of a given element were identical. This idea persisted for over 100 years, until James Chadwick discovered that the nuclei of most atoms contain neutrons as well as protons. (This is a good example of how a theory changes as new observations are made.) After the discovery of the neu ...
Intro to the Periodic Table
... a. All atoms with 1 proton will be hydrogen atoms. b. All atoms with 6 protons will be carbon atoms. c. The number of protons in an atom changes very rarely and only with certain substances. 2. Each different type of atom is shown on the periodic table. a. There are 118 different types of atoms, eac ...
... a. All atoms with 1 proton will be hydrogen atoms. b. All atoms with 6 protons will be carbon atoms. c. The number of protons in an atom changes very rarely and only with certain substances. 2. Each different type of atom is shown on the periodic table. a. There are 118 different types of atoms, eac ...
1.1 - cloudfront.net
... contains six electrons, allowing the atom to remain electrically neutral. However the number of neutrons varies from six to eight. Isotopes are atoms that have the same atomic number but different mass numbers due to a change in the number of neutrons. The three isotopes of carbon can be referred to ...
... contains six electrons, allowing the atom to remain electrically neutral. However the number of neutrons varies from six to eight. Isotopes are atoms that have the same atomic number but different mass numbers due to a change in the number of neutrons. The three isotopes of carbon can be referred to ...
- Orangefield ISD
... • 6(D) Use isotopic composition to calculate average atomic mass of an element. • 2(G) Express and manipulate chemical quantities using scientific conventions and mathematical procedures, including dimensional analysis, scientific notation, and significant figures. • 2(I) Communicate valid conclusi ...
... • 6(D) Use isotopic composition to calculate average atomic mass of an element. • 2(G) Express and manipulate chemical quantities using scientific conventions and mathematical procedures, including dimensional analysis, scientific notation, and significant figures. • 2(I) Communicate valid conclusi ...
Unit 2 Complete 2016 2017
... 1a. Description of each scientists’ contribution to the development of the atomic theory. 2. Law of conservation of mass/matter: matter cannot be created nor destroyed (Lavoisier). 3. Law of definite proportions: atoms combine in specific whole number ratios (Proust). 4. Law of multiple proportions: ...
... 1a. Description of each scientists’ contribution to the development of the atomic theory. 2. Law of conservation of mass/matter: matter cannot be created nor destroyed (Lavoisier). 3. Law of definite proportions: atoms combine in specific whole number ratios (Proust). 4. Law of multiple proportions: ...
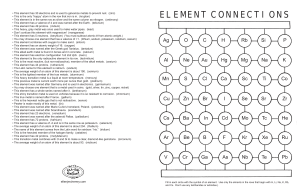
element connections
... • This element has 30 electrons and is used to galvanize metals to prevent rust. (zinc) • This is the only “happy” atom in the row that iron is in. (krypton) • This element is in the same row as silver and the same column as nitrogen. (antimony) • This element has a valence of 4 and was named after ...
... • This element has 30 electrons and is used to galvanize metals to prevent rust. (zinc) • This is the only “happy” atom in the row that iron is in. (krypton) • This element is in the same row as silver and the same column as nitrogen. (antimony) • This element has a valence of 4 and was named after ...
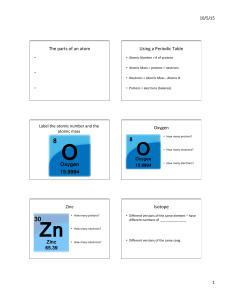
The parts of an atom - Norwell Public Schools
... • Atomic Mass = 2 • Atomic Number = 1 (stays the same as normal hydrogen because the protons stay the same) ...
... • Atomic Mass = 2 • Atomic Number = 1 (stays the same as normal hydrogen because the protons stay the same) ...
Matching - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
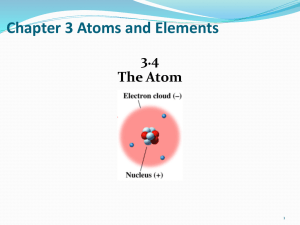
... a. Protons, electrons, and neutrons are evenly distributed throughout the volume of the atom. b. The nucleus is made of protons, electrons, and neutrons. c. Electrons are distributed around the nucleus and occupy almost all the volume of the atom. d. The nucleus is made of electrons and protons. ___ ...
... a. Protons, electrons, and neutrons are evenly distributed throughout the volume of the atom. b. The nucleus is made of protons, electrons, and neutrons. c. Electrons are distributed around the nucleus and occupy almost all the volume of the atom. d. The nucleus is made of electrons and protons. ___ ...
Symbols of Elements - Chemistry with Mr. Patmos
... In naturally occurring magnesium, there are three isotopes. Isotopes of Mg ...
... In naturally occurring magnesium, there are three isotopes. Isotopes of Mg ...
