vocab - SALAZAR!!
... transition metals are in the middle of the periodic table. 5. Lanthanide series- When you look at the periodic table, you will see two rows that kind of sit off to the bottom. Sentence: The Lanthanide series is the second row from the bottom. ...
... transition metals are in the middle of the periodic table. 5. Lanthanide series- When you look at the periodic table, you will see two rows that kind of sit off to the bottom. Sentence: The Lanthanide series is the second row from the bottom. ...
SCH 3U - Norbraten
... a) From your observations, what physical properties do the elements in each of your groups have in common? b) From your observations, what chemical properties do the elements in each of your groups have in common? 3. Is the solution that is produced when a metal reacts with water acidic or basic? 4. ...
... a) From your observations, what physical properties do the elements in each of your groups have in common? b) From your observations, what chemical properties do the elements in each of your groups have in common? 3. Is the solution that is produced when a metal reacts with water acidic or basic? 4. ...
C Carbon Cu Copper
... electrons in their very outermost energy level (This is called the rule of octet.) Atoms bond until this level is complete. Atoms with few valence electrons lose them during bonding. Atoms with 6, 7, or 8 valence electrons gain electrons during bonding. ...
... electrons in their very outermost energy level (This is called the rule of octet.) Atoms bond until this level is complete. Atoms with few valence electrons lose them during bonding. Atoms with 6, 7, or 8 valence electrons gain electrons during bonding. ...
CP-Chem Ch 5 PowerPoint(The Periodic Table)
... because of their position in the periodic table. • A transition metal may lose one, two, or even three valence electrons depending on the element with which it reacts. • Generally, the transition metals are less reactive than the alkali metals and the alkaline-earth metals are. ...
... because of their position in the periodic table. • A transition metal may lose one, two, or even three valence electrons depending on the element with which it reacts. • Generally, the transition metals are less reactive than the alkali metals and the alkaline-earth metals are. ...
Periodic Table - Chemistry R: 4(AE)
... Helium with 2 valence electrons, but it is still associated with this group because its properties match these elements. – Extremely stable and occur as monoatomic gases in nature – Although they do not readily combine with other elements, but compounds of Krypton and Xenon have been ...
... Helium with 2 valence electrons, but it is still associated with this group because its properties match these elements. – Extremely stable and occur as monoatomic gases in nature – Although they do not readily combine with other elements, but compounds of Krypton and Xenon have been ...
PART 1: ATOMIC NUMBER - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... hand corner and moves from left to right. The numbers skip any blank spaces in between, so Helium (He) has atomic number 2. The numbers then jump back to left again, so lithium (Li), atomic number 3 is next. TO DO: record the atomic numbers 1, 2, 3 for hydrogen, helium and lithium, respectively on t ...
... hand corner and moves from left to right. The numbers skip any blank spaces in between, so Helium (He) has atomic number 2. The numbers then jump back to left again, so lithium (Li), atomic number 3 is next. TO DO: record the atomic numbers 1, 2, 3 for hydrogen, helium and lithium, respectively on t ...
1. discuss the contributions of early scie
... electrons. This family includes a metalloid (boron), and the rest are metals. This family includes the most abundant metal in the earth’s crust (aluminum). Carbon Family has 4 valence electrons. The element carbon is called the “basis of life.” There is an entire branch of chemistry devoted to carbo ...
... electrons. This family includes a metalloid (boron), and the rest are metals. This family includes the most abundant metal in the earth’s crust (aluminum). Carbon Family has 4 valence electrons. The element carbon is called the “basis of life.” There is an entire branch of chemistry devoted to carbo ...
Packet 4 - 16-17 Periodic Table
... of which are soluble and some are not. • Density of Group 2 is greater that Group 1 (see table S). • Group one can be cut with a knife, elements in Group2 are harder, and elements in Group 3-12 (transition elements) are much harder. ...
... of which are soluble and some are not. • Density of Group 2 is greater that Group 1 (see table S). • Group one can be cut with a knife, elements in Group2 are harder, and elements in Group 3-12 (transition elements) are much harder. ...
