oslecture2
... Provide hardware support to differentiate between at least two modes of operation: 1. User mode -- execution done on behalf of a user. 2. Monitor mode (supervisor/kernel/system mode) -execution done on behalf of operating system. ...
... Provide hardware support to differentiate between at least two modes of operation: 1. User mode -- execution done on behalf of a user. 2. Monitor mode (supervisor/kernel/system mode) -execution done on behalf of operating system. ...
What Is Operating System? Operating Systems, System Calls, and Buffered I/O
... write writes up to count bytes to the file referenced by the file descriptor fd from the buffer starting at buf. RETURN VALUE On success, the number of bytes written is returned (zero indicates nothing was written). It is not an error if this number is smaller than the number of bytes requested . . ...
... write writes up to count bytes to the file referenced by the file descriptor fd from the buffer starting at buf. RETURN VALUE On success, the number of bytes written is returned (zero indicates nothing was written). It is not an error if this number is smaller than the number of bytes requested . . ...
I/O Systems 2.
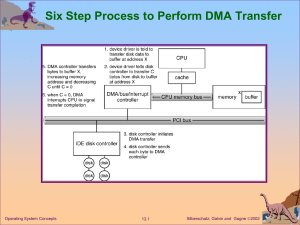
... controllers from kernel Devices vary in many dimensions Character-stream or block Sequential or random-access ...
... controllers from kernel Devices vary in many dimensions Character-stream or block Sequential or random-access ...
Unit I Operating Systems in Distributed Environments
... • Some OS use the microkernel concept, this have the function to coordinate to the other parts of an OS such as : I/O Devices, Process, Memory and File Systems. • The structure of and OS could be different but in most of the time are very similar because some OS use Open Standards. ...
... • Some OS use the microkernel concept, this have the function to coordinate to the other parts of an OS such as : I/O Devices, Process, Memory and File Systems. • The structure of and OS could be different but in most of the time are very similar because some OS use Open Standards. ...
UNIX Operating System
... Utilized by Linux and UNIX OS to create an artificial root directory. Creating a temporary root directory prevents a program from accessing or modifying files outside the directory hierarchy starting at its root. Chroot affects only the current process and its child processes. The files need to be p ...
... Utilized by Linux and UNIX OS to create an artificial root directory. Creating a temporary root directory prevents a program from accessing or modifying files outside the directory hierarchy starting at its root. Chroot affects only the current process and its child processes. The files need to be p ...
Linux Systems Programming I
... Waiting for events, alarm(), pause(), general signal handling with the signal library c. Using a signal handler System calls a. The difference between C library and system calls, why do you need system calls? b. Classes of system calls: process management, file I/O, memory management, and signal han ...
... Waiting for events, alarm(), pause(), general signal handling with the signal library c. Using a signal handler System calls a. The difference between C library and system calls, why do you need system calls? b. Classes of system calls: process management, file I/O, memory management, and signal han ...
Introduction to Computer Science
... message. The transport layer address is the process identification, called a port number. 5. What are the components of an operating system? (10%) Components of an operating systems are user interface, memory manager, process manager, device manager, and file manager. 6. How is demand paging more ef ...
... message. The transport layer address is the process identification, called a port number. 5. What are the components of an operating system? (10%) Components of an operating systems are user interface, memory manager, process manager, device manager, and file manager. 6. How is demand paging more ef ...
CS 471-001: Operating Systems Spring 2017 Department of
... Show an understanding of the need for the concurrent operation of multiple tasks (processes/threads) and an ability to solve basic process synchronization problems that arise from concurrent operation settings ...
... Show an understanding of the need for the concurrent operation of multiple tasks (processes/threads) and an ability to solve basic process synchronization problems that arise from concurrent operation settings ...
Unit-5 - Ipemgzb.ac.in
... also runs on a variety of other platforms. The core Linux operating system kernel is entirely original, but it can run much existing free UNIX software, resulting in an entire UNIX-compatible operating system free from proprietary code. ...
... also runs on a variety of other platforms. The core Linux operating system kernel is entirely original, but it can run much existing free UNIX software, resulting in an entire UNIX-compatible operating system free from proprietary code. ...
hw1_wet
... Upon creation, each process has a tag that equals to half of the tag of its parent at the time of creation (integer division, if the parent's tag is 3 the son's tag will be 1). The tag of the first process created (swapper, pid 0) should be 0 (0/2=0). Processes may read and change their tags and per ...
... Upon creation, each process has a tag that equals to half of the tag of its parent at the time of creation (integer division, if the parent's tag is 3 the son's tag will be 1). The tag of the first process created (swapper, pid 0) should be 0 (0/2=0). Processes may read and change their tags and per ...
Operating System Structures
... involve a file or an I/O device. File-system manipulation - The file system is of particular interest. Obviously, programs need to read and write files and directories, create and delete them, search them, list file Information, permission management. ...
