Unit I Introduction
... • Some OS use the microkernel concept, this have the function to coordinate to the other parts of an OS such as : I/O Devices, Process, Memory and File Systems. • The structure of and OS could be different but in most of the time are very similar because some OS use Open Standards. ...
... • Some OS use the microkernel concept, this have the function to coordinate to the other parts of an OS such as : I/O Devices, Process, Memory and File Systems. • The structure of and OS could be different but in most of the time are very similar because some OS use Open Standards. ...
1.1 What is an Operating System?
... transfer of data from the device to its local buffer. Once the transfer of data is complete, the device controller informs the CPU that it has finished its operation. It accomplishes this communication by causing an interrupt. When the CPU is interrupted, it stops what it is doing and transfers exec ...
... transfer of data from the device to its local buffer. Once the transfer of data is complete, the device controller informs the CPU that it has finished its operation. It accomplishes this communication by causing an interrupt. When the CPU is interrupted, it stops what it is doing and transfers exec ...
CS307-slides13
... processes in the system When process Pj receives a request message, it may reply immediately or it ...
... processes in the system When process Pj receives a request message, it may reply immediately or it ...
Process Concept
... • “system call” == “a function call that invokes the operating system services” • These OS services typically written in a high-level language (C or C++), are isolated from the user programs. • OS provides service to user program via system calls. ...
... • “system call” == “a function call that invokes the operating system services” • These OS services typically written in a high-level language (C or C++), are isolated from the user programs. • OS provides service to user program via system calls. ...
process - United International College
... • Reactive operation: Embedded software may execute in response to external events. If these events do not occur periodically or at predictable intervals, the embedded software may need to take into account worst-case conditions and set priorities for execution of routines. • Configurability: There ...
... • Reactive operation: Embedded software may execute in response to external events. If these events do not occur periodically or at predictable intervals, the embedded software may need to take into account worst-case conditions and set priorities for execution of routines. • Configurability: There ...
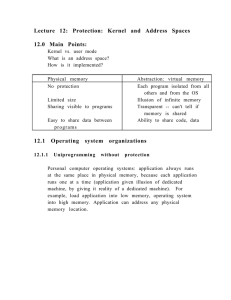
Lecture 12: Protection: Kernel and Address Spaces 12.0 Main Points
... sets processor status to kernel changes execution stack to kernel saves current program counter jumps to handler in kernel handler saves previous state of any registers it uses Context switching between programs: same as with threads, except now also save and restore pointer to translation table. To ...
... sets processor status to kernel changes execution stack to kernel saves current program counter jumps to handler in kernel handler saves previous state of any registers it uses Context switching between programs: same as with threads, except now also save and restore pointer to translation table. To ...
Memory Protection: Kernel and User Address Spaces
... Address Translation Each process is associated with an address space, or all the physical addresses a process can touch However, each process believes that it owns the entire memory, starting with the virtual address 0 The missing piece is a translation table Translate every memory referenc ...
... Address Translation Each process is associated with an address space, or all the physical addresses a process can touch However, each process believes that it owns the entire memory, starting with the virtual address 0 The missing piece is a translation table Translate every memory referenc ...
Slides - Bilkent University Computer Engineering Department
... Running application software may generate interrupts as well. – They are called software interrupts (also called traps) • 1. exceptions (caused by errors) • 2. system calls (service request) – trap or syscall instruction is used ...
... Running application software may generate interrupts as well. – They are called software interrupts (also called traps) • 1. exceptions (caused by errors) • 2. system calls (service request) – trap or syscall instruction is used ...
CSS430: Introduction - UW Faculty Web Server
... This is a logical extension of multiprogramming. Each user has at least one separate program in memory. A program in execution is referred to as a process. Process switch occur so frequently that the users can interact with each program while it is running. File system allows users to access data an ...
... This is a logical extension of multiprogramming. Each user has at least one separate program in memory. A program in execution is referred to as a process. Process switch occur so frequently that the users can interact with each program while it is running. File system allows users to access data an ...
PDF
... – Creates L4 threads for its user processes – Maps parts of its address space to user process threads (using L4 primitives) – Acts as pager thread for its user threads – Has its own logical page table – Multiplexes its own single thread (to avoid having to change Linux source code) ...
... – Creates L4 threads for its user processes – Maps parts of its address space to user process threads (using L4 primitives) – Acts as pager thread for its user threads – Has its own logical page table – Multiplexes its own single thread (to avoid having to change Linux source code) ...
