dx cx dx and x - Cameron University
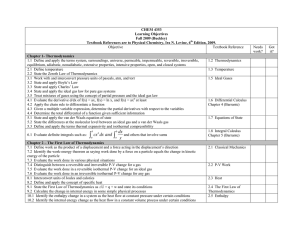
... Chapter 7 – One-Component Phase Equilibrium and Surfaces 30.1 State the phase rule 30.2 Define the terms phase, component, and degree of freedom 30.3 Apply the phase rule to physical systems 31.1 Given sufficient information, construct a one-component phase diagram 31.2 Interpret regions of the one- ...
... Chapter 7 – One-Component Phase Equilibrium and Surfaces 30.1 State the phase rule 30.2 Define the terms phase, component, and degree of freedom 30.3 Apply the phase rule to physical systems 31.1 Given sufficient information, construct a one-component phase diagram 31.2 Interpret regions of the one- ...
Document
... Effect of Volume and Temperature Change on the System • If we increase volume, there are more positions possible for the molecules. This results in more microstates, so increased entropy. • If we increase temperature, the average kinetic energy increases. This results in a greater distribution of m ...
... Effect of Volume and Temperature Change on the System • If we increase volume, there are more positions possible for the molecules. This results in more microstates, so increased entropy. • If we increase temperature, the average kinetic energy increases. This results in a greater distribution of m ...
Review - The University of Texas at Dallas
... entropies of system and surrounding can decrease as long as their sum does not. TSUniverse = T Ssystem + T Ssurroundings – G T SUniverse = T Ssystem – Hsystem Free Energy, G = H – TS, must decrease ...
... entropies of system and surrounding can decrease as long as their sum does not. TSUniverse = T Ssystem + T Ssurroundings – G T SUniverse = T Ssystem – Hsystem Free Energy, G = H – TS, must decrease ...
Computational simulation of Molecular dynamics
... Argon and other inert gases) The parameters in the LJ potential have to be extracted from experimental data Not predicted from first principle Different system has different values of a, b, k System of different interactions may not be described by the LJ potential – other empirical form of potentia ...
... Argon and other inert gases) The parameters in the LJ potential have to be extracted from experimental data Not predicted from first principle Different system has different values of a, b, k System of different interactions may not be described by the LJ potential – other empirical form of potentia ...
Ideal gas
... the volume occupied by an ideal gas is proportional to the amount of moles (or molecules) present in the container. Graham's law: the rate at which gas molecules diffuse is inversely proportional to the square root of its density. Combined with Avogadro's law (i.e. since equal volumes have equal num ...
... the volume occupied by an ideal gas is proportional to the amount of moles (or molecules) present in the container. Graham's law: the rate at which gas molecules diffuse is inversely proportional to the square root of its density. Combined with Avogadro's law (i.e. since equal volumes have equal num ...
Pre-AP Chemistry Kinetic Theory and Heat Quiz
... 1. According to the kinetic theory, the primary difference in the phases of matter (of the same substance) is the __speed_ of the particles. Thus, the two factors that influence which state of matter exists are __pressure_ and temperature. 2. The higher the energy of the particles, the faster they m ...
... 1. According to the kinetic theory, the primary difference in the phases of matter (of the same substance) is the __speed_ of the particles. Thus, the two factors that influence which state of matter exists are __pressure_ and temperature. 2. The higher the energy of the particles, the faster they m ...