Chapter_6_Phases_and_Gas_Laws
... Ex: A mixture has 40 atmospheres of O2 and 60 moles of N2 at 25C. What is the total pressure exerted by the mixture? ...
... Ex: A mixture has 40 atmospheres of O2 and 60 moles of N2 at 25C. What is the total pressure exerted by the mixture? ...
Topic 3.3 Kinetic Model of Ideal Gas
... walls more often. The force from each molecule remains the same, but an increased number of collisions in a given time means that the pressure increases. 3. Ideal gases increase in pressure when their temperature increases. The increased temperature means the molecules are moving faster, and thus th ...
... walls more often. The force from each molecule remains the same, but an increased number of collisions in a given time means that the pressure increases. 3. Ideal gases increase in pressure when their temperature increases. The increased temperature means the molecules are moving faster, and thus th ...
Word - IPFW
... of particles, Newton’s second law, energy and momentum methods. Systems of particles. Kinematics and plane motion of rigid bodies, forces and accelerations, energy and momentum methods. Introduction to mechanical vibrations. ...
... of particles, Newton’s second law, energy and momentum methods. Systems of particles. Kinematics and plane motion of rigid bodies, forces and accelerations, energy and momentum methods. Introduction to mechanical vibrations. ...
ch 12- states of matter
... A piece of metal with a mass of 35.0 g and a temperature of 100.0 C is placed into 105.0 g of water at a temperature of 25.0C. After the metal cools the final temperature of the system is 31.5 C. What is the specific heat of the metal? ...
... A piece of metal with a mass of 35.0 g and a temperature of 100.0 C is placed into 105.0 g of water at a temperature of 25.0C. After the metal cools the final temperature of the system is 31.5 C. What is the specific heat of the metal? ...
T h - Website Staff UI
... H2 = H + CP(T2-T1) assume CP,i constant wrt T H (273) = Ho(298) + CP(H2O,g) - CP (H2O,l)(273-298) ...
... H2 = H + CP(T2-T1) assume CP,i constant wrt T H (273) = Ho(298) + CP(H2O,g) - CP (H2O,l)(273-298) ...
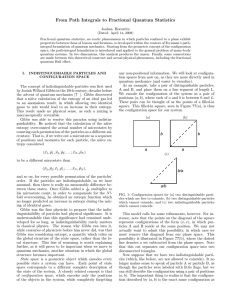
The role of angular momentum conservation law in statistical
... As shown in [1,2] the statistical mechanics of charged particles gas in magnetic field can be formulated without paradoxes if the density of distribution (or the statistical operator in quantum theory) is considered to be also dependent on the angular momentum. The role of various motion integrals i ...
... As shown in [1,2] the statistical mechanics of charged particles gas in magnetic field can be formulated without paradoxes if the density of distribution (or the statistical operator in quantum theory) is considered to be also dependent on the angular momentum. The role of various motion integrals i ...
Elementary gas kinetic theory.
... random motion. Such systems of randomly moving particles are described by statistical mechanics. ...
... random motion. Such systems of randomly moving particles are described by statistical mechanics. ...