ch3 - ChemistryVCE
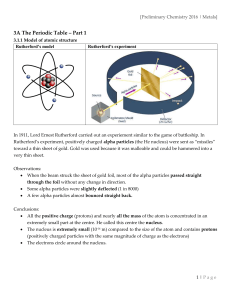
... same period. Magnesium has a nuclear charge of +12 but, with completed inner shells of 1s22s22p6, the outer electrons experience the attraction of a core charge of +2. The outer-shell electrons of phosphorus, which has a nuclear charge of +15 and the same number of inner shells as magnesium, are att ...
... same period. Magnesium has a nuclear charge of +12 but, with completed inner shells of 1s22s22p6, the outer electrons experience the attraction of a core charge of +2. The outer-shell electrons of phosphorus, which has a nuclear charge of +15 and the same number of inner shells as magnesium, are att ...
ch3 - sscyr11chemistry
... same period. Magnesium has a nuclear charge of +12 but, with completed inner shells of 1s22s22p6, the outer electrons experience the attraction of a core charge of +2. The outer-shell electrons of phosphorus, which has a nuclear charge of +15 and the same number of inner shells as magnesium, are att ...
... same period. Magnesium has a nuclear charge of +12 but, with completed inner shells of 1s22s22p6, the outer electrons experience the attraction of a core charge of +2. The outer-shell electrons of phosphorus, which has a nuclear charge of +15 and the same number of inner shells as magnesium, are att ...
Station 1: The Periodic Table 1a. Students know how to relate the
... 1b. Students know how to use the periodic table to identify metals, semimetals, non-metals, alkali metals, alkaline earth metals and transition metals and halogens. 1c. Students know the nucleus of the atom is much smaller than the atom yet contains most of its mass. 1d. Students know how to use the ...
... 1b. Students know how to use the periodic table to identify metals, semimetals, non-metals, alkali metals, alkaline earth metals and transition metals and halogens. 1c. Students know the nucleus of the atom is much smaller than the atom yet contains most of its mass. 1d. Students know how to use the ...
Chapter 5 The Periodic Table Section 1 Organizing the Elements
... Changing the Arrangement > How are elements arranged in the modern periodic table? > The modern periodic table organizes elements by atomic number. When the elements are arranged in this way, elements that have similar properties appear at regular intervals. • As scientists learned more about the st ...
... Changing the Arrangement > How are elements arranged in the modern periodic table? > The modern periodic table organizes elements by atomic number. When the elements are arranged in this way, elements that have similar properties appear at regular intervals. • As scientists learned more about the st ...
The Periodic Law - Mona Shores Blogs
... Certain characteristic physical and chemical properties were associated with each element. The physical property called atomic mass provided chemists with a convenient way to organize the elements. At the same time, it was recognized that there were certain elements that had similar chemical propert ...
... Certain characteristic physical and chemical properties were associated with each element. The physical property called atomic mass provided chemists with a convenient way to organize the elements. At the same time, it was recognized that there were certain elements that had similar chemical propert ...
Learning Guide 3
... 1.) What is the trend in ionization energy as you go from left to right across any period on the table? 2.) What is the trend in the number of protons (nuclear charge) as you go from left to right across any period on the table? 3.) Use your answers to #1 & 2 to write a statement explaining the rela ...
... 1.) What is the trend in ionization energy as you go from left to right across any period on the table? 2.) What is the trend in the number of protons (nuclear charge) as you go from left to right across any period on the table? 3.) Use your answers to #1 & 2 to write a statement explaining the rela ...
How is the Periodic Table organized?
... • With the elements arranged by atomic number, their chemical and physical properties are found to show a repeating, or periodic, pattern. • Elements within a family have similar properties. ...
... • With the elements arranged by atomic number, their chemical and physical properties are found to show a repeating, or periodic, pattern. • Elements within a family have similar properties. ...
Chapter 5 Reading Guide Please answer the following questions in
... At quick glance of the Mendeleev’s periodic table (bottom of page 127), what are some differences you spot from the modern periodic table (like the one on the wall or in your ...
... At quick glance of the Mendeleev’s periodic table (bottom of page 127), what are some differences you spot from the modern periodic table (like the one on the wall or in your ...
Periodic Table Ch4 Honors
... Graphite is not the only pure form of carbon, C. Diamond is also carbon; the color comes from impurities caught within the crystal ...
... Graphite is not the only pure form of carbon, C. Diamond is also carbon; the color comes from impurities caught within the crystal ...
Chemistry 1 Chapter 4, The Periodic Table
... • group 1 – alkali metals, they have a single valence electrons and are very reactive • they are never found in nature as pure elements because they are so reactive they are always combined with other elements as compounds •group 2 – alkaline-earth metals, they have 2 valence electrons, they must lo ...
... • group 1 – alkali metals, they have a single valence electrons and are very reactive • they are never found in nature as pure elements because they are so reactive they are always combined with other elements as compounds •group 2 – alkaline-earth metals, they have 2 valence electrons, they must lo ...
Atomic size - McKnightScience
... green gas that was first used as a form of chemical WARFARE in WWII ...