... involve a file or an I/O device. File-system manipulation - The file system is of particular interest. Obviously, programs need to read and write files and directories, create and delete them, search them, list file Information, permission management. ...
PPT - Course Website Directory
... System calls for process management Example of fork used in simplified shell program ...
... System calls for process management Example of fork used in simplified shell program ...
Chapter One
... Describe the options for connecting to a UNIX system Define the syntax used for entering UNIX commands ...
... Describe the options for connecting to a UNIX system Define the syntax used for entering UNIX commands ...
Operating Systems CSLO - Barbara Hecker
... operating systems. Discuss the various different hardware platforms that have operating systems and what they are used for. Also discuss the desktop PC operating systems and how it has evolved. 2. What is the KERNEL? Describe the difference between kernel mode and user mode. Provide a complete overv ...
... operating systems. Discuss the various different hardware platforms that have operating systems and what they are used for. Also discuss the desktop PC operating systems and how it has evolved. 2. What is the KERNEL? Describe the difference between kernel mode and user mode. Provide a complete overv ...
CS 111
... risk involved in programs and memory protection, the kernel is in fact the only program that is allowed to run in supervisor mode. This policy maintains safe access to files and programs. The kernel is the only program that starts and maintains user processes. This seems like a fairly simple idea bu ...
... risk involved in programs and memory protection, the kernel is in fact the only program that is allowed to run in supervisor mode. This policy maintains safe access to files and programs. The kernel is the only program that starts and maintains user processes. This seems like a fairly simple idea bu ...
PowerPoint XP
... How do we make different file systems work together, even across machines? How do we provide consistency, availability, and reliability to copies of a file across multiple machines? How do we handle very large data ...
... How do we make different file systems work together, even across machines? How do we provide consistency, availability, and reliability to copies of a file across multiple machines? How do we handle very large data ...
Kernel Control Path
... used by kernel functions for implementing a critical region. This technique does not always prevent kernel control path interleaving. Critical section should be short because any communication between CPU and I/O is blocked while a kernel control path is running in this section. ...
... used by kernel functions for implementing a critical region. This technique does not always prevent kernel control path interleaving. Critical section should be short because any communication between CPU and I/O is blocked while a kernel control path is running in this section. ...
COMP 3410
... The purpose of this course is to provide students basic knowledge of operating systems, difference between the kernel and user modes, concepts of application program interfaces, methods and implementations of interrupts. Students are introduced to the schedulers, policies, processes, threads, memory ...
... The purpose of this course is to provide students basic knowledge of operating systems, difference between the kernel and user modes, concepts of application program interfaces, methods and implementations of interrupts. Students are introduced to the schedulers, policies, processes, threads, memory ...
IPC
... • However, there are other types of file descriptors. For example, when you say write(1, buf, size), you are saying to print those bytes to standard output, which often is not a disk file, but instead is a terminal. When fd is the writing end of a pipe, the write() specifies for the operating system ...
... • However, there are other types of file descriptors. For example, when you say write(1, buf, size), you are saying to print those bytes to standard output, which often is not a disk file, but instead is a terminal. When fd is the writing end of a pipe, the write() specifies for the operating system ...
Chapter 3: Processes(PPT)
... machine can have computation performed by calling a procedure (function) that is executed by a different process on another machine Issues with endianism, data encoding Must define a common data representation Issues with synchronisation of processes and returning of results ...
... machine can have computation performed by calling a procedure (function) that is executed by a different process on another machine Issues with endianism, data encoding Must define a common data representation Issues with synchronisation of processes and returning of results ...
OS_Structure
... • Specific events cause execution of each unit. • Many portions of the OS are executed by specific request of a program, as by a call instruction, or in response to interrupts or other separate events. • When these components are invoked, they may complete their work before returning to the program, ...
... • Specific events cause execution of each unit. • Many portions of the OS are executed by specific request of a program, as by a call instruction, or in response to interrupts or other separate events. • When these components are invoked, they may complete their work before returning to the program, ...
Operating System
... This course introduces the fundamentals of operating systems. Topics include interprocess communication, process scheduling, deadlock, memory management, virtual memory, and file system. Formal principles are illustrated with examples and case studies of one or more contemporary operating system. ...
... This course introduces the fundamentals of operating systems. Topics include interprocess communication, process scheduling, deadlock, memory management, virtual memory, and file system. Formal principles are illustrated with examples and case studies of one or more contemporary operating system. ...
Ch2 OS Structures 1
... – Resource allocation ‐ When multiple users or multiple jobs running concurrently, resources must be allocated to each of them • Many types of resources ‐ CPU cycles, main memory, file storage, I/O devices. – Accounting ‐ To keep track of which users use how much and what kinds of computer resou ...
... – Resource allocation ‐ When multiple users or multiple jobs running concurrently, resources must be allocated to each of them • Many types of resources ‐ CPU cycles, main memory, file storage, I/O devices. – Accounting ‐ To keep track of which users use how much and what kinds of computer resou ...