Name - TeacherWeb
... 19. An electron that is in the highest occupied energy level of an atom is a(n) valence electron. 20. Elements within a group have the same number of valence electrons. 21. The reactivity of alkali metals increase from the top of Group 1A to the bottom. 22. Differences in reactivity among alkaline e ...
... 19. An electron that is in the highest occupied energy level of an atom is a(n) valence electron. 20. Elements within a group have the same number of valence electrons. 21. The reactivity of alkali metals increase from the top of Group 1A to the bottom. 22. Differences in reactivity among alkaline e ...
The History and Arrangement of the Periodic Table
... electricity better than nonmetals but not as well as metals ► Both ductile and malleable ...
... electricity better than nonmetals but not as well as metals ► Both ductile and malleable ...
Arrangement of the Periodic Table
... electricity better than nonmetals but not as well as metals ► Both ductile and malleable ...
... electricity better than nonmetals but not as well as metals ► Both ductile and malleable ...
e - WordPress.com
... A vertical column in the periodic table is called a group or family. Elements have similar chemical properties due to their valence electrons, so elements in the same group/family have the same number of valence electrons ...
... A vertical column in the periodic table is called a group or family. Elements have similar chemical properties due to their valence electrons, so elements in the same group/family have the same number of valence electrons ...
The Periodic Table - Science Education at Jefferson Lab
... • Elements that are reactive bond easily with other elements to make compounds. • Some elements are only found in nature bonded with other elements. • What makes an element reactive? – An incomplete valence electron level. – All atoms (except hydrogen and helium) want to have 8 electrons in their ve ...
... • Elements that are reactive bond easily with other elements to make compounds. • Some elements are only found in nature bonded with other elements. • What makes an element reactive? – An incomplete valence electron level. – All atoms (except hydrogen and helium) want to have 8 electrons in their ve ...
Periodic Table Metals, Non
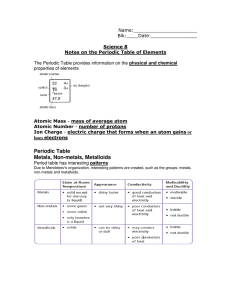
... Notes on the Periodic Table of Elements The Periodic Table provides information on the physical and chemical properties of elements ...
... Notes on the Periodic Table of Elements The Periodic Table provides information on the physical and chemical properties of elements ...
What makes a group of elements
... The main group elements silicon and oxygen account for four of every five atoms found on or near the Earth’s surface. ...
... The main group elements silicon and oxygen account for four of every five atoms found on or near the Earth’s surface. ...
The Periodic Table
... number of ____________________ • They will form the same kinds of _____________. ...
... number of ____________________ • They will form the same kinds of _____________. ...
The Periodic Table - Mr Linseman`s wiki
... Alkali metals: shiny, silvery metals that react easily, form compounds that are soluble in water (group 1) Alkaline earth metals: shiny, silvery metals, form compounds that are often insoluble in water (group 2) Halogens: poisonous, react readily with alkali metals (group 17) Noble gases: do ...
... Alkali metals: shiny, silvery metals that react easily, form compounds that are soluble in water (group 1) Alkaline earth metals: shiny, silvery metals, form compounds that are often insoluble in water (group 2) Halogens: poisonous, react readily with alkali metals (group 17) Noble gases: do ...
Regions of the Periodic Table
... (The “extra” section below the rest of the table.) are part of the transition metals have a partially-filled f sub-level officially have 2 valence electrons, but can shift electrons between s, d, and f sub-levels. Usually form ions with +3 charges. are rare noble gases: elements in group 18 ...
... (The “extra” section below the rest of the table.) are part of the transition metals have a partially-filled f sub-level officially have 2 valence electrons, but can shift electrons between s, d, and f sub-levels. Usually form ions with +3 charges. are rare noble gases: elements in group 18 ...
Periodic Table Notes
... electricity better than nonmetals but not as well as metals ► Both ductile and malleable ...
... electricity better than nonmetals but not as well as metals ► Both ductile and malleable ...
Periodic Table – Organizing the Elements
... are good conductors of heat and electricity Metals are all solids, except Mercury (Hg) which is a liquid Nonmetals are usually dull (no luster) & are poor conductors of heat and electricity Nonmetals can be solid (C & S), liquid (Br) or gas (O & H) ...
... are good conductors of heat and electricity Metals are all solids, except Mercury (Hg) which is a liquid Nonmetals are usually dull (no luster) & are poor conductors of heat and electricity Nonmetals can be solid (C & S), liquid (Br) or gas (O & H) ...
The Periodic Table - Miss Schaefer`s Science Grade 8
... • Elements on the periodic table can be grouped into families (or groups) based on their chemical properties. – We call them “families” because the elements in each family are “related.” ...
