Chapter 8 Reading Guide Name: AP Chemistry 2016
... Understanding the arrangement of the elements in the periodic table is key foundational knowledge in chemistry. The relationships and patterns observed explain trends of the elements. The emphasis in AP Chemistry is the explanation of the concepts, not memorizing trends. For example, the size of the ...
... Understanding the arrangement of the elements in the periodic table is key foundational knowledge in chemistry. The relationships and patterns observed explain trends of the elements. The emphasis in AP Chemistry is the explanation of the concepts, not memorizing trends. For example, the size of the ...
HS standard 4 2017
... Sr behaves MOST like magnesium because it is in the same family, the alkaline earth metals. Members of the same family have the same number of valence electrons; this is an important reason why they behave alike. 17) A researcher is trying to create a new super conductive wire. Which category on the ...
... Sr behaves MOST like magnesium because it is in the same family, the alkaline earth metals. Members of the same family have the same number of valence electrons; this is an important reason why they behave alike. 17) A researcher is trying to create a new super conductive wire. Which category on the ...
Document
... periodic table. Locate and name the four blocks of the periodic table, as well as explain the reason for these names. Discuss the relationship between group configurations and group numbers. Describe the locations in the periodic table and the general properties of the alkali metals, the alkal ...
... periodic table. Locate and name the four blocks of the periodic table, as well as explain the reason for these names. Discuss the relationship between group configurations and group numbers. Describe the locations in the periodic table and the general properties of the alkali metals, the alkal ...
The Periodic Table and Periodic Law
... • The metals of the p block are generally harder and denser than the s-block alkaline-earth metals, but softer and less dense than the dblock metals. • The Noble Gases round out the p block elements and are in general, very un-reactive or inert gases. We have no known compounds of He, Ne, and Ar. ...
... • The metals of the p block are generally harder and denser than the s-block alkaline-earth metals, but softer and less dense than the dblock metals. • The Noble Gases round out the p block elements and are in general, very un-reactive or inert gases. We have no known compounds of He, Ne, and Ar. ...
Topic 3-Periodicity
... Essential idea: The arrangement of elements in the periodic table helps to predict their electron configuration. 3.1 Periodic table Nature of science: Obtain evidence for scientific theories by making and testing predictions based on them—scientists organize subjects based on structure and function; ...
... Essential idea: The arrangement of elements in the periodic table helps to predict their electron configuration. 3.1 Periodic table Nature of science: Obtain evidence for scientific theories by making and testing predictions based on them—scientists organize subjects based on structure and function; ...
Periodicity PPt
... The energy required to remove an efrom an atom. The larger the atom, the less energy is required because the e- are farther from the positive center. As atoms get larger ionization energy decreases because of the shielding effect (which says that the farther an electron is from the nucleus, the ...
... The energy required to remove an efrom an atom. The larger the atom, the less energy is required because the e- are farther from the positive center. As atoms get larger ionization energy decreases because of the shielding effect (which says that the farther an electron is from the nucleus, the ...
First Term Science Al-Karma Language School Prep 2 Question (1
... weight, while Moseley arranged them ascending according to atomic number. 10)-Calcium (Ca) and Magnesium (Mg) elements are examples of alkaline earth metals. 11)-The valency energy level of halogen contains seven electrons, while that of alkaline earth metal has two electrons. 12)-Sodium and potassi ...
... weight, while Moseley arranged them ascending according to atomic number. 10)-Calcium (Ca) and Magnesium (Mg) elements are examples of alkaline earth metals. 11)-The valency energy level of halogen contains seven electrons, while that of alkaline earth metal has two electrons. 12)-Sodium and potassi ...
Learn About the Different Types of Elements on the Periodic Table
... Trends in the Periodic Table The properties of the elements exhibit trends. These trends can be predicted using the periodic table and can be explained and understood by analyzing the electron configurations of the elements. Elements tend to gain or lose valence electrons to achieve stable octet for ...
... Trends in the Periodic Table The properties of the elements exhibit trends. These trends can be predicted using the periodic table and can be explained and understood by analyzing the electron configurations of the elements. Elements tend to gain or lose valence electrons to achieve stable octet for ...