... green gas that was first used as a form of chemical WARFARE in WWII ...
The Periodic Table
... less reactive, but similar to alkali metals; low electron affinity, CALCIUM – 5th most abundant element on earth (lime, calcium chloride, body functions) ...
... less reactive, but similar to alkali metals; low electron affinity, CALCIUM – 5th most abundant element on earth (lime, calcium chloride, body functions) ...
File - Lenora Henderson`s Flipped Chemistry Classroom
... same time as Lothar Meyer (German chemist); these periodic tables were identical, but because Mendeleev published his table first and was able to explain its periodic trends better his was given the credit. ...
... same time as Lothar Meyer (German chemist); these periodic tables were identical, but because Mendeleev published his table first and was able to explain its periodic trends better his was given the credit. ...
Homework Packet - Chemistry from AZ
... same number of valence electrons and therefore have similar chemical properties. Note there are some variations in the transition metals. Group 1 Alkali Metals: hydrogen is NOT a member; good conductors of heat and electricity; extremely reactive; 1 valence electron; never found uncombined in nature ...
... same number of valence electrons and therefore have similar chemical properties. Note there are some variations in the transition metals. Group 1 Alkali Metals: hydrogen is NOT a member; good conductors of heat and electricity; extremely reactive; 1 valence electron; never found uncombined in nature ...
The Periodic Table - Anderson High School
... Table Gets Useful!! • Elements in the same group have similar chemical and physical properties!! (Mendeleev did that on purpose.) • Elements in the”A” groups are called representative elements. ...
... Table Gets Useful!! • Elements in the same group have similar chemical and physical properties!! (Mendeleev did that on purpose.) • Elements in the”A” groups are called representative elements. ...
The Periodic Table
... Table Gets Useful!! • Elements in the same group have similar chemical and physical properties!! (Mendeleev did that on purpose.) • Elements in the”A” groups are called representative elements. ...
... Table Gets Useful!! • Elements in the same group have similar chemical and physical properties!! (Mendeleev did that on purpose.) • Elements in the”A” groups are called representative elements. ...
Power point notes - Social Circle City Schools
... Noble Gases are colorless gases that are extremely unreactive. One important property of the noble gases is their inactivity. They are inactive because their outermost energy level is full. Because they do not readily combine with other elements to form compounds, the noble gases are called inert. T ...
... Noble Gases are colorless gases that are extremely unreactive. One important property of the noble gases is their inactivity. They are inactive because their outermost energy level is full. Because they do not readily combine with other elements to form compounds, the noble gases are called inert. T ...
THE PERIODIC TABLE
... • Describe how the naturally occurring elements form. • Explain how a transmutation changes one element into another. • Describe how particle accelerators are used to create synthetic elements. A. Natural Elements 1. Of all the elements listed in the periodic table, 93 are found in nature. 2. Of the ...
... • Describe how the naturally occurring elements form. • Explain how a transmutation changes one element into another. • Describe how particle accelerators are used to create synthetic elements. A. Natural Elements 1. Of all the elements listed in the periodic table, 93 are found in nature. 2. Of the ...
Periodic Table of Elements
... Noble Gases are colorless gases that are extremely unreactive. One important property of the noble gases is their inactivity. They are inactive because their outermost energy level is full. Because they do not readily combine with other elements to form compounds, the noble gases are called inert. T ...
... Noble Gases are colorless gases that are extremely unreactive. One important property of the noble gases is their inactivity. They are inactive because their outermost energy level is full. Because they do not readily combine with other elements to form compounds, the noble gases are called inert. T ...
A scientist named Henry Mosley developed the modern period table
... the structure and properties of elements. Today we will investigate these patterns and discover that the periodic table is a useful tool when studying chemistry. Materials: Periodic table, colored pencils, Science textbook Part one… Origins of the periodic table Use your science notes and chapter 6 ...
... the structure and properties of elements. Today we will investigate these patterns and discover that the periodic table is a useful tool when studying chemistry. Materials: Periodic table, colored pencils, Science textbook Part one… Origins of the periodic table Use your science notes and chapter 6 ...
The Periodic Law
... • Why could most of the elements be arranged by increasing atomic mass and others couldn’t? • What was the reason for chemical periodicity? • Moseley, while working with Ernest Rutherford found other patterns that Mendeleev didn’t find. • Moseley found that the elements fit into the periodic table b ...
... • Why could most of the elements be arranged by increasing atomic mass and others couldn’t? • What was the reason for chemical periodicity? • Moseley, while working with Ernest Rutherford found other patterns that Mendeleev didn’t find. • Moseley found that the elements fit into the periodic table b ...
CH 6: The Periodic Table
... • In 1829, the German chemist J.W. Döbereiner observed that several elements could be classified into groups of three, or triads. • All three elements in a triad showed very similar chemical properties and an orderly trend in physical properties. ...
... • In 1829, the German chemist J.W. Döbereiner observed that several elements could be classified into groups of three, or triads. • All three elements in a triad showed very similar chemical properties and an orderly trend in physical properties. ...