Greece Notes Student
... Only a small minority The art of memory was Socrates claimed This required the learner The main subjects of Greek education were Greek Religion In the religion of ancient Greece, there was no The Greeks generally did not believe Greek Writers and Thinkers Drama Drama in Athens brought together Drama ...
... Only a small minority The art of memory was Socrates claimed This required the learner The main subjects of Greek education were Greek Religion In the religion of ancient Greece, there was no The Greeks generally did not believe Greek Writers and Thinkers Drama Drama in Athens brought together Drama ...
chapter 4 - Lone Star College
... b. brought to an end the hopes of those who were prospering from expanded commercial ...
... b. brought to an end the hopes of those who were prospering from expanded commercial ...
Beginnings of Ancient Greek Civilization
... The “Minoans” developed a great civilization on Crete. ...
... The “Minoans” developed a great civilization on Crete. ...
Chapter 11 The Ancient Greeks
... each other, that is why there were many individual city-states Due to closeness of sea, Greeks traveled and others traveled to Greece ...
... each other, that is why there were many individual city-states Due to closeness of sea, Greeks traveled and others traveled to Greece ...
Classical Greece
... Greece produced groundbreaking art and literature that is still considered relevant. ARCHITECTURE AND SCULPTURE Most important form the temple Columns that were once made of wood and then marble Famous building in Athens the Parthenon example of a classical Greek temple, dedicated to Athen ...
... Greece produced groundbreaking art and literature that is still considered relevant. ARCHITECTURE AND SCULPTURE Most important form the temple Columns that were once made of wood and then marble Famous building in Athens the Parthenon example of a classical Greek temple, dedicated to Athen ...
The Rise of Greek Civilization
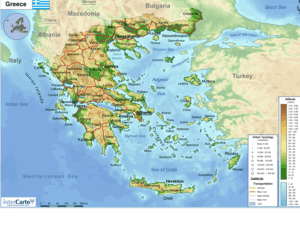
... smashed it to pieces. Some pieces drifted away forming rocky islands. Others barely cling to the mainland. Because of these shapes, Greece is a country made up of peninsulas – area of land surrounded by water on three sides. ...
... smashed it to pieces. Some pieces drifted away forming rocky islands. Others barely cling to the mainland. Because of these shapes, Greece is a country made up of peninsulas – area of land surrounded by water on three sides. ...
Greek City States
... and lasted for about one hundred years. Over time, trade began to grow between the peoples of Greece. Marketplaces grew up in Greek villages and communities began to gather together into large defensive units, building fortifications to use in common. Hundreds of city-states formed in ancient Greece ...
... and lasted for about one hundred years. Over time, trade began to grow between the peoples of Greece. Marketplaces grew up in Greek villages and communities began to gather together into large defensive units, building fortifications to use in common. Hundreds of city-states formed in ancient Greece ...
1 Greece Notes 2016
... considered harsh and cruel, rather they were seen as leaders who would work for the interests of the ordinary people. ...
... considered harsh and cruel, rather they were seen as leaders who would work for the interests of the ordinary people. ...
Greece Test 2010
... C. They were focused on the rights and pleasure of the individual D. They did not practice any form of slavery. In 500 bc, the only thing that stood in the way of Persia taking over all of Europe was: A. Deserts B. Greece C. Oceans D. Jungles Which of the following shows us that the Minoans were obs ...
... C. They were focused on the rights and pleasure of the individual D. They did not practice any form of slavery. In 500 bc, the only thing that stood in the way of Persia taking over all of Europe was: A. Deserts B. Greece C. Oceans D. Jungles Which of the following shows us that the Minoans were obs ...
Ancient Greece Geography and Religion
... development of city-states. What is a city-state? City-states are small communities formed instead of one united Greece. ...
... development of city-states. What is a city-state? City-states are small communities formed instead of one united Greece. ...
geography - Humble ISD
... • ___________________ - mountains separated different areas from one another. • ___________________- most are dry a good part of the year. • Only _____________ of Land can be ___________________ - forced Greeks outward to find food. • Excellent ___________________- led to trade and colonization Beca ...
