Chapter 3 Physical Science - St. Pius X Classical Academy
... Organizing the Elements Mendeleev’s Periodic Table In his periodic table, Mendeleev left blank spaces. He predicted that the blank spaces would be filled by elements that had not yet been discovered. He even correctly predicted the properties of those new elements. ...
... Organizing the Elements Mendeleev’s Periodic Table In his periodic table, Mendeleev left blank spaces. He predicted that the blank spaces would be filled by elements that had not yet been discovered. He even correctly predicted the properties of those new elements. ...
Periodic Table
... up and the electrons are freed so that the resulting atoms consist of bare protons. This produces a state in which the hydrogen becomes metallic. Alkali Metal Properties Lower densities than other metals One loosely bound valence electron Largest atomic radii in their periods Low ionization energies ...
... up and the electrons are freed so that the resulting atoms consist of bare protons. This produces a state in which the hydrogen becomes metallic. Alkali Metal Properties Lower densities than other metals One loosely bound valence electron Largest atomic radii in their periods Low ionization energies ...
Week 9 (wk9) - Riverside Local Schools
... 2. In 1860, at the First International Congress of Chemists in Karlsruhe, Germany, Italian chemist Stanislao Cannizzaro presented a convincing method for accurately… 3. Cannizzaro's method enabled chemists to search for relationships between atomic mass and other properties of the… MENDELEEV AND CHE ...
... 2. In 1860, at the First International Congress of Chemists in Karlsruhe, Germany, Italian chemist Stanislao Cannizzaro presented a convincing method for accurately… 3. Cannizzaro's method enabled chemists to search for relationships between atomic mass and other properties of the… MENDELEEV AND CHE ...
The Periodic Table
... a. gallium 9. noble gases b. nobelium 10. representative elements c. argon 11. transition metals d. vanadium 12. inner transition metals ...
... a. gallium 9. noble gases b. nobelium 10. representative elements c. argon 11. transition metals d. vanadium 12. inner transition metals ...
Name Date Class ORGANIZING THE ELEMENTS Section Review
... 10. In his periodic table, Mendeleev arranged the elements in order of atomic number. 11. There are six periods in a periodic table. 12. Most of the elements in the periodic table are metals. 13. The elements within a period have similar properties. ...
... 10. In his periodic table, Mendeleev arranged the elements in order of atomic number. 11. There are six periods in a periodic table. 12. Most of the elements in the periodic table are metals. 13. The elements within a period have similar properties. ...
Periodic table of elements
... never found as free elements in nature. They are always bonded with another element. ...
... never found as free elements in nature. They are always bonded with another element. ...
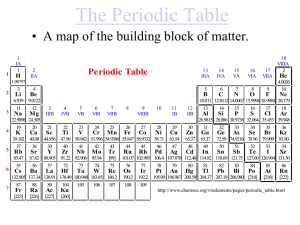
The Periodic Table
... 1. The elements in periods 2 through 7 that are to the left of the zigzagged line are metals. List five metals. 2. The elements in periods 1 through 6 that are to the right of the zigzagged line are nonmetals. List five nonmetals. 3. The elements that border either side of the zigzagged line are met ...
... 1. The elements in periods 2 through 7 that are to the left of the zigzagged line are metals. List five metals. 2. The elements in periods 1 through 6 that are to the right of the zigzagged line are nonmetals. List five nonmetals. 3. The elements that border either side of the zigzagged line are met ...
2015-2016 periodic table Jeopardy ppt
... $100 PERIODIC TABLE Periodic law states that a. elements are either gases, solids, or liquids. b. mercury is a liquid at room temperature. c. properties of elements change periodically with the elements’ atomic numbers. d. some elements only stay in a liquid state for ...
... $100 PERIODIC TABLE Periodic law states that a. elements are either gases, solids, or liquids. b. mercury is a liquid at room temperature. c. properties of elements change periodically with the elements’ atomic numbers. d. some elements only stay in a liquid state for ...
5.3 Representative Groups PPT
... n Relate the number of valence electrons to groups in the periodic table and to properties of elements in those groups. n Predict the reactivity of some elements based on their locations within a group. n Identify some properties of common A group elements. ...
... n Relate the number of valence electrons to groups in the periodic table and to properties of elements in those groups. n Predict the reactivity of some elements based on their locations within a group. n Identify some properties of common A group elements. ...
The Periodic Table
... Poor conductors of electric current React violently with alkali metals to form salts Never found uncombined in nature ...
... Poor conductors of electric current React violently with alkali metals to form salts Never found uncombined in nature ...
File u1 sec2.2 slide show
... Chemical Family – Alkaline Earth Metals Alkaline Earth Metals (Column 2) Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra Fairly Reactive – will burn in air if heated ...
... Chemical Family – Alkaline Earth Metals Alkaline Earth Metals (Column 2) Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra Fairly Reactive – will burn in air if heated ...
Our modern Periodic Table
... a) Chemists in the 19th century wished to organize elements b) Attempts focused on grouping elements with similar properties c) In 1867, Dimitri Mendeleev found patterns in the elements and organized them into a table d) The resulting table had holes for elements not yet discovered ...
... a) Chemists in the 19th century wished to organize elements b) Attempts focused on grouping elements with similar properties c) In 1867, Dimitri Mendeleev found patterns in the elements and organized them into a table d) The resulting table had holes for elements not yet discovered ...
1 February 04, 2016
... Elements in the periodic table are arranged in periods (rows) and groups/families (columns). ...
... Elements in the periodic table are arranged in periods (rows) and groups/families (columns). ...