Name: Date:______ Period:____ Isotopes and Atomic Mass
... The name atom comes from the Greek word "ἄτομος"—átomos, which means uncuttable or indivisible, something that cannot be divided further. The concept of an atom as an indivisible component of matter was first proposed by early Indian and Greek philosophers. In the 17th and 18th centuries, chemists p ...
... The name atom comes from the Greek word "ἄτομος"—átomos, which means uncuttable or indivisible, something that cannot be divided further. The concept of an atom as an indivisible component of matter was first proposed by early Indian and Greek philosophers. In the 17th and 18th centuries, chemists p ...
Review Unit 5
... CHEMICALLY STABLE: Elements that are nonreactive because their last electron shell is completely filled with 8 electrons. (e.g. Neon, Argon, Krypton.) ISOTOPE: ...
... CHEMICALLY STABLE: Elements that are nonreactive because their last electron shell is completely filled with 8 electrons. (e.g. Neon, Argon, Krypton.) ISOTOPE: ...
Atoms, Isotopes, and Ions.pptx
... • Atomic Number = 1 (stays the same as normal hydrogen because the protons stay the same) ...
... • Atomic Number = 1 (stays the same as normal hydrogen because the protons stay the same) ...
Ch 3 Sec 3 Highlighted
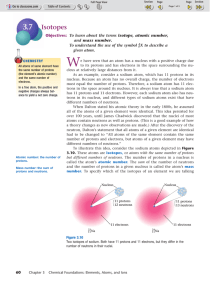
... and tells you how many protons it has, and how many electrons it has. If you want to know which element has atomic number 47 look at the periodic table it is silver, Ag. All silver atoms contain 47 protons in their nuclei. Because atoms are neutral, we know from the atomic number that all silver ato ...
... and tells you how many protons it has, and how many electrons it has. If you want to know which element has atomic number 47 look at the periodic table it is silver, Ag. All silver atoms contain 47 protons in their nuclei. Because atoms are neutral, we know from the atomic number that all silver ato ...
Chapter 3 Atoms and Elements
... Calculating Atomic Mass The calculation for atomic mass requires the • percent(%) abundance of each isotope. • atomic mass of each isotope of that element. • sum of the weighted averages. ...
... Calculating Atomic Mass The calculation for atomic mass requires the • percent(%) abundance of each isotope. • atomic mass of each isotope of that element. • sum of the weighted averages. ...
Periodicity - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... THE ORIGINS OF NATURALLY OCCURING ELEMENTS Natural and synthetic elements are created in different ways ...
... THE ORIGINS OF NATURALLY OCCURING ELEMENTS Natural and synthetic elements are created in different ways ...
What`s Inside an Element
... Cut the colored paper (to match colors of periodic table) into square shapes about 2/3 to 1/2 size of the front of the tri-fold. Using the periodic table as a guide, copy the information from an element onto the colored piece of paper (atomic number, symbol, name, atomic mass). Put glue on back 1/2 ...
... Cut the colored paper (to match colors of periodic table) into square shapes about 2/3 to 1/2 size of the front of the tri-fold. Using the periodic table as a guide, copy the information from an element onto the colored piece of paper (atomic number, symbol, name, atomic mass). Put glue on back 1/2 ...
Einsteinium

Einsteinium is a synthetic element with symbol Es and atomic number 99. It is the seventh transuranic element, and an actinide.Einsteinium was discovered as a component of the debris of the first hydrogen bomb explosion in 1952, and named after Albert Einstein. Its most common isotope einsteinium-253 (half life 20.47 days) is produced artificially from decay of californium-253 in a few dedicated high-power nuclear reactors with a total yield on the order of one milligram per year. The reactor synthesis is followed by a complex process of separating einsteinium-253 from other actinides and products of their decay. Other isotopes are synthesized in various laboratories, but at much smaller amounts, by bombarding heavy actinide elements with light ions. Owing to the small amounts of produced einsteinium and the short half-life of its most easily produced isotope, there are currently almost no practical applications for it outside of basic scientific research. In particular, einsteinium was used to synthesize, for the first time, 17 atoms of the new element mendelevium in 1955.Einsteinium is a soft, silvery, paramagnetic metal. Its chemistry is typical of the late actinides, with a preponderance of the +3 oxidation state; the +2 oxidation state is also accessible, especially in solids. The high radioactivity of einsteinium-253 produces a visible glow and rapidly damages its crystalline metal lattice, with released heat of about 1000 watts per gram. Difficulty in studying its properties is due to einsteinium-253's conversion to berkelium and then californium at a rate of about 3% per day. The isotope of einsteinium with the longest half life, einsteinium-252 (half life 471.7 days) would be more suitable for investigation of physical properties, but it has proven far more difficult to produce and is available only in minute quantities, and not in bulk. Einsteinium is the element with the highest atomic number which has been observed in macroscopic quantities in its pure form, and this was the common short-lived isotope einsteinium-253.Like all synthetic transuranic elements, isotopes of einsteinium are very radioactive and are considered highly dangerous to health on ingestion.