Li K-edge XANES and Li(1s) XPS Spectra of Lithium Compounds
... alloyed with aluminum and magnesium for lightweight, high-performance metals for aircraft. Lithium reacts slowly with water to form a colorless solution of lithium hydroxide and molecular hydrogen and vigorously with all halogens to form halides. In four lithium halides, lithium fluoride is insolubl ...
... alloyed with aluminum and magnesium for lightweight, high-performance metals for aircraft. Lithium reacts slowly with water to form a colorless solution of lithium hydroxide and molecular hydrogen and vigorously with all halogens to form halides. In four lithium halides, lithium fluoride is insolubl ...
Unit Expectations – Periodic Table
... 1. How is the periodic table organized and how does that organization maximize the periodic table’s usefulness? 2. What similar properties do major groups (alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, transition metals, inner transition metals, halogens, noble gases) in the periodic table share? 3. How do ...
... 1. How is the periodic table organized and how does that organization maximize the periodic table’s usefulness? 2. What similar properties do major groups (alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, transition metals, inner transition metals, halogens, noble gases) in the periodic table share? 3. How do ...
File - dr. stephen alfred
... Atoms will often take, give, or share electrons with other atoms in order to have a complete set of electrons in their outer energy level. Elements whose atoms undergo such processes are called Reactive and can combine to form compounds. Since “Groups” [columns] are similar because they have the sam ...
... Atoms will often take, give, or share electrons with other atoms in order to have a complete set of electrons in their outer energy level. Elements whose atoms undergo such processes are called Reactive and can combine to form compounds. Since “Groups” [columns] are similar because they have the sam ...
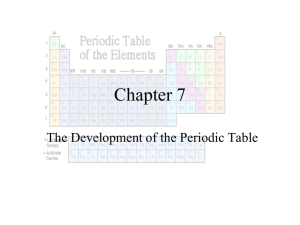
Chapter 7 The Development of the Periodic Table
... • Elements that are reactive bond easily with other elements to make compounds. • Some elements are only found in nature bonded with other elements. • What makes an element reactive? – An incomplete valence electron level. – All atoms (except hydrogen) want to have 8 electrons in their very outermos ...
... • Elements that are reactive bond easily with other elements to make compounds. • Some elements are only found in nature bonded with other elements. • What makes an element reactive? – An incomplete valence electron level. – All atoms (except hydrogen) want to have 8 electrons in their very outermos ...
The Periodic Table
... First to suggest that there were ‘elements’ that could not be further separated into different substances. ...
... First to suggest that there were ‘elements’ that could not be further separated into different substances. ...
CHAPTER-3 CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS
... Ans- The 1st ionisation enthalpy of magnesium is higher than that of Na due to higher nuclear charge and slightly smaller atomic radius of Mg than Na. After the loss of first electron, Na+ formed has the electronic configuration of neon (2,8). The higher stability of the completely filled noble gas ...
... Ans- The 1st ionisation enthalpy of magnesium is higher than that of Na due to higher nuclear charge and slightly smaller atomic radius of Mg than Na. After the loss of first electron, Na+ formed has the electronic configuration of neon (2,8). The higher stability of the completely filled noble gas ...
TEST-Periodic Table
... a. Rb is the most reactive element shown. Group 1A alkaline earth metals are the most reactive metals, and the reactivity of elements in Group 1A increases from top to bottom. b. Li is the most reactive element shown. Group 1A alkaline earth metals are the most reactive metals, and the reactivity of ...
... a. Rb is the most reactive element shown. Group 1A alkaline earth metals are the most reactive metals, and the reactivity of elements in Group 1A increases from top to bottom. b. Li is the most reactive element shown. Group 1A alkaline earth metals are the most reactive metals, and the reactivity of ...
Chem Periodicity, Reactivity, Redox 2009 Yingxin
... @ Density = mass/volume @ Though both mass and volume increase, the increase in mass is greater than the increase in volume @ Lithium, Sodium, Potassium float on water Metals tarnish easily in air (react with air) @ Must be kept under oil to prevent contact with air React with water to give alkaline ...
... @ Density = mass/volume @ Though both mass and volume increase, the increase in mass is greater than the increase in volume @ Lithium, Sodium, Potassium float on water Metals tarnish easily in air (react with air) @ Must be kept under oil to prevent contact with air React with water to give alkaline ...
Chapter 6 Periodic Table Lecture Notes
... • Columns of elements are called groups. • Rows of elements are called periods. • Elements in groups 1,2, and 13-18 possess a wide variety of chemical and physical properties and are called the representative elements. • Elements in groups 3-12 are known as the transition metals. ...
... • Columns of elements are called groups. • Rows of elements are called periods. • Elements in groups 1,2, and 13-18 possess a wide variety of chemical and physical properties and are called the representative elements. • Elements in groups 3-12 are known as the transition metals. ...
Untitled
... • Columns of elements are called groups. • Rows of elements are called periods. • Elements in groups 1,2, and 13-18 possess a wide variety of chemical and physical properties and are called the representative elements. • Elements in groups 3-12 are known as the transition metals. ...
... • Columns of elements are called groups. • Rows of elements are called periods. • Elements in groups 1,2, and 13-18 possess a wide variety of chemical and physical properties and are called the representative elements. • Elements in groups 3-12 are known as the transition metals. ...
Section 6.1 Development of the Modern Periodic Table
... • Columns of elements are called groups. • Rows of elements are called periods. • Elements in groups 1,2, and 13-18 possess a wide variety of chemical and physical properties and are called the representative elements. • Elements in groups 3-12 are known as the transition metals. ...
... • Columns of elements are called groups. • Rows of elements are called periods. • Elements in groups 1,2, and 13-18 possess a wide variety of chemical and physical properties and are called the representative elements. • Elements in groups 3-12 are known as the transition metals. ...
The Alkaline Earth Metals (Group 2) - Chemwiki
... The Learning Objectives of this Module are: 1. To describe how to isolate the alkaline earth metals. 2. To be familiar with the reactions, compounds, and complexes of the alkaline earth metals. Like the alkali metals, the alkaline earth metals are so reactive that they are never found in elemental f ...
... The Learning Objectives of this Module are: 1. To describe how to isolate the alkaline earth metals. 2. To be familiar with the reactions, compounds, and complexes of the alkaline earth metals. Like the alkali metals, the alkaline earth metals are so reactive that they are never found in elemental f ...
Periodic Table Oakland Schools Chemistry Resource Unit Andrew D. Hulbert
... elements repeated. He placed elements in the new row directly below elements of similar chemical properties in the preceding row. Amazingly, Mendeleev predicted the properties of the missing elements in his table, leaving blanks to be filled in later. Mendeleev did not have knowledge of atomic numbe ...
... elements repeated. He placed elements in the new row directly below elements of similar chemical properties in the preceding row. Amazingly, Mendeleev predicted the properties of the missing elements in his table, leaving blanks to be filled in later. Mendeleev did not have knowledge of atomic numbe ...
Lesson 7.8 Basic Properties of the Main Group Elements Suggested
... the main-group elements. We will look at some of the major characteristic of these elements, paying particular attention to the oxides. In the case of the nonmetals, we will also examine the compounds with hydrogen. You may want to make flash cards to help you remember the major characteristics of t ...
... the main-group elements. We will look at some of the major characteristic of these elements, paying particular attention to the oxides. In the case of the nonmetals, we will also examine the compounds with hydrogen. You may want to make flash cards to help you remember the major characteristics of t ...
First Term Science Al-Karma Language School Prep 2 Question (1
... 13)-Each period in the modern periodic table starts with ------- and ends with ---------. 14)-The positive ion carries a number of ---------- charges equals to the number -------- electrons. 15)-An element whose electronic configuration is (2,8) so, it exists in group ------- and period -------- in ...
... 13)-Each period in the modern periodic table starts with ------- and ends with ---------. 14)-The positive ion carries a number of ---------- charges equals to the number -------- electrons. 15)-An element whose electronic configuration is (2,8) so, it exists in group ------- and period -------- in ...
Periodic Table Presentation Lesson
... The elements are arranged on the periodic table according to their atomic numbers. On the table the atomic numbers increase from left to right. ...
... The elements are arranged on the periodic table according to their atomic numbers. On the table the atomic numbers increase from left to right. ...
3.1 Periodic Table and Trends PPT Periodic Table 2015_2
... In most transition elements, d electrons can become involved in the reaction Iron can lose 2 electrons (the 2 in the 4s) (Fe2+) or 3 electrons (the 2 in the 4s and 1 in the 3d) (Fe3+) ...
... In most transition elements, d electrons can become involved in the reaction Iron can lose 2 electrons (the 2 in the 4s) (Fe2+) or 3 electrons (the 2 in the 4s and 1 in the 3d) (Fe3+) ...
Patterns in The Periodic Table
... ductile, and they conduct electricity and heat. However, compared to other metals, the alkali metals have low melting points. They are all soft enough to cut with a knife. In addition, they all react violently with water (thus the reason they are stored in a non-reactive oil or kerosene). ...
... ductile, and they conduct electricity and heat. However, compared to other metals, the alkali metals have low melting points. They are all soft enough to cut with a knife. In addition, they all react violently with water (thus the reason they are stored in a non-reactive oil or kerosene). ...
Rem001 - The Vital Chemist
... characterised by possession of two valence electrons. Other characteristics include: a. They ionise by loss of the 2 electrons, hence they are divalent and good reducing agents. M -----→ M2+ + 2eb. They are silvery white, malleable and ductile, harder than group Ia c. Their reactivity increases from ...
... characterised by possession of two valence electrons. Other characteristics include: a. They ionise by loss of the 2 electrons, hence they are divalent and good reducing agents. M -----→ M2+ + 2eb. They are silvery white, malleable and ductile, harder than group Ia c. Their reactivity increases from ...
Periodic Table Student Outline
... To determine those weights, scientists had passed currents through various solutions to break them up into their constituent atoms. Responding to a battery’s polarity, the atoms of one element would go this away, the atoms of another that away. The atoms were collected in separate containers and the ...
... To determine those weights, scientists had passed currents through various solutions to break them up into their constituent atoms. Responding to a battery’s polarity, the atoms of one element would go this away, the atoms of another that away. The atoms were collected in separate containers and the ...
Chemical Periodicity
... • Heath Chemistry: Experiments and Principles, Chapter 7 Order Among Atomsdels of Atomic ...
... • Heath Chemistry: Experiments and Principles, Chapter 7 Order Among Atomsdels of Atomic ...
worksheet i—extra credit
... Describe the development of the periodic table Define periodic table and periodic law Identify and define groups and periods Name the groups on the periodic table Identify an element as either a solid, liquid, or gas based on the periodic table. Determine if an element is radioactive or synthetic ba ...
... Describe the development of the periodic table Define periodic table and periodic law Identify and define groups and periods Name the groups on the periodic table Identify an element as either a solid, liquid, or gas based on the periodic table. Determine if an element is radioactive or synthetic ba ...
File - CCHS Chemistry
... It is sometimes possible to force the outer level of an elem in 3rd or higher period to hold more than 8 e-’s ◦ - Extended Octet Noble gas comps are formed this way ...
... It is sometimes possible to force the outer level of an elem in 3rd or higher period to hold more than 8 e-’s ◦ - Extended Octet Noble gas comps are formed this way ...
D. - Taylor County Schools
... Development of the Periodic Table (cont.) • The 1800s brought large amounts of information and scientists needed a way to organize knowledge about elements. • John Newlands proposed an arrangement where elements were ordered by increasing atomic mass. ...
... Development of the Periodic Table (cont.) • The 1800s brought large amounts of information and scientists needed a way to organize knowledge about elements. • John Newlands proposed an arrangement where elements were ordered by increasing atomic mass. ...