Chapter 1: Introduction
... Running application software may generate interrupts as well. – They are called software interrupts (also called traps) • 1. exceptions (caused by errors) • 2. system calls (service request) – trap or syscall instruction is used ...
... Running application software may generate interrupts as well. – They are called software interrupts (also called traps) • 1. exceptions (caused by errors) • 2. system calls (service request) – trap or syscall instruction is used ...
PPT
... – Creates L4 threads for its user processes – Maps parts of its address space to user process threads (using L4 primitives) – Acts as pager thread for its user threads – Has its own logical page table – Multiplexes its own single thread (to avoid having to change Linux source code) ...
... – Creates L4 threads for its user processes – Maps parts of its address space to user process threads (using L4 primitives) – Acts as pager thread for its user threads – Has its own logical page table – Multiplexes its own single thread (to avoid having to change Linux source code) ...
OSPP: The Kernel Abstraction
... • Locate arguments – In registers or on user stack – Translate user addresses into kernel addresses ...
... • Locate arguments – In registers or on user stack – Translate user addresses into kernel addresses ...
Chapter 2: System Structures
... Protection and security - The owners of information stored in a multiuser or networked computer system may want to control use of that information, concurrent processes should not interfere with each other 4 Protection involves ensuring that all access to system resources is ...
... Protection and security - The owners of information stored in a multiuser or networked computer system may want to control use of that information, concurrent processes should not interfere with each other 4 Protection involves ensuring that all access to system resources is ...
Norman Matloff, Unix Processes
... A process is an instance of running a program. If, for example, three people are running the same program simultaneously, there are three processes there, not just one. In fact, we might have more than one process running even with only person executing the program, because (you will see later) the ...
... A process is an instance of running a program. If, for example, three people are running the same program simultaneously, there are three processes there, not just one. In fact, we might have more than one process running even with only person executing the program, because (you will see later) the ...
Mac OSX Kernel(XNU)
... Traditionally user must write separate kernel code and a logging code to get the data which results in decrease of System performance. ...
... Traditionally user must write separate kernel code and a logging code to get the data which results in decrease of System performance. ...
ppt
... Where does most of LRPC’s overhead come from? How can the kernel be eliminated from the call path on SMMPs with user-level threads? To a thread URPC is synchronous, but to the thread library it is asynchronous … explain. Why do kernel thread switches have long term cache and TLB effects that user th ...
... Where does most of LRPC’s overhead come from? How can the kernel be eliminated from the call path on SMMPs with user-level threads? To a thread URPC is synchronous, but to the thread library it is asynchronous … explain. Why do kernel thread switches have long term cache and TLB effects that user th ...
Peter Sirokman
... specific interfaces to allow the user to have more control over the component Key: these specialized interfaces are optional E.g. the memory manager can be used as a simple malloc, or it can manipulate physical memory and the free list directly Components can offer multiple COM interfaces to d ...
... specific interfaces to allow the user to have more control over the component Key: these specialized interfaces are optional E.g. the memory manager can be used as a simple malloc, or it can manipulate physical memory and the free list directly Components can offer multiple COM interfaces to d ...
CS111—Operating System Principles
... In 1991, a Finnish undergraduate student named Linus Torvalds wanted to learn about Intel’s new CPU, the 80386, and he decided that writing his own OS kernel would be a good way to go about it. This desire, plus his dissatisfaction with the weak UNIX variants then available for 80386-class machines ...
... In 1991, a Finnish undergraduate student named Linus Torvalds wanted to learn about Intel’s new CPU, the 80386, and he decided that writing his own OS kernel would be a good way to go about it. This desire, plus his dissatisfaction with the weak UNIX variants then available for 80386-class machines ...
Operating Systems Introduction
... we need to make sure that an error in a user program could cause problems only for the one program running. if a process gets stuck in an infinite loop, this loop could prevent the correct operation of many other processes. in a multiprogramming system, one erroneous program might modify ano ...
... we need to make sure that an error in a user program could cause problems only for the one program running. if a process gets stuck in an infinite loop, this loop could prevent the correct operation of many other processes. in a multiprogramming system, one erroneous program might modify ano ...
7.2 Peripheral Supplementary
... The OS may support the interrupt requests to control the devices of the system ...
... The OS may support the interrupt requests to control the devices of the system ...