... • Elements on the periodic table can be grouped into families (or groups) based on their chemical properties. – We call them “families” because the elements in each family are “related.” ...
Study Guide for Quiz on Tuesday February 26th - seys
... SEPUP 16: the periodic table, Medeleev (the maker of the table), how to read it (groups, periods, why the elements are in what position) SEPUP 17: Making molecules, bonding similar/ different atoms together, how many bonds different elements have, how many each have for hydrogen CI 1.2: Elements in ...
... SEPUP 16: the periodic table, Medeleev (the maker of the table), how to read it (groups, periods, why the elements are in what position) SEPUP 17: Making molecules, bonding similar/ different atoms together, how many bonds different elements have, how many each have for hydrogen CI 1.2: Elements in ...
The Periodic Law Notes (Chapter 5) – Part 2
... -reacts with water to form alkaline or basic solutions – store under kerosene -whenever you mix Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, or Fr with water it will explode and produce an alkaline solution -ns1 (ending of all electron configurations for this group) http://www.teachertube.com/members/viewVideo.php?title=Grou ...
... -reacts with water to form alkaline or basic solutions – store under kerosene -whenever you mix Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, or Fr with water it will explode and produce an alkaline solution -ns1 (ending of all electron configurations for this group) http://www.teachertube.com/members/viewVideo.php?title=Grou ...
The History of the Modern Periodic Table
... Periodic Table • Periodic Table: arrangement of elements in order of their atomic numbers so that elements with similar properties fall in the same column. ...
... Periodic Table • Periodic Table: arrangement of elements in order of their atomic numbers so that elements with similar properties fall in the same column. ...
Ch. 6 - The Periodic Table
... Relatively soft, but harder than alkali metals. Two valence electrons. Although not as reactive as alkali metals, still very reactive and not found in nature in the elemental state. ◦ Obtained in the pure form through electrolysis of their fused salts. ...
... Relatively soft, but harder than alkali metals. Two valence electrons. Although not as reactive as alkali metals, still very reactive and not found in nature in the elemental state. ◦ Obtained in the pure form through electrolysis of their fused salts. ...
Unit 4: The Periodic Table and Periodicity Name - Teach-n
... 31. Why are the electrons drawn closer to the nucleus when a sodium atom loses an electron? the attraction between the remaining electrons and the nucleus is increased 32. As the number of electrons _increases_, the attraction of the nucleus for any one electron decreases. 33. What is electronegativ ...
... 31. Why are the electrons drawn closer to the nucleus when a sodium atom loses an electron? the attraction between the remaining electrons and the nucleus is increased 32. As the number of electrons _increases_, the attraction of the nucleus for any one electron decreases. 33. What is electronegativ ...
Chapter 5
... • The elements in Group 2A are called alkaline earth metals • All alkaline earth metals have two valence electrons • They are harder than group 1A • Differences in reactivity among the alkaline earth metals are shown by the ways they react with water • Calcium, strontium and barium react easily with ...
... • The elements in Group 2A are called alkaline earth metals • All alkaline earth metals have two valence electrons • They are harder than group 1A • Differences in reactivity among the alkaline earth metals are shown by the ways they react with water • Calcium, strontium and barium react easily with ...
Anticipation Guide Before After The periodic table is a collection of
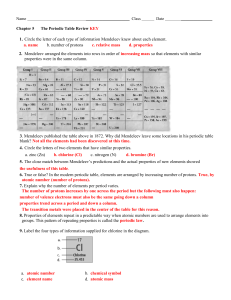
... The periodic table is a collection of all elements known to us. The atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus. The atomic number is written below the element on the Periodic Table. The atomic mass is the sum of protons and electrons in the nucleus. The atomic mass is written above the el ...
... The periodic table is a collection of all elements known to us. The atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus. The atomic number is written below the element on the Periodic Table. The atomic mass is the sum of protons and electrons in the nucleus. The atomic mass is written above the el ...
Chapter 7 - HCC Learning Web
... outermost electron from the nucleus becomes larger. Hence the atomic radius increases. • As we move across the periodic table, the number of core electrons remains constant, however, the nuclear charge increases. Therefore, there is an increased attraction between the nucleus and the outermost elect ...
... outermost electron from the nucleus becomes larger. Hence the atomic radius increases. • As we move across the periodic table, the number of core electrons remains constant, however, the nuclear charge increases. Therefore, there is an increased attraction between the nucleus and the outermost elect ...
The Periodic Law (Unit #5) Study Guide 1. Who is credited with
... 3. Henry Moseley found that elements in the periodic table fit into patterns better when arranged in increasing order according to nuclear charge or _atomic number______. 4. The _periodic_______ law states that the physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their _ato ...
... 3. Henry Moseley found that elements in the periodic table fit into patterns better when arranged in increasing order according to nuclear charge or _atomic number______. 4. The _periodic_______ law states that the physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their _ato ...