Chapter 6 Review
... ________ 12. Removing one electron from an atom results in the formation of a positive ion with a 1! charge. ________ 13. An anion has more electrons than protons. ________ 14. Elements with a high electronegativity value tend to form positive ions. ...
... ________ 12. Removing one electron from an atom results in the formation of a positive ion with a 1! charge. ________ 13. An anion has more electrons than protons. ________ 14. Elements with a high electronegativity value tend to form positive ions. ...
Water Metal Hydroxide + Hydrogen
... reductants. The non-metals (P, S, Cl) are increasingly strong oxidants as EN increases and AR decreases, causing them to attract electrons more strongly. Si is a metalloid and hence any redox properties are not easy to predict. Ar is a Noble Gas and as such is unreactive with no redox properties ...
... reductants. The non-metals (P, S, Cl) are increasingly strong oxidants as EN increases and AR decreases, causing them to attract electrons more strongly. Si is a metalloid and hence any redox properties are not easy to predict. Ar is a Noble Gas and as such is unreactive with no redox properties ...
Alkaline Earth Metals
... nucleus is less when they are farther from the nucleus. • As you go across a period, nuclear charge is increasing and thus attracting electrons to a greater extent. • Why do the inert gases have an ...
... nucleus is less when they are farther from the nucleus. • As you go across a period, nuclear charge is increasing and thus attracting electrons to a greater extent. • Why do the inert gases have an ...
5.3 Representative Groups - Chemistry with Mr. Saval
... 1: What are the three main categories of elements on the periodic table? 2: As you go from left to right across a period, the elements get (more/less) metallic. ...
... 1: What are the three main categories of elements on the periodic table? 2: As you go from left to right across a period, the elements get (more/less) metallic. ...
Periodic Table Funsheet
... 19. Elements within a group have a similar number of ______________________________________________. 20. Elements across a series have the same number of ______________________________________________. 21. As you go down a group, the elements generally become (more / less) metallic. 22. The majority ...
... 19. Elements within a group have a similar number of ______________________________________________. 20. Elements across a series have the same number of ______________________________________________. 21. As you go down a group, the elements generally become (more / less) metallic. 22. The majority ...
Homework Answers - Chemistry from AZ
... same number of valence electrons and therefore have similar chemical properties. Note there are some variations in the transition metals. Group 1 Alkali Metals: hydrogen is NOT a member; good conductors of heat and electricity; extremely reactive; 1 valence electron; never found uncombined in nature ...
... same number of valence electrons and therefore have similar chemical properties. Note there are some variations in the transition metals. Group 1 Alkali Metals: hydrogen is NOT a member; good conductors of heat and electricity; extremely reactive; 1 valence electron; never found uncombined in nature ...
Periodic Table 2015
... • 3.1.1 Describe the arrangement of elements in the periodic table in order of increasing atomic number. • 3.1.2 Distinguish between the terms group and period. • 3.1.3 Apply the relationship between the electron arrangement of elements and their position in the periodic table up to Z = 20. • 3.1.4 ...
... • 3.1.1 Describe the arrangement of elements in the periodic table in order of increasing atomic number. • 3.1.2 Distinguish between the terms group and period. • 3.1.3 Apply the relationship between the electron arrangement of elements and their position in the periodic table up to Z = 20. • 3.1.4 ...
lanthanides - schultz915
... The alkali metals are soft and can be easily cut with a _____________. a. b. c. d. ...
... The alkali metals are soft and can be easily cut with a _____________. a. b. c. d. ...
Elements – (Metals)
... Can have explosive reaction with water - more reactive as go down group 2K + 2 H2O 2 KOH (aq) + H2(g) + energy Less reactive metals will react only if water and acid (not just water) Zn (s) + 2 H+ (aq) Zn2+ (aq) + H2 (g) Group 1 metals have strong tendency to oxidize + Eoox The larger the +Eoox ...
... Can have explosive reaction with water - more reactive as go down group 2K + 2 H2O 2 KOH (aq) + H2(g) + energy Less reactive metals will react only if water and acid (not just water) Zn (s) + 2 H+ (aq) Zn2+ (aq) + H2 (g) Group 1 metals have strong tendency to oxidize + Eoox The larger the +Eoox ...