Powerpoint for Periodicity and Density
... The energy required to remove an efrom an atom. The larger the atom, the less energy is required because the e- are farther from the positive center. As atoms get larger ionization energy decreases because of the shielding effect (which says that the farther an electron is from the nucleus, the ...
... The energy required to remove an efrom an atom. The larger the atom, the less energy is required because the e- are farther from the positive center. As atoms get larger ionization energy decreases because of the shielding effect (which says that the farther an electron is from the nucleus, the ...
Slider Metals - slider-chemistry-11
... The order of elements was re-arranged if their properties dictated it, eg, tellurium is heavier than iodine but comes before it in the Periodic Table. Mendeleev's Periodic Table was important because it enabled the properties of elements to be predicted by means of the 'periodic law': properties of ...
... The order of elements was re-arranged if their properties dictated it, eg, tellurium is heavier than iodine but comes before it in the Periodic Table. Mendeleev's Periodic Table was important because it enabled the properties of elements to be predicted by means of the 'periodic law': properties of ...
8.3 Metals - slider-chemistry-11
... The order of elements was re-arranged if their properties dictated it, eg, tellurium is heavier than iodine but comes before it in the Periodic Table. Mendeleev's Periodic Table was important because it enabled the properties of elements to be predicted by means of the 'periodic law': properties of ...
... The order of elements was re-arranged if their properties dictated it, eg, tellurium is heavier than iodine but comes before it in the Periodic Table. Mendeleev's Periodic Table was important because it enabled the properties of elements to be predicted by means of the 'periodic law': properties of ...
Slider Metals - slider-chemistry-11
... The order of elements was re-arranged if their properties dictated it, eg, tellurium is heavier than iodine but comes before it in the Periodic Table. Mendeleev's Periodic Table was important because it enabled the properties of elements to be predicted by means of the 'periodic law': properties of ...
... The order of elements was re-arranged if their properties dictated it, eg, tellurium is heavier than iodine but comes before it in the Periodic Table. Mendeleev's Periodic Table was important because it enabled the properties of elements to be predicted by means of the 'periodic law': properties of ...
PROFESSIONAL LEARNING COMMUNITY MODEL FOR ENTRY
... Dmitri Mendeleev, the Russian professor and chemist, is credited with conceptualizing the first periodic table. Mendeleev overcame sickness and strife in his youth to become a professor at Saint Petersburg State University. After becoming a teacher, he wrote the Principles of Chemistry (18681870). " ...
... Dmitri Mendeleev, the Russian professor and chemist, is credited with conceptualizing the first periodic table. Mendeleev overcame sickness and strife in his youth to become a professor at Saint Petersburg State University. After becoming a teacher, he wrote the Principles of Chemistry (18681870). " ...
Unit 5 – The Periodic Table
... How is the periodic table arranged? How does periodicity explain the chemical and physical properties of the elements? How can chemical and physical properties of the elements be predicted based on their positions in the periodic table? ...
... How is the periodic table arranged? How does periodicity explain the chemical and physical properties of the elements? How can chemical and physical properties of the elements be predicted based on their positions in the periodic table? ...
Metals
... Ch9.5 Naming Acids and Bases (Discuss these in more detail later) Acids: A compound that contains one or more hydrogen atoms and produces hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water. (The names of compounds can change when acids are present). The name of an acidic compound depends on the type of a ...
... Ch9.5 Naming Acids and Bases (Discuss these in more detail later) Acids: A compound that contains one or more hydrogen atoms and produces hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water. (The names of compounds can change when acids are present). The name of an acidic compound depends on the type of a ...
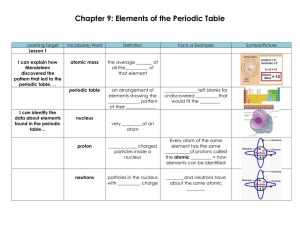
Chapter 9: Elements of the Periodic Table
... I can explain how Mendeleev discovered the pattern that led to the periodic table. . . Mendeleev noticed a ____________ of properties in elements arranged by increasing atomic ___________________. I can identify the data about elements found in the periodic table… The periodic table includes each el ...