... • ___________________ - mountains separated different areas from one another. • ___________________- most are dry a good part of the year. • Only _____________ of Land can be ___________________ - forced Greeks outward to find food. • Excellent ___________________- led to trade and colonization Beca ...
ch 5.1 cultures of mountains and seas - mrs
... – What would their names be? – Be prepared to share with the class ...
... – What would their names be? – Be prepared to share with the class ...
on Greek mainland
... Mesopotamian influences that they passed on to later Greeks. They traded with Sicily, Italy, Egypt, Mesopotamia, and the Phoenicians, considered to be the greatest sea-trading people of the ancient world, who invented a 22-letter alphabet from which the Greek alphabet was adapted. Greek poet, Homer, ...
... Mesopotamian influences that they passed on to later Greeks. They traded with Sicily, Italy, Egypt, Mesopotamia, and the Phoenicians, considered to be the greatest sea-trading people of the ancient world, who invented a 22-letter alphabet from which the Greek alphabet was adapted. Greek poet, Homer, ...
Chapter 4 Study Guide Athens – focused on government and
... Upper-‐class Athenian women – could not leave home without a male relative Strait – narrow body of water with land on both sides Athenian soldiers -‐ group that promised to pass on their fatherland ...
... Upper-‐class Athenian women – could not leave home without a male relative Strait – narrow body of water with land on both sides Athenian soldiers -‐ group that promised to pass on their fatherland ...
chapter 4 sg - Mr. Vakselis LA/SS Blog
... Upper-class Athenian women – could not leave home without a male relative Strait – narrow body of water with land on both sides Athenian soldiers - group that promised to pass on their fatherland in a better condition Herodotus – wrote The History of the Persian Wars Mycenaeans- came to Greece from ...
... Upper-class Athenian women – could not leave home without a male relative Strait – narrow body of water with land on both sides Athenian soldiers - group that promised to pass on their fatherland in a better condition Herodotus – wrote The History of the Persian Wars Mycenaeans- came to Greece from ...
Chapter 5 Ancient Greece p. 102 Section 1 early people of the
... Sea traders – Italy, Sicily, Egypt and Mesopotamia. Carried home info and technology to their own people – had a system of writing that is later developed into written Greek probably acquired from their travels (Phoenicians) Lived in separate city-states on the Peloponnesus Heavily fortified cities ...
... Sea traders – Italy, Sicily, Egypt and Mesopotamia. Carried home info and technology to their own people – had a system of writing that is later developed into written Greek probably acquired from their travels (Phoenicians) Lived in separate city-states on the Peloponnesus Heavily fortified cities ...
Chapter 4 homework
... b. Battle and hunting scenes dominate their art. c. Ares, god of war, was their patron deity. d. They buried their dead with armor and weapons. 8. What new architectural form did the Mycenaeans develop to bury their kings? a. the catacomb b. the dolmen c. the necropolis d. the tholos 9. All of the f ...
... b. Battle and hunting scenes dominate their art. c. Ares, god of war, was their patron deity. d. They buried their dead with armor and weapons. 8. What new architectural form did the Mycenaeans develop to bury their kings? a. the catacomb b. the dolmen c. the necropolis d. the tholos 9. All of the f ...
Chapter 4 homework (2)
... b. add length and drama. c. fit a given name into the line’s meter. d. maintain the rhyme in the heroic couplets. 11. In the Iliad, why does Achilles become angry with the Greek leader Agamemnon and withdraw from the Trojan War? a. Agamemnon takes the beautiful Briseis from Achilles. b. Agamemnon na ...
... b. add length and drama. c. fit a given name into the line’s meter. d. maintain the rhyme in the heroic couplets. 11. In the Iliad, why does Achilles become angry with the Greek leader Agamemnon and withdraw from the Trojan War? a. Agamemnon takes the beautiful Briseis from Achilles. b. Agamemnon na ...
1 Greece Notes 2016 AK
... 1. Spread of ideas or technology from one culture to another. a. Two major types: i. diffusion through choice (want to adopt new concept) ii. diffusion by coercion (forced to adopt by war or domination) The Trojan War 1. During the 1200s BCE, the Mycenaeans fought a ten-year war against Troy. 2. Las ...