File
... elements. • By the year 1700, only 13 elements had been identified and isolated. • From 1765-1775, five new elements including H, N, and O had been isolated. • As soon as elements were (are) identified, scientists begin to look for similarities and ...
... elements. • By the year 1700, only 13 elements had been identified and isolated. • From 1765-1775, five new elements including H, N, and O had been isolated. • As soon as elements were (are) identified, scientists begin to look for similarities and ...
Chemistry Chapter 5 The Periodic Law
... what groups of elements have been added to it. Know the groups and names and unique properties of the alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens, noble gases, transition metals, lanthanides, and actinides. Know the definition of the periodic law, periods, groups. Identify the period & grou ...
... what groups of elements have been added to it. Know the groups and names and unique properties of the alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens, noble gases, transition metals, lanthanides, and actinides. Know the definition of the periodic law, periods, groups. Identify the period & grou ...
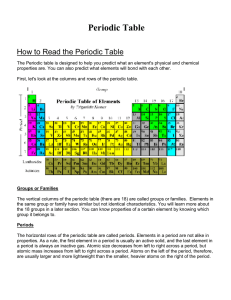
How to Read the Periodic Table
... 6. What is the most common type of element on the Periodic Table? (metals, nonmetals, metalloids) 7. What are the physical properties of metals? 8. What are the physical properties of nonmetals? 9. What kind of element would best make a coffee cup that would not burn your hand? 10. What kind of elem ...
... 6. What is the most common type of element on the Periodic Table? (metals, nonmetals, metalloids) 7. What are the physical properties of metals? 8. What are the physical properties of nonmetals? 9. What kind of element would best make a coffee cup that would not burn your hand? 10. What kind of elem ...
Periodic Trends Notes 14-15
... – For metals, the lower the inner nuclear force the more reactive. – For nonmetals, the higher the inner nuclear force the more reactive. ...
... – For metals, the lower the inner nuclear force the more reactive. – For nonmetals, the higher the inner nuclear force the more reactive. ...
Periodic Table HW Unit
... Some elements exist in two or more forms in the same phase. These forms differ in their molecular or crystal structure, and hence in their properties. For Groups 1, 2, and 13-‐18 on the Perio ...
... Some elements exist in two or more forms in the same phase. These forms differ in their molecular or crystal structure, and hence in their properties. For Groups 1, 2, and 13-‐18 on the Perio ...
The Periodic Table of Elements
... The Transition Metals are in groups #3-12. These include most of the familiar metals such as iron, copper, nickel, silver and gold. Most are hard and shiny and are good conductors of electricity. Shade these in green. In groups 13-15 on the Periodic table, only some elements are metals. Most are ...
... The Transition Metals are in groups #3-12. These include most of the familiar metals such as iron, copper, nickel, silver and gold. Most are hard and shiny and are good conductors of electricity. Shade these in green. In groups 13-15 on the Periodic table, only some elements are metals. Most are ...
Study guide for periodic table trends. A. By referring to electron
... a. Cl-, Ar, K+ b. K+, Ar, Clc. Cl-, K+, Ar d. Ar, Cl- K+ 17. What increases in equal steps of one from left to right in the periodic table for the elements lithium to neon? a. The number of occupied electron energy levels b. The number of neutrons in the most common isotope c. The number of electron ...
... a. Cl-, Ar, K+ b. K+, Ar, Clc. Cl-, K+, Ar d. Ar, Cl- K+ 17. What increases in equal steps of one from left to right in the periodic table for the elements lithium to neon? a. The number of occupied electron energy levels b. The number of neutrons in the most common isotope c. The number of electron ...
8th Science LF Sept 7-11
... 8.5(A) The student is expected to describe the structure of atoms, including the masses, electrical charges, and locations, of protons and neutrons in the nucleus and electrons in the electron cloud. 8.5(C) The student is expected to interpret the arrangement of the Periodic Table, including groups ...
... 8.5(A) The student is expected to describe the structure of atoms, including the masses, electrical charges, and locations, of protons and neutrons in the nucleus and electrons in the electron cloud. 8.5(C) The student is expected to interpret the arrangement of the Periodic Table, including groups ...
alkali metal
... Which of the sets of elements have similar physical and chemical properties? a. b. c. ...
... Which of the sets of elements have similar physical and chemical properties? a. b. c. ...
PERIODIC TABLE
... Periodic table: an arrangement of the elements in order of their atomic numbers so that elements with similar properties fall into the same column or “group”. ...
... Periodic table: an arrangement of the elements in order of their atomic numbers so that elements with similar properties fall into the same column or “group”. ...
Introduction The Periodic Law
... elements in a table by increasing atomic weight, although he sometimes had to ignore the atomic weights in order to group elements with similar chemical behaviors together. The work of Henry Moseley led to the arrangement of elements based on their properties and atomic numbers, not atomic masses, w ...
... elements in a table by increasing atomic weight, although he sometimes had to ignore the atomic weights in order to group elements with similar chemical behaviors together. The work of Henry Moseley led to the arrangement of elements based on their properties and atomic numbers, not atomic masses, w ...
Periodic_Tendancies
... Down the Periodic Table •Family: Are arranged vertically down the periodic table (columns or group, 1- 18 or 1-8 A,B) •These elements have the same number electrons in the outer most shells, the valence shell. ...
... Down the Periodic Table •Family: Are arranged vertically down the periodic table (columns or group, 1- 18 or 1-8 A,B) •These elements have the same number electrons in the outer most shells, the valence shell. ...