... I can explain how Mendeleev discovered the pattern that led to the periodic table. . . Mendeleev noticed a ____________ of properties in elements arranged by increasing atomic ___________________. I can identify the data about elements found in the periodic table… The periodic table includes each el ...
Chapter 5: What you should know when you finish. Describe the
... Magnesium and calcium have essential biological functions and they provide materials used in construction and transportation. Magnesium plays a key role in the process that uses sunlight to produce sugar in plants A mixture of magnesium and other metals can be as strong as steel, but much ligh ...
... Magnesium and calcium have essential biological functions and they provide materials used in construction and transportation. Magnesium plays a key role in the process that uses sunlight to produce sugar in plants A mixture of magnesium and other metals can be as strong as steel, but much ligh ...
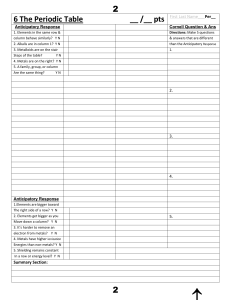
6 The Periodic Tableааааааааааааааааааааааааа__ /__ pts First
... ________ 10. In his periodic table, Mendeleev arranged the elements in order of atomic number. ________ 11. There are six periods in a periodic table. ________ 12. Most of the elements in the periodic table are metals. ________ 13. The elements within a period have similar properties. ...
... ________ 10. In his periodic table, Mendeleev arranged the elements in order of atomic number. ________ 11. There are six periods in a periodic table. ________ 12. Most of the elements in the periodic table are metals. ________ 13. The elements within a period have similar properties. ...
B - SchoolRack
... Across a period of eight elements in the periodic table, the number of valence electrons – F ...
... Across a period of eight elements in the periodic table, the number of valence electrons – F ...
Unit Six: Atomic structure
... time, there were only 60 known element and Mendeleev organized them according to their atomic mass. Mendeleev was able to predict the properties of missing elements which were later discovered. These elements fit perfectly in the missing gaps. 2. Henry Mosely later rearranged the periodic table base ...
... time, there were only 60 known element and Mendeleev organized them according to their atomic mass. Mendeleev was able to predict the properties of missing elements which were later discovered. These elements fit perfectly in the missing gaps. 2. Henry Mosely later rearranged the periodic table base ...
chapter 7- periodic properties of the elements
... • For p block metals- They will either lose just the outer p electrons, or both the outer s and p electrons • Al3+ - what block did the electrons this metal lost belong to? • Sn2+ - what block did the electrons this metal lost belong to? • Sn4+- what block did the electrons this metal lost belong t ...
... • For p block metals- They will either lose just the outer p electrons, or both the outer s and p electrons • Al3+ - what block did the electrons this metal lost belong to? • Sn2+ - what block did the electrons this metal lost belong to? • Sn4+- what block did the electrons this metal lost belong t ...
Unit 3: The Periodic Table
... 3. Identify and state the properties, including physical state, of metals, metalloids, and non-metals. 4. Distinguish between the terms groups or families and periods. 5. Relate the position of any main group element in the periodic table to its number of valence electrons and ...
... 3. Identify and state the properties, including physical state, of metals, metalloids, and non-metals. 4. Distinguish between the terms groups or families and periods. 5. Relate the position of any main group element in the periodic table to its number of valence electrons and ...
File
... 5) Metals are placed on the left side and the nonmetals are placed on the right . Q9)Discuss the position of hydrogen in the periodic table OR –how does hydrogen resemble alkali metals and halogens in its properties Ans 9)Hydrogen has single electron in its valence shell and forms a positively charg ...
... 5) Metals are placed on the left side and the nonmetals are placed on the right . Q9)Discuss the position of hydrogen in the periodic table OR –how does hydrogen resemble alkali metals and halogens in its properties Ans 9)Hydrogen has single electron in its valence shell and forms a positively charg ...
the periodic table
... • Atomic masses were known in comparison to hydrogen, which was set as "1" ...
... • Atomic masses were known in comparison to hydrogen, which was set as "1" ...