... 1. Spread of ideas or technology from one culture to another. a. Two major types: i. diffusion through choice (want to adopt new concept) ii. diffusion by coercion (forced to adopt by war or domination) The Trojan War 1. During the 1200s BCE, the Mycenaeans fought a ten-year war against Troy. 2. Las ...
World History 6/11 Exam
... b.) Rebelled against the Persians c.) Admired the Persians d.) Perished 30.)Which of the following is not a component of a typical Athenian house? a.) Two main rooms b.) Several small rooms c.) A courtyard d.) A basement 31.) What event led to the decline of Greek population and caused many City-Sta ...
... b.) Rebelled against the Persians c.) Admired the Persians d.) Perished 30.)Which of the following is not a component of a typical Athenian house? a.) Two main rooms b.) Several small rooms c.) A courtyard d.) A basement 31.) What event led to the decline of Greek population and caused many City-Sta ...
16- Cultures of the Mountains and the Sea Geography Shapes
... Mediterranean Sea. It also included about 2,000 islands in the Aegean (ih•JEE•uhn) and Ionian (eye•OH•nee•uhn) seas. Lands on the eastern edge of the Aegean were also part of ancient Greece. The region's physical geography directly shaped Greek traditions and customs. The sea shaped Greek civilizati ...
... Mediterranean Sea. It also included about 2,000 islands in the Aegean (ih•JEE•uhn) and Ionian (eye•OH•nee•uhn) seas. Lands on the eastern edge of the Aegean were also part of ancient Greece. The region's physical geography directly shaped Greek traditions and customs. The sea shaped Greek civilizati ...
TOURISM IN GREECE Greece is one of the most popular
... Greece is one of the most popular destinations worldwide as it attracts more than 2 million tourists annually. Here are some of Greece most popular tourists attractions: THE PARTHENON The Parthenon is a former temple on the Athenian Acropolis dedicated to the goddess Athena, whom the people of Athen ...
... Greece is one of the most popular destinations worldwide as it attracts more than 2 million tourists annually. Here are some of Greece most popular tourists attractions: THE PARTHENON The Parthenon is a former temple on the Athenian Acropolis dedicated to the goddess Athena, whom the people of Athen ...
Dorians
The Dorians (/ˈdɔriənz, ˈdɔər-/; Greek: Δωριεῖς, Dōrieis, singular Δωριεύς, Dōrieus) were one of the four major ethnic groups among which the Hellenes (or Greeks) of Classical Greece considered themselves divided (along with the Aeolians, Achaeans and Ionians). They are almost always referred to as just ""the Dorians"", as they are in the earliest literary mention of them in Odyssey, where they already can be found inhabiting the island of Crete.They were diverse in way of life and social organization, varying from the populous trade center of the city of Corinth, known for its ornate style in art and architecture, to the isolationist, military state of Sparta. And yet, all Hellenes knew which localities were Dorian, and which were not. Dorian states at war could more likely, but not always, count on the assistance of other Dorian states. Dorians were distinguished by the Doric Greek dialect and by characteristic social and historical traditions.In the 5th century BC, Dorians and Ionians were the two most politically important Greek ethne, whose ultimate clash resulted in the Peloponnesian War. The degree to which fifth-century Hellenes self-identified as ""Ionian"" or ""Dorian"" has itself been disputed. At one extreme Édouard Will concludes that there was no true ethnic component in fifth-century Greek culture, in spite of anti-Dorian elements in Athenian propaganda. At the other extreme John Alty reinterprets the sources to conclude that ethnicity did motivate fifth-century actions. Moderns viewing these ethnic identifications through the fifth- and fourth-century BC literary tradition have been profoundly influenced by their own social politics. Also, according to E.N. Tigerstedt, nineteenth-century European admirers of virtues they considered ""Dorian"" identified themselves as ""Laconophile"" and found responsive parallels in the culture of their day as well; their biases contribute to the traditional modern interpretation of ""Dorians"".