The Periodic Table
... lanthanides (or rare-earth). • Lanthanides are shiny metals similar in reactivity to alkaline earth metals. • Elements in period 7 of the f-block are called actinides. • Actinides are all radioactive, and many of them are known only as man-made elements. ...
... lanthanides (or rare-earth). • Lanthanides are shiny metals similar in reactivity to alkaline earth metals. • Elements in period 7 of the f-block are called actinides. • Actinides are all radioactive, and many of them are known only as man-made elements. ...
Episode 7 - The Periodic Table
... Mendeleev 12. What did Mendeleev do for elements that had not yet been discovered? He left spaces for them and predicted many of their properties with high accuracy. 13. How did Glenn Seaborg change the periodic table? He proposed the actinide series. He was also involved in the discovery of many of ...
... Mendeleev 12. What did Mendeleev do for elements that had not yet been discovered? He left spaces for them and predicted many of their properties with high accuracy. 13. How did Glenn Seaborg change the periodic table? He proposed the actinide series. He was also involved in the discovery of many of ...
The Periodic Table - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... Mendeleev 12. What did Mendeleev do for elements that had not yet been discovered? He left spaces for them and predicted many of their properties with high accuracy. 13. How did Glenn Seaborg change the periodic table? He proposed the actinide series. He was also involved in the discovery of many of ...
... Mendeleev 12. What did Mendeleev do for elements that had not yet been discovered? He left spaces for them and predicted many of their properties with high accuracy. 13. How did Glenn Seaborg change the periodic table? He proposed the actinide series. He was also involved in the discovery of many of ...
The Periodic Table
... React readily with Group 6 React readily with water (though not as rapidly as the alkali metals) Two valence electron so they want to lose 2 electrons and achieve a noble configuration (an octet) form +2 cations ...
... React readily with Group 6 React readily with water (though not as rapidly as the alkali metals) Two valence electron so they want to lose 2 electrons and achieve a noble configuration (an octet) form +2 cations ...
Unit 9: Periodicity
... periodic functions of their atomic numbers. What this means is that if we arrange the elements in order of increasing atomic number, we will periodically encounter elements that have similar chemical and physical properties. These elements appear in the same vertical column (group). ...
... periodic functions of their atomic numbers. What this means is that if we arrange the elements in order of increasing atomic number, we will periodically encounter elements that have similar chemical and physical properties. These elements appear in the same vertical column (group). ...
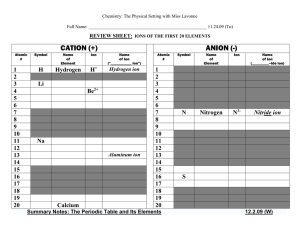
IONS OF THE FIRST 20 ELEMENTS
... The alkali metals, found in group 1 of the periodic table (formerly known as group IA), are very reactive metals that do not occur freely in nature. These metals have only one electron in their outer shell. Therefore, they are ready to lose that one electron in ionic bonding with other elements. As ...
... The alkali metals, found in group 1 of the periodic table (formerly known as group IA), are very reactive metals that do not occur freely in nature. These metals have only one electron in their outer shell. Therefore, they are ready to lose that one electron in ionic bonding with other elements. As ...
Periodic Table
... • Mendeleev found an important pattern − repetition of properties. But does it make sense to think that the pattern is caused by mass? • What parts of an atom affect its mass? protons and neutrons • What parts of an atom affect its properties? protons and electrons • Today we know that different is ...
... • Mendeleev found an important pattern − repetition of properties. But does it make sense to think that the pattern is caused by mass? • What parts of an atom affect its mass? protons and neutrons • What parts of an atom affect its properties? protons and electrons • Today we know that different is ...
CHAPTER-3 CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS AND PERIODICITY
... number of electrons which an atom loses or gains or shares with other atom to attain the noble gas configuration is termed as its valency.” Periodicity: (i) In period- The valency first increases then decreases from left to right in a ...
... number of electrons which an atom loses or gains or shares with other atom to attain the noble gas configuration is termed as its valency.” Periodicity: (i) In period- The valency first increases then decreases from left